Introduction to teh Cahto Tribe of the Laytonville rancheria
Nestled in the picturesque hills of Northern California, the Cahto Tribe of the Laytonville Rancheria represents a vibrant thread in the rich tapestry of native American history. Known for thier deep-rooted connection to the land, the Cahto people have inhabited this region for thousands of years, cultivating a profound relationship with nature that continues to inspire their cultural practices today.
The tribe is part of the larger Pomo linguistic group and is renowned for it’s unique heritage, traditions, and contributions to the surrounding communities. Today, the Cahto Tribe operates the Laytonville Rancheria, a region that serves as both a cultural hub and a center for economic growth, showcasing their resilience and adaptability in modern society.
Through a commitment to preserving their ancestral traditions while navigating contemporary challenges, the Cahto Tribe offers insights into sustainable living, cultural preservation, and community empowerment. From their customary crafts to their environmental stewardship efforts, the tribe serves as a model for fostering harmony with nature and promoting cultural pride. In this introduction, we delve deeper into the history, culture, and future of the Cahto Tribe, celebrating their enduring legacy and vibrant community.
Origin Of The People
The Cahto Tribe, part of the Laytonville Rancheria in Northern California, has a rich and complex history steeped in the traditions and culture of the Indigenous peoples of the region. The Cahto people are believed to have inhabited the coastal and inland areas of Mendocino County for thousands of years,with evidence of their presence dating back to prehistoric times. Their territory encompassed a diverse landscape,from the majestic redwood forests to the rugged coastal regions,providing abundant resources for hunting,fishing,and gathering.The tribe’s name, “Cahto,” which means “to swallow,” reflects their connection to the land and the natural elements that surround them. The Cahto relied heavily on their habitat, utilizing acorns, fish, game, and native plants for food, shelter, and medicinal purposes. This deep understanding of nature also played a crucial role in their spiritual beliefs and practices, with ceremonies often centered around the changing seasons and the cycles of life.Historically, the Cahto people experienced significant disruption due to European colonization in the 19th century, which brought waves of settlers and devastating conflicts. The arrival of non-Indigenous populations led to loss of land, resources, and cultural practices. Despite these challenges, the Cahto people have shown remarkable resilience. They have worked diligently to preserve their identity, language, and traditions through generations, emphasizing the importance of cultural heritage.
Today, the Laytonville Rancheria serves as a focal point for the tribe, providing a venue for cultural events, gatherings, and educational initiatives aimed at revitalizing the Cahto language and traditions. The tribe actively engages in community development and environmental stewardship, reflecting their ongoing commitment to honor their ancestors while adapting to contemporary challenges. Through these efforts, the Cahto Tribe continues to thrive, ensuring that their rich history and cultural legacy are passed down to future generations.
Tribal Homelands
the Cahto Tribe of the Laytonville Rancheria is deeply rooted in the land of Northern California, specifically in Mendocino County. Their traditional homelands span the stunning landscapes of the region,encompassing the rich valleys,hills,and lush forests that have nurtured their community for centuries. This area is not just a geographical location; it is imbued with cultural meaning and spirituality, providing a sense of identity and belonging to the tribe.
Historically, the Cahto people inhabited a vast territory characterized by its diverse ecosystems. The region is home to an array of wildlife, abundant plant life, and natural resources that sustained the tribe. The coastal mountains served as a boundary for their territories,while the rivers and streams provided water,fish,and transportation routes vital for trade and communication with neighboring tribes. The culture of the Cahto is intricately tied to the land; they practiced sustainable hunting, fishing, and foraging methods respectful of the natural balance.
Today, the Laytonville Rancheria, established as a federally recognized tribe, includes a small portion of this ancestral land. The tribe actively works to preserve their heritage and reestablish a connection with their ancient homelands through cultural programs, environmental stewardship, and educational initiatives. Their commitment to land conservation reflects their traditional ecological knowledge, emphasizing the importance of preserving the environment for future generations.
The Cahto Tribe also engages in tribal governance and economic development as means to support their community while honoring their cultural roots and the legacy of their ancestors.By fostering a strong connection to their traditional homeland, the Cahto people continue to share their rich history, language, and customs with younger generations, ensuring that their identity remains vibrant in today’s world.
the tribal homelands of the Cahto Tribe of the Laytonville Rancheria represent a profound connection to the earth, showcasing a heritage that thrives through commitment to preservation, cultural education, and community strength. The tribe’s ongoing efforts to reclaim and protect their ancestral lands exemplify their resilience and reverence for their history.
Interactions With settlers
The interactions between the Cahto Tribe of the Laytonville Rancheria and settlers in Northern California present a complex tapestry of experiences, marked by both positive exchanges and significant challenges. Historically, the onset of European settlement brought about profound changes in the lives of the Cahto people, affecting their social structures, economy, and cultural practices.
On the positive side,there were instances of cooperation and mutual benefit. Some settlers established relationships with the Cahto Tribe, engaging in trade that included food, goods, and knowledge. The settlers gained essential insights into the local environment, learning about native plants and resources that were crucial for survival in the unfamiliar landscape. Similarly, the Cahto people sometimes exchanged their expertise in hunting and gathering techniques, which helped settlers adapt to their new surroundings. These interactions fostered a limited form of coexistence, where both groups recognized the advantages of sharing their skills and resources.
However, the narrative of settler interactions with the Cahto Tribe is also steeped in adversity. As settlers expanded their territories, they encroached upon the lands traditionally inhabited by the Cahto, leading to significant land loss and disruption of their way of life. The influx of settlers often brought about competition for resources such as water and game, resulting in increased tensions.Additionally, diseases introduced by settlers had devastating effects on the indigenous population, causing dramatic declines in the Cahto numbers and altering their community dynamics.
The later part of the 19th and early 20th centuries saw intensified conflicts, as settlers and miners sought to exploit the region’s natural resources, including timber and minerals. These actions led to further dispossession of the Cahto lands and the erosion of their cultural identity as traditional practices were sidelined. Moreover, the U.S. goverment policies during this period often marginalized Native communities, forcing many into reservations and limiting their autonomy.
the interactions between the Cahto Tribe of the Laytonville Rancheria and settlers reflect a microcosm of broader themes in Native American history, characterized by moments of collaboration amidst overwhelming challenges. Understanding these dynamics is essential in appreciating the resilience of the Cahto people and their ongoing efforts to preserve their culture and heritage in the face of historical adversity.
Most Notable Events In Their Tribal History
The Cahto Tribe of the Laytonville rancheria has a rich and complex history marked by resilience and cultural revival.One of the most notable events in their tribal history is the establishment of the Laytonville Rancheria in the late 20th century. Originally, the Cahto people relied on a nomadic lifestyle, sustaining themselves through hunting, fishing, and gathering in the lush landscapes of what is now Northern California. However, the forced removals and settlement policies of the 19th century severely disrupted their traditional way of life.
In 1958, the Cahto Tribe was federally recognized, a significant milestone that enabled them to reclaim a portion of their ancestral lands and cultural heritage. this recognition facilitated the tribe’s efforts in land restoration, leading to the establishment of the Laytonville Rancheria, which continues to serve as a cultural and community center for tribal members today.
In the decades that followed,the tribe undertook vital initiatives to preserve their language,traditions,and customs. The cahto language Restoration Program, initiated in the early 2000s, aimed to revive the endangered Cahto language, fostering intergenerational learning and cultural transmission.
another major event in the tribe’s recent history is their involvement in environmental conservation projects. The Cahto Tribe has actively participated in sustainable forest management practices to maintain the health of their ancestral lands. This commitment to environmental stewardship not only honors their ancestors’ teachings but also contributes to broader ecological efforts in Northern California.
In addition, the Cahto Tribe has made strides in economic development through various enterprises, including timber management and tourism. By diversifying their economic base, they have enhanced their community’s sustainability and improved quality of life for tribal members.
Throughout their history,the Cahto Tribe has demonstrated a profound commitment to cultural preservation,environmental stewardship,and community empowerment,making them a resilient and vibrant community in contemporary society.
Where are Their Tribal Lands Now And How Were They Established
The Cahto Tribe of the Laytonville Rancheria is located in Northern California, primarily within Mendocino County. Their tribal lands encompass approximately 88 acres in and around Laytonville, situated in a picturesque region that highlights the tribe’s deep connection to the diverse landscapes, which include forests, rivers, and mountains. Historically, the Cahto people inhabited much larger territories, traditionally living off the land and practicing sustainable hunting, fishing, and gathering.
The establishment of the Laytonville Rancheria as a designated tribal land occurred in the 1950s,notably through the United States’ Indian Reorganization Act of 1934,which sought to reverse the assimilation policies of previous decades. This law allowed the Cahto Tribe to regain a portion of their ancestral lands. However, the process was fraught with challenges, including historical land dispossession and periods of federal recognition and lack thereof.
In 1983, the tribe was officially recognized by the federal government, which further solidified their status and rights to their lands. Today, the Laytonville Rancheria is not only a spiritual and cultural center for the Cahto tribe but also operates various enterprises aimed at preserving their heritage while providing economic stability and promoting community development. The ongoing efforts to protect their tribal lands and enhance the welfare of their members reflect the resilience and determination of the Cahto people to maintain their cultural identity in the modern world.
Modern Concerns Of The Tribe
The Cahto Tribe of the Laytonville Rancheria is currently navigating a series of modern challenges that resonate deeply with their cultural heritage and goals for sustainability. One of the foremost concerns is the preservation of their ancestral lands and natural resources, which are integral not only to their identity but also to environmental stewardship. The tribe actively seeks to manage and protect these lands against threats from commercial development, environmental degradation, and climate change.
Water rights have also emerged as a pressing issue,particularly in light of California’s ongoing drought and the increasing demands on freshwater resources. the tribe advocates for equitable access to clean water,essential for both traditional practices and community health. Initiatives aimed at sustainable agricultural practices are being explored to ensure that land use aligns with their traditional values while providing economic opportunities for community members.
Economic development is another key focus for the cahto Tribe, as they seek to bolster their economy through various ventures, including eco-tourism and culturally oriented businesses. This approach not only provides economic stability but also offers a platform to educate visitors about their rich history and traditions.
Moreover, the tribe is concerned about the health and well-being of its members, especially among the youth. Addressing higher rates of substance abuse and mental health issues is critical. The tribe is working to implement holistic approaches that incorporate traditional healing practices alongside modern healthcare initiatives, fostering a healthier community and preserving cultural identity.
the tribe is actively engaged in education and advocacy to ensure that their voices are heard in local, state, and national discussions concerning Indigenous rights and sovereignty. By forming alliances with other tribes and organizations, the Cahto Tribe aims to amplify its concerns and promote policies that honor their cultural heritage and protect their future.
Events And Other Social And Political Activities
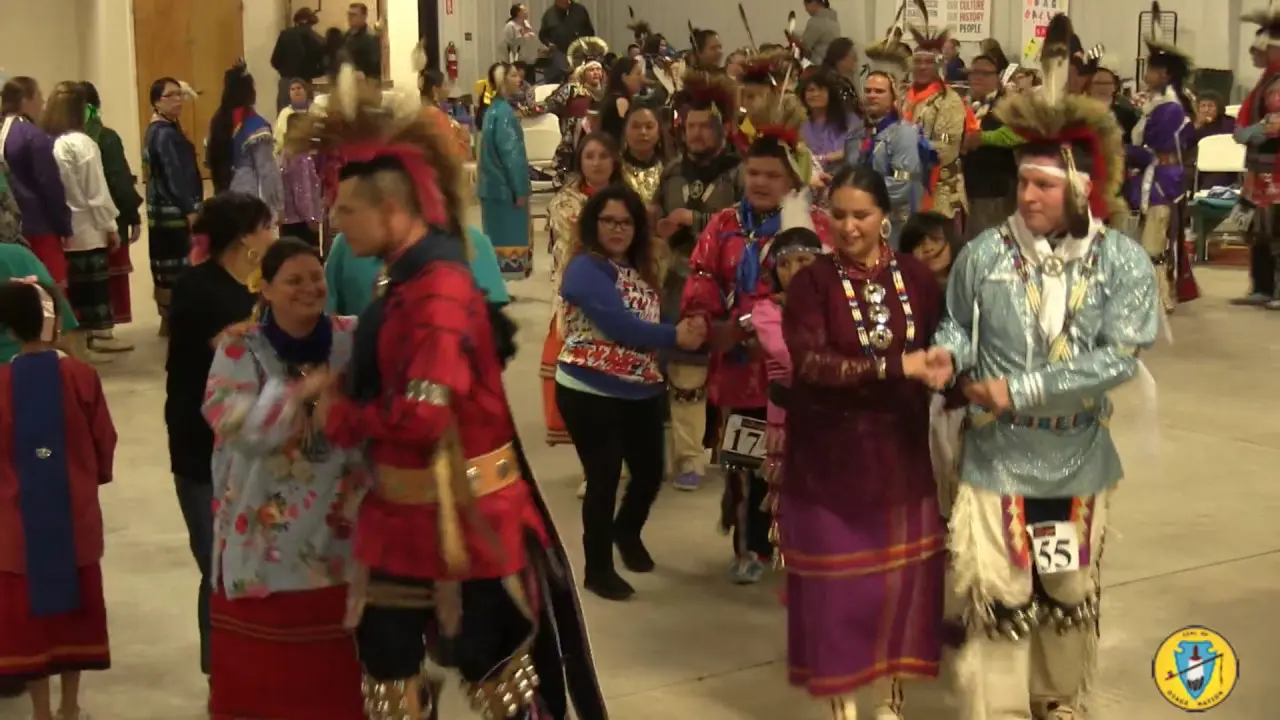
The Cahto tribe of the Laytonville Rancheria is an active community engaged in a variety of social and political activities that reflect their rich culture and commitment to advocating for their rights and interests. One significant event organized by the tribe is the annual Cahto Tribe Wellness Fair, which brings together tribal members and local residents to promote health awareness, cultural pride, and community connections. The fair features health screenings,workshops on nutrition and mental health,and traditional activities that celebrate the tribe’s heritage.
In addition to wellness initiatives, the Cahto tribe actively participates in legislative advocacy, addressing issues affecting Native American communities. The tribe collaborates with various organizations to influence policy decisions at both state and federal levels. Their involvement in the California Native American Legislative Summit is crucial, as it provides a platform for tribal leaders to collaborate on pressing issues such as land rights, environmental protection, and economic development.
Moreover, the tribe has taken significant strides towards preserving their cultural identity through educational programs and partnerships with local schools. They regularly host cultural workshops where members teach traditional crafts, storytelling, and practices that have been passed down through generations.Events like these not only strengthen community bonds but also enhance the cultural understanding of non-Native audiences.
Environmental stewardship is another focal point of the tribe’s activities. The Cahto Tribe engages in restoration projects aimed at protecting their ancestral lands and promoting biodiversity. By working on these initiatives, the tribe not only ensures the preservation of its natural resources but also sets an example for sustainable practices within the region.
Throughout the year, the tribe also holds traditional ceremonies and gatherings that reinforce their cultural heritage. These events embody a spirit of unity and provide an essential space for community members to share in the celebration of their identity and values.The Cahto Tribe’s continued involvement in various social and political activities underscores their dedication to preserving their cultural legacy while navigating the modern challenges faced by Indigenous communities.