Introduction to the Jicarilla Apache Nation: A Rich Tapestry of Culture and Heritage in New Mexico
The Jicarilla Apache Nation, nestled in the breathtaking landscapes of northern New Mexico, is a vibrant community that embodies a rich cultural heritage and a deep connection to its ancestral lands. Recognized as a federally recognized tribe, the Jicarilla Apache Nation has preserved its unique customs, language, and traditions through generations, creating a fascinating tapestry of history that attracts visitors and researchers alike.
Spanning approximately 1.6 million acres, the lands of the Jicarilla Apache Nation are characterized by a diverse surroundings ranging from scenic mountains and sprawling forests to arid plains. This picturesque setting not only provides a backdrop for the tribe’s rich cultural practices but also serves as a foundation for their economic growth efforts today.
The Jicarilla Apache people have a storied past that dates back thousands of years, where their origins are steeped in legends and oral histories. Known for their resilience and adaptability, the tribe has navigated the challenges of colonization and modernization while maintaining a strong sense of identity. Their commitment to education, community development, and cultural preservation is evident in the various programs and initiatives they undertake, ensuring that the vibrant traditions of the Jicarilla Apache Nation will thrive for future generations.
Visitors to the Jicarilla Apache Nation can explore the herculean spirit of this remarkable tribe through various cultural events, art exhibits, and ancient sites, providing a unique prospect to engage with their history and way of life. By understanding the Jicarilla Apache Nation, one not only gains insight into their rich cultural identity but also appreciates the broader narrative of Native American resilience and creativity in the face of adversity.
the Jicarilla Apache Nation stands as a testament to enduring heritage, cultural pride, and the ongoing journey of a people committed to preserving their identity in modern America.
Origin Of The People
The origin of the Jicarilla Apache Nation, based in northern New Mexico, is deeply interwoven with the rich tapestry of Apache history and culture. The Jicarilla Apache people are one of the numerous sub-groups within the larger Apache tribal family, which traditionally inhabited areas of the Southwestern United States.Their name, “Jicarilla,” derives from the Spanish term meaning “little basket,” reflecting their distinctive craftsmanship.
Legend has it that the Jicarilla Apache emerged from a sacred, underworld realm guided by the spirits and ancestors. For centuries, they lived as nomadic hunter-gatherers, relying on the natural resources of the vast landscapes, from the rugged mountains to the open plains. Their adaptability allowed them to live off the land, hunting deer, gathering wild plants, and engaging in trade with neighboring tribes, including the Pueblo people.
The Jicarilla Apache Nation consists of two primary divisions: the Eastern Jicarilla and the Western Jicarilla. While both groups share similar languages and cultural practices, they developed unique identities based on their geographic and environmental circumstances. The Eastern Jicarilla traditionally occupied regions in New Mexico characterized by dense forests and mountains, while the Western Jicarilla thrived in more arid regions.
Historically, the Jicarilla Apache people were known for their remarkable skills in warfare and strategy, which allowed them to defend their territory against encroachment by settlers and rival tribes. However, by the late 19th century, the Jicarilla, like many Indigenous nations, faced significant challenges due to colonization, forced relocations, and U.S. military campaigns. In response to these pressures,they sought to adapt and integrate elements of European culture while retaining their fundamental identity.
Today, the Jicarilla Apache Nation is a vibrant community dedicated to preserving its rich heritage while adapting to contemporary times. They continue to engage in customary practices, such as their renowned beadwork and basketry, while also participating in modern economies, including tourism and natural resource management. The Jicarilla Apache Nation’s resilience and commitment to cultural identity serve as a testament to their storied history and enduring spirit.
Tribal Homelands
The Jicarilla Apache Nation,located in northern New Mexico,spans approximately 1.5 million acres of stunning landscape. The tribal homelands are characterized by diverse geographical features, including rugged mountains, rolling plains, and verdant river valleys. The region is primarily situated in the foothills of the Southern Rocky Mountains, offering a breathtaking backdrop that sustains both wildlife and cultural heritage.Historically, the Jicarilla Apache people have inhabited this land for centuries, navigating through periods of conflict and adaptation.The name “Jicarilla” itself translates to “little basket,” referencing a traditional craft that remains integral to their cultural identity. Their homelands, rich with resources, provided an abundant life through hunting, gathering, and agriculture.
The Jicarilla Apache Nation’s territory is not only significant for its natural beauty but also for its archaeological and historical sites. These areas hold artifacts that reflect the tribe’s heritage and the stories of their ancestors. Sacred sites dot the landscape, with many still considered critical to the spiritual practices and ceremonies of the tribe today.
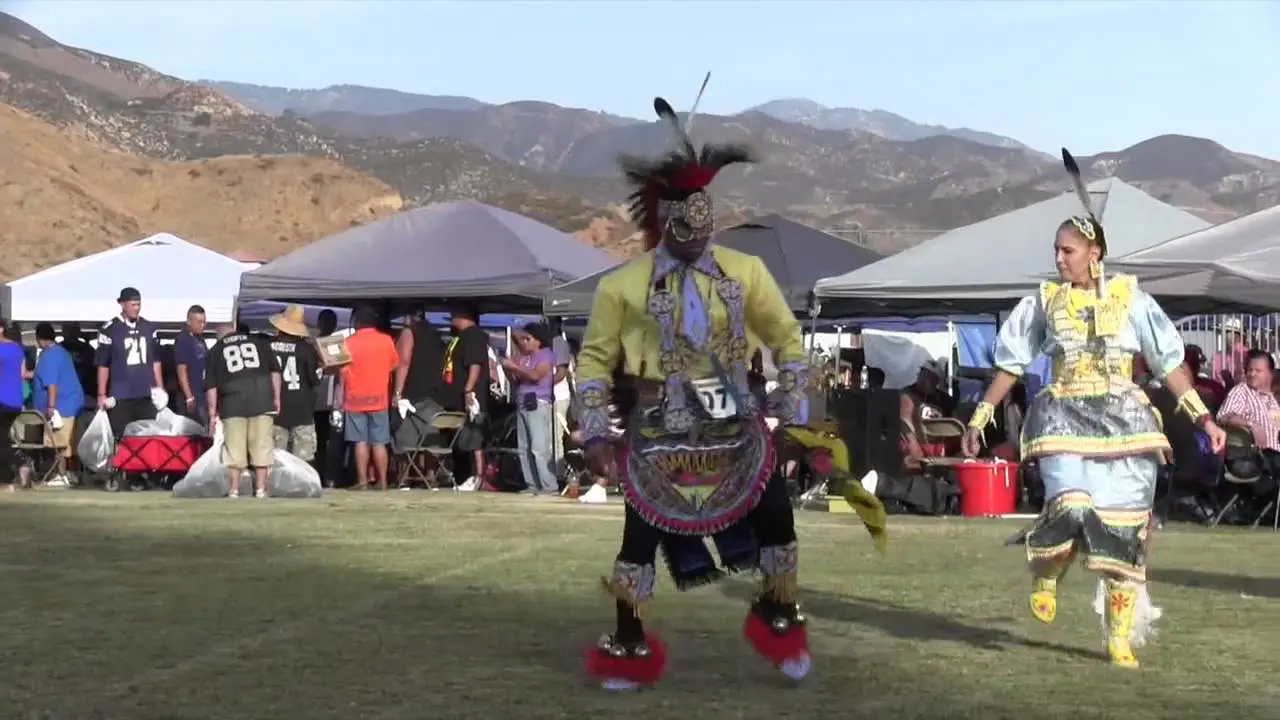
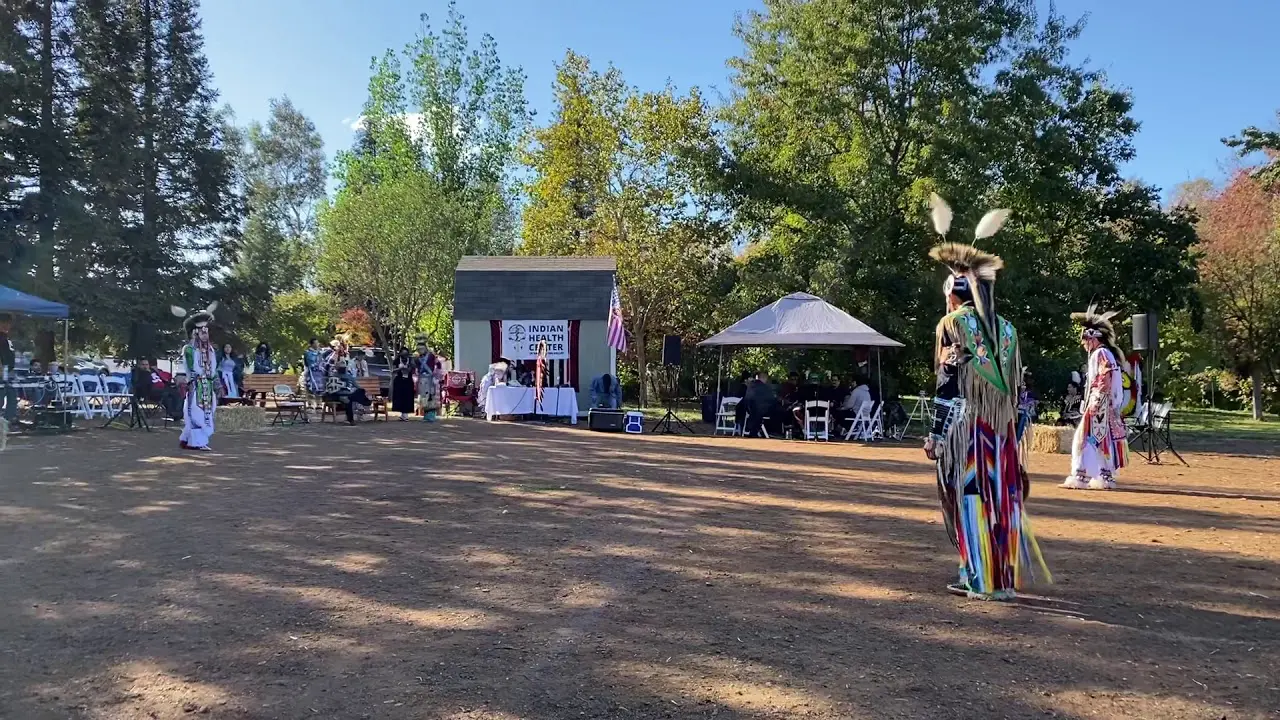
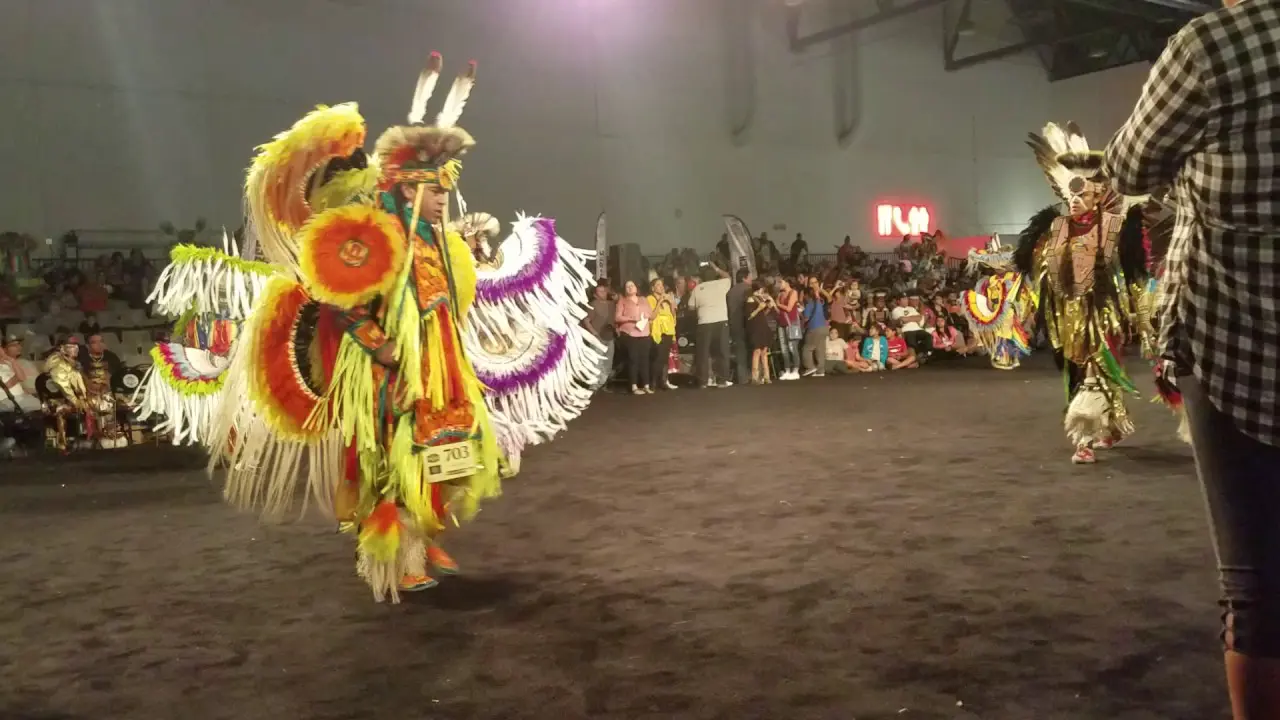
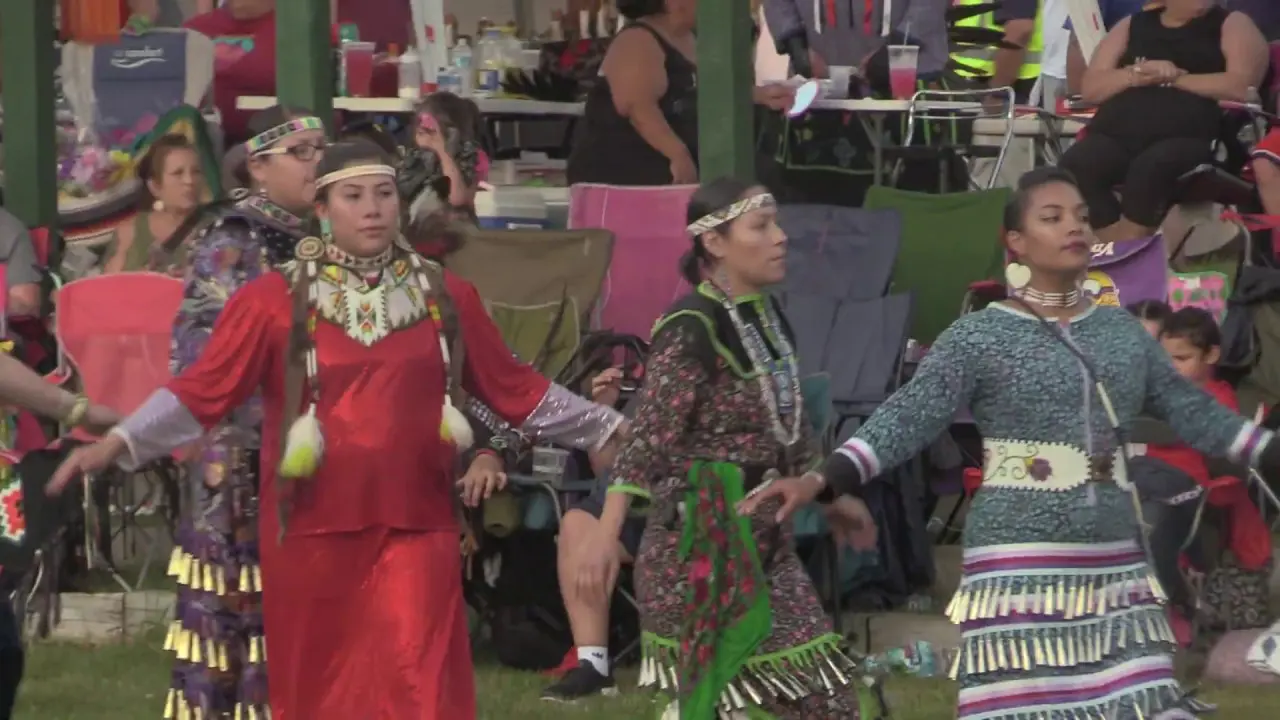
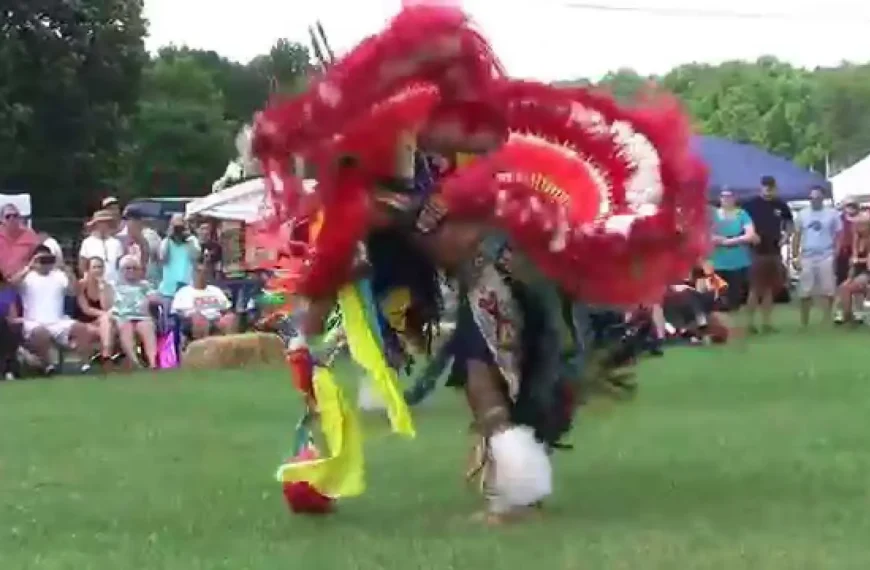
Culturally, the Jicarilla Apache Nation takes pride in their vibrant traditions, which include intricate beadwork, basket weaving, and storytelling. The tribe’s cultural events,such as the annual Jicarilla Apache Nation Fair,foster community spirit and celebrate their unique heritage. These gatherings also attract visitors and showcase the tribe’s rich history, art, and music.
Through sustainable development and land stewardship,the Jicarilla Apache Nation aims to preserve their homelands for future generations. The focus on eco-tourism and cultural education helps to empower the community economically while maintaining a strong connection to the land. As stewards of their ancestral territory, the Jicarilla Apache people continue to uphold their traditions and foster a deeper understanding of their culture and history within wider society.
Interactions With Settlers
The interactions between the Jicarilla Apache Nation and settlers in New Mexico were marked by both positive and negative experiences that shaped the tribe’s history and cultural landscape. Initially,encounters with European settlers brought opportunities for trade and the exchange of goods,which were integral to the survival and adaptation of the Jicarilla Apache people.With the arrival of settlers, the tribe traded goods like hides and pottery for metal tools, ammunition, and other resources that enhanced their daily lives.
However, these early interactions soon turned complex and often tumultuous. As settlers moved further into Jicarilla territory, tensions escalated over land disputes, resources, and differing lifestyles. The encroachment of ranchers and farmers disrupted traditional hunting grounds and sacred sites, leading to a loss of territory that created significant grievances within the tribe. Conflicts, such as raids and retaliatory skirmishes, became more frequent during the 19th century, complicating relations between the Jicarilla Apache and settlers.
Another critical aspect of these interactions was the impact of U.S. government policies on the Jicarilla Apache people. The establishment of reservations in the late 1800s sought to manage the conflicts between settlers and Native tribes but often stripped the Jicarilla of their ancestral lands and autonomy. This imposition led to a series of negotiations and treaties, with varying degrees of success and compliance from both sides.While some settlers sought to coexist and forge partnerships with the Jicarilla, others viewed them as obstacles to expansion, perpetuating cycles of mistrust and violence.
Despite the challenges, the Jicarilla Apache Nation has demonstrated resilience, with numerous cultural exchanges enriching their history. Through cooperation in trade and the sharing of agricultural practices, both settlers and the Jicarilla Apache contributed to the cultural tapestry of New Mexico. Today, the Jicarilla Apache Nation continues to navigate the legacy of these interactions, focusing on cultural preservation and revitalization while fostering relationships with surrounding communities. The duality of these historical encounters—where adversity meets opportunity—remains a crucial part of the Jicarilla Apache narrative, highlighting their enduring spirit in the face of ongoing challenges.
Most Notable Events In Their Tribal History
The Jicarilla Apache Nation, based in northern New Mexico, boasts a rich and complex history marked by resilience and adaptability. One of the most notable events in their tribal history was the signing of the Treaty of Santa Fe in 1855. This treaty established a reservation for the Jicarilla Apache, which formally recognized their rights to their ancestral lands and aimed to bring peace between the tribe and the encroaching settlers. However, this treaty was not fully honored in subsequent years, leading to conflicts and struggles for sovereignty.
Throughout the late 19th century, the Jicarilla faced significant challenges due to U.S. government policies. One major event was the outbreak of hostilities in the 1860s, leading to the 1866 Jicarilla War, which resulted in the loss of many lives and the eventual U.S. military intervention. Following this period of violent conflict, the Jicarilla Apache were forced onto smaller portions of their traditional lands, prompting their persistent fight for recognition and their rights as a tribe.
In the early 20th century, a pivotal moment for the Jicarilla Apache Nation was the establishment of the tribal government in 1936 with the passage of the Indian Reorganization Act. This act allowed the tribe to create their constitution and governance structure, thereby laying the groundwork for modern tribal sovereignty and self-determination. The restoration of government enabled the Jicarilla to reclaim some control over their cultural and economic resources, allowing for significant developments in education, health, and community welfare.
The finding of oil on their lands in the 1940s marked another turning point for the Jicarilla Apache Nation.This event led to economic opportunities that transformed the tribe’s financial landscape.However, it also brought new challenges, including the necessity to balance economic development with environmental stewardship and cultural preservation.
In recent decades, the Jicarilla Apache Nation has made strides in economic diversification, establishing businesses and fostering partnerships to ensure sustainable development. A notable event in the tribe’s recent history is their involvement in green energy initiatives, showcasing a commitment to innovation while respecting traditional values.
These key events highlight the resilience of the Jicarilla Apache Nation and their ongoing journey toward self-determination and cultural preservation. The Jicarilla Apache Nation continues to embrace its rich heritage while adapting to contemporary challenges, ensuring that their history remains a foundation for future generations.
Where Are Their Tribal Lands Now And How Were They Established
The Jicarilla Apache Nation is primarily located in northern New Mexico, occupying a reservation that encompasses approximately 1,200 square miles. Established in the late 19th century, this reservation originated from a series of treaties and land negotiations that were influenced by the U.S.government’s policies towards Native American tribes.
The Jicarilla Apache people have inhabited this area for centuries, whereas their current reservation was officially recognized in 1887 when Congress passed the Dawes Act, which aimed to assimilate Native Americans into American society. The Act fragmented tribal lands, allotting specific parcels to individual families and ultimately reducing the overall land available to the Jicarilla Apache.
Over time, land disputes and additional treaties further shaped the boundaries of their tribal lands. The 1934 Indian Reorganization Act provided a framework for restoring some tribal authority over their lands, offering a new opportunity for the Jicarilla Apache Nation to manage its resources and governance more autonomously. Today, the tribe actively engages in economic development initiatives and efforts to preserve their cultural heritage while managing their natural resources, including timber, minerals, and recreational opportunities found within their reservation.
The Jicarilla Apache Nation continues to prioritize the well-being of its members, promoting sustainable practices that respect their rich traditions while fostering growth and development within their community. As stewards of their land, they play a vital role in maintaining environmental balance and cultural continuity.
Modern Concerns Of The Tribe
The Jicarilla Apache Nation, located in Northern New Mexico, faces a range of modern concerns that reflect the complexities of maintaining their cultural heritage while adapting to contemporary challenges.One significant issue is the preservation of their language and traditional practices.With younger generations becoming increasingly influenced by modern technology and lifestyles, there is an urgent need for revitalization efforts. Language programs and cultural workshops aim to engage youth and instill a sense of pride in their heritage.
Economic development is another prominent concern for the Jicarilla Apache Nation. While the tribe has made strides in diversifying its economy, including ventures in tourism, gaming, and energy resources, there are ongoing challenges in balancing development with environmental sustainability. The tribe is actively seeking ways to leverage its natural resources,particularly in the renewable energy sector,to create jobs while preserving their land and traditions.
Healthcare access remains a critical issue, as many community members face barriers to obtaining quality medical services. The Jicarilla Apache Nation has been working to improve healthcare infrastructure and access through collaborations with federal programs and local health initiatives. Addressing mental health and substance abuse issues is also a priority, as these are pressing concerns that affect the overall well-being of the community.
Additionally, the tribe is focused on enhancing education for its members. By investing in educational resources and programs, the Jicarilla Apache Nation aims to empower its youth and ensure that future generations have the tools needed for success in a changing world. This includes integrating cultural teachings into the school curriculum, thereby fostering a strong sense of identity and community.
Environmental concerns also play a major role in the tribe’s modern agenda. Like many indigenous communities, the Jicarilla Apache Nation is deeply connected to its land and resources. The impact of climate change, particularly on water resources and wildlife, presents challenges that the tribe is actively addressing through conservation initiatives. Sustainability efforts are crucial for maintaining not only their physical environment but also their cultural identity tied to the land.
the Jicarilla Apache Nation is navigating a complex landscape of cultural preservation, economic development, healthcare access, education, and environmental sustainability. Balancing these concerns while fostering a strong sense of identity is essential for the tribe’s future. Through dedicated efforts and community engagement, the Jicarilla Apache Nation continues to work towards achieving its goals in a modern context.
Events And Other Social And Political Activities
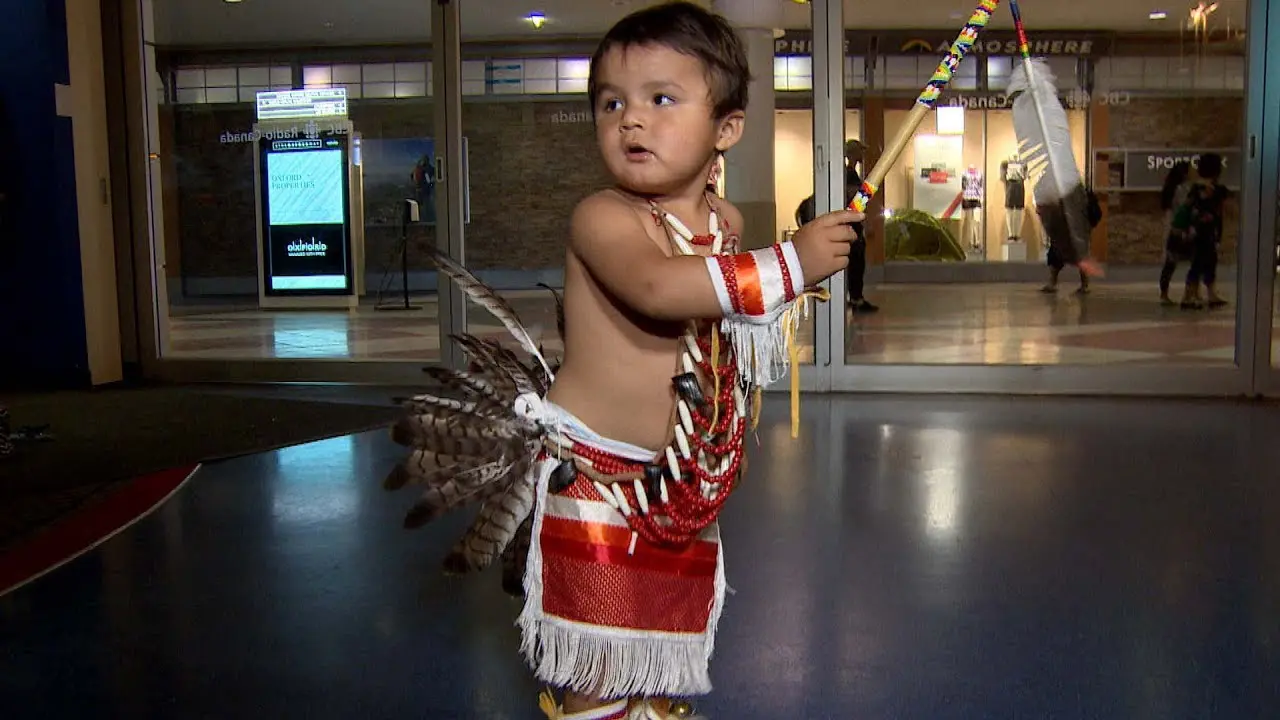
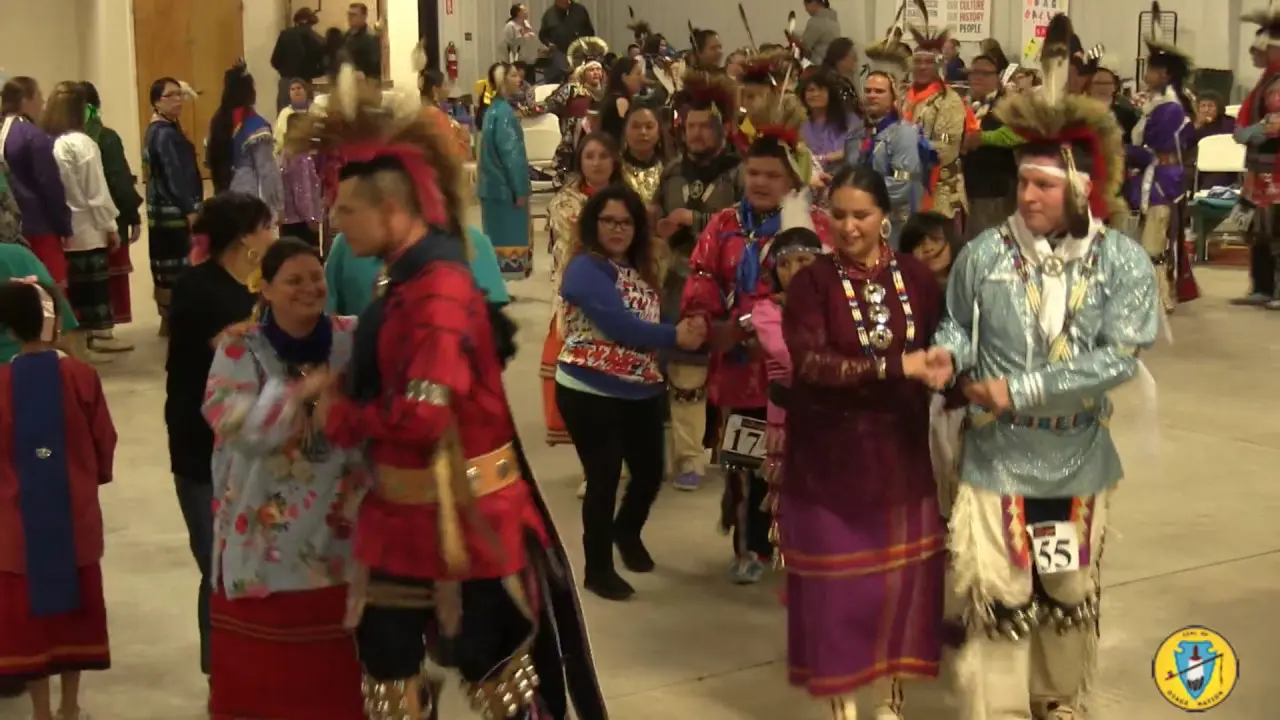
The Jicarilla Apache Nation, located in northern New Mexico, actively participates in a variety of events and social activities that reflect their rich culture and community spirit.One of the most significant annual events is the Jicarilla Apache Fair,held every September,which features traditional dances,art showcases,rodeos,and cultural demonstrations. This vibrant gathering serves as an opportunity for tribal members and visitors alike to celebrate Jicarilla heritage, fostering a sense of unity and pride within the community.
In addition to the fair, the Jicarilla Apache Nation organizes and supports various cultural workshops and educational programs aimed at preserving their language and traditions. Language revitalization initiatives are particularly crucial, as they engage younger generations in learning the Jicarilla Apache language through immersive experiences and structured classes.
Political engagement within the tribe is also paramount,with the Jicarilla Apache Nation actively participating in national dialogues concerning tribal sovereignty,natural resource management,and economic development. Tribal leadership works closely with federal and state governments to advocate for the interests of their community, ensuring that their voices are heard in matters that affect their lands and livelihoods.
Furthermore, the tribe hosts events like the annual Tribal Council elections, fostering a democratic process that encourages civic participation among its members.These elections not only emphasize the importance of representation but also strengthen the community’s commitment to self-governance.
The Jicarilla Apache Nation also collaborates with neighboring tribes and organizations on environmental and educational initiatives,promoting sustainability and cultural exchange. Through these partnerships, they engage in discussions on issues like land conservation, economic development, and the preservation of indigenous practices.
the Jicarilla Apache Nation’s events and activities not only celebrate their cultural heritage but also underscore their role as proactive participants in political advocacy and social responsibility. Through their dedicated efforts to preserve their traditions while navigating contemporary challenges, the Jicarilla Apache people continue to thrive and evolve in today’s world.