Introduction to the Manzanita Band of Diegueño Mission Indians
Nestled in the heart of Southern California, the Manzanita Band of Diegueño Mission Indians of the Manzanita Reservation represents a rich tapestry of history, culture, and resilience. This Indigenous tribe, part of the larger Diegueño or Kumeyaay people, has deep-rooted connections to the land that spans thousands of years. Located in San Diego County, the Manzanita Reservation is not just a geographical area; it is indeed a living testament to the tribe’s enduring spirit and commitment to preserving their heritage.
The Manzanita Band embodies a vibrant culture that honors its ancestors while navigating the complexities of modern society. Like many Native American communities, the tribe has faced challenges, from displacement to cultural erosion, but they have continually worked to reclaim and revitalize their traditions. Through various community initiatives and cultural activities, the Manzanita Band fosters an environment where their rich history is not only preserved but celebrated.
Visitors and locals alike are drawn to the Manzanita Reservation for its stunning natural landscapes and the chance to engage with the tribe’s cultural events and programs. The Manzanita Band is dedicated to education, empowering future generations to uphold their rich legacy while creating a sustainable future.Whether it’s through traditional arts, language revitalization, or community service, the tribe stands as a beacon of hope and resilience in an ever-changing world. Explore the vibrant life of the Manzanita Band of Diegueño Mission Indians and discover how they are weaving the past into a luminous and promising future.
Origin Of The People
The Manzanita Band of Diegueno Mission Indians, situated on the Manzanita Reservation in Southern California, traces its origins to the broader cultural group known as the Kumeyaay. This Indigenous people have inhabited the region for thousands of years, with a rich heritage tied to the diverse ecosystems of the Southern California landscape. The Kumeyaay are known for their deep spiritual connection to the land,utilizing its resources for sustenance,shelter,and cultural practices.
Historically, the Diegueno people, considered among the various groups of Kumeyaay, established their communities in what is now San Diego County and the adjacent areas. They lived in semi-nomadic societies, maintaining an intricate network of trade routes and social interactions with neighboring tribes. Their traditional territory encompassed a broad range of environments, from the coastal regions to the mountainous areas, allowing for a varied diet consisting of acorns, game, fish, and wild plants.
The founding of missions in California during the Spanish colonization substantially impacted the Kumeyaay people, including the Diegueno. Mission San Diego de Alcalá, established in 1769, marked the beginning of a tumultuous period characterized by forced assimilation, land dispossession, and cultural disruption. Despite these challenges, the resilience of the Manzanita Band and other Kumeyaay descendants carried forth traditions, languages, and practices that have persisted through generations.
The Manzanita Reservation, established in the early 20th century, serves as a crucial site for the preservation of cultural identity and the revitalization of traditional practices. Members of the Manzanita Band continue to engage in community-building efforts, cultural events, and educational programs aimed at sharing their rich heritage. Today,the Manzanita Band of Diegueno Mission Indians is dedicated to the preservation of their history,language,and cultural practices,ensuring that the legacy of their ancestors lives on for future generations.
Tribal Homelands
The Manzanita Band of Diegueno Mission Indians, also known as the Manzanita Reservation, is situated in the picturesque foothills of the dehesa region of California, specifically in San Diego County. This tribe is part of the larger Diegueno cultural group, which occupies a historically rich ancestral territory encompassing parts of Southern California, particularly within the San Diego and Riverside counties.
The homelands of the Manzanita Band are characterized by a diverse landscape that includes rolling hills, oak woodlands, and chaparral, providing a unique habitat that supports local flora and fauna. This environment has a deep meaning to the tribe, not just ecologically but also culturally and spiritually. The natural resources found within their ancestral lands, including water sources and medicinal plants, have sustained the Manzanita Band for generations, playing a crucial role in their traditional practices, community gatherings, and ceremonies.
The tribal community actively promotes the preservation of their heritage,often engaging in educational programs that highlight the historical and cultural significance of their homelands. Through these efforts, the Manzanita Band fosters a deep connection to the land, emphasizing the importance of stewardship and environmental responsibility.
Culturally, the Manzanita Reservation serves as a vital gathering place for tribal members to celebrate traditions, share stories, and pass down knowledge. Activities such as traditional dances and storytelling events are not only pivotal to maintaining their cultural identity but also serve to strengthen community bonds. The tribal lands represent more than just physical space; they embody the history, resilience, and enduring spirit of the Manzanita Band of Diegueno Mission Indians.
Interactions With Settlers
The interactions between the Manzanita Band of Diegueno Mission Indians and settlers in California have been marked by a complex blend of both positive and negative experiences, significantly shaping the community’s history and cultural landscape.
On the positive side, early interactions frequently enough involved trade and cultural exchange. The settlers and the Manzanita Band shared knowledge about agriculture, which led to the introduction of new farming techniques and crops. This exchange allowed the tribe to adapt to changing economic realities while maintaining elements of their traditional practices. As a notable example, settlers introduced the cultivation of different fruits and vegetables, enhancing the local diet and providing economic opportunities for tribe members. Additionally,some settlers acted as advocates for the rights of the Manzanita Band,helping them navigate the complexities of land ownership and legal recognition.
However, the impact of settlement was not uniformly positive. The influx of settlers led to significant land loss for the Manzanita Band, as their traditional hunting and gathering grounds were frequently enough reallocated for agriculture or urban advancement. This loss of territory disrupted their cultural practices and diminished access to natural resources vital for their sustenance and identity. Conflicts occasionally arose over land rights,as settlers encroached on reservation boundaries,resulting in tensions that sometimes escalated into confrontations.
Moreover, the introduction of foreign diseases by settlers had devastating effects on the Manzanita population, leading to loss of life and further destabilizing the social structure of the community. As settlers moved in, many members of the tribe found it increasingly difficult to sustain their way of life, forcing some to adapt rapidly to a changing environment that often did not favor their traditional practices.
In contemporary times, the Manzanita Band of Diegueno Mission Indians continues to navigate the legacies of these interactions. Efforts to preserve their cultural heritage and assert sovereignty are paramount, as they work to build relationships with neighboring communities while educating others about their history and resilience. The duality of their interactions with settlers – characterized by both collaboration and conflict – reflects the broader narrative of Native American experiences in California, emphasizing the importance of understanding these historical dynamics in fostering mutual respect and cooperation moving forward.
Most Notable Events In Their Tribal History
The Manzanita Band of Diegueno Mission Indians, located on the Manzanita Reservation in California, has a rich and complex tribal history marked by various notable events that have shaped their cultural identity and ongoing resilience.
One of the most significant events for the Manzanita Band was their acknowledgment as a federally recognized tribe in 1970. This recognition allowed them to reclaim their sovereignty and establish a government-to-government relationship with the United States, paving the way for greater self-determination and the ability to manage their own affairs.The early 20th century brought challenges as the Manzanita Band, like many Native American tribes, faced pressure from external forces that threatened their traditional lifestyles. In 1958, the federal government initiated the Termination Policy, which aimed to dissolve the tribal status of many tribes, including the Manzanita Band. This period led to loss of land,resources,and cultural connections,imposing significant hardships on the tribe. However, as awareness of Native American rights grew, the Manzanita Band actively participated in movements advocating for indigenous sovereignty and land rights.
A pivotal moment in the tribe’s revival came in the late 20th century, particularly during the Indian Gaming Regulatory Act of 1988. This legislation drastically transformed the socio-economic landscape for many tribes across the United States. The Manzanita Band saw an opportunity to create economic development through gaming ventures, which became a vital source of income. The success from these initiatives enabled the tribe to invest in education, healthcare, and cultural preservation efforts.
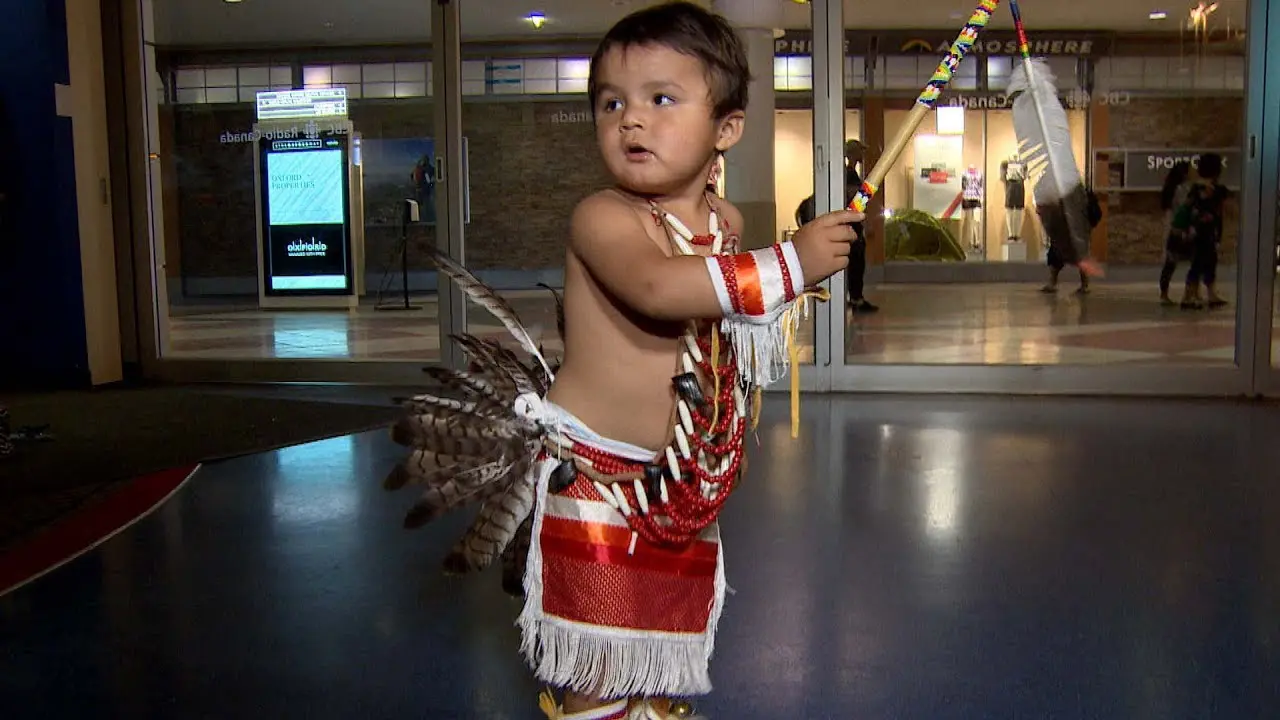
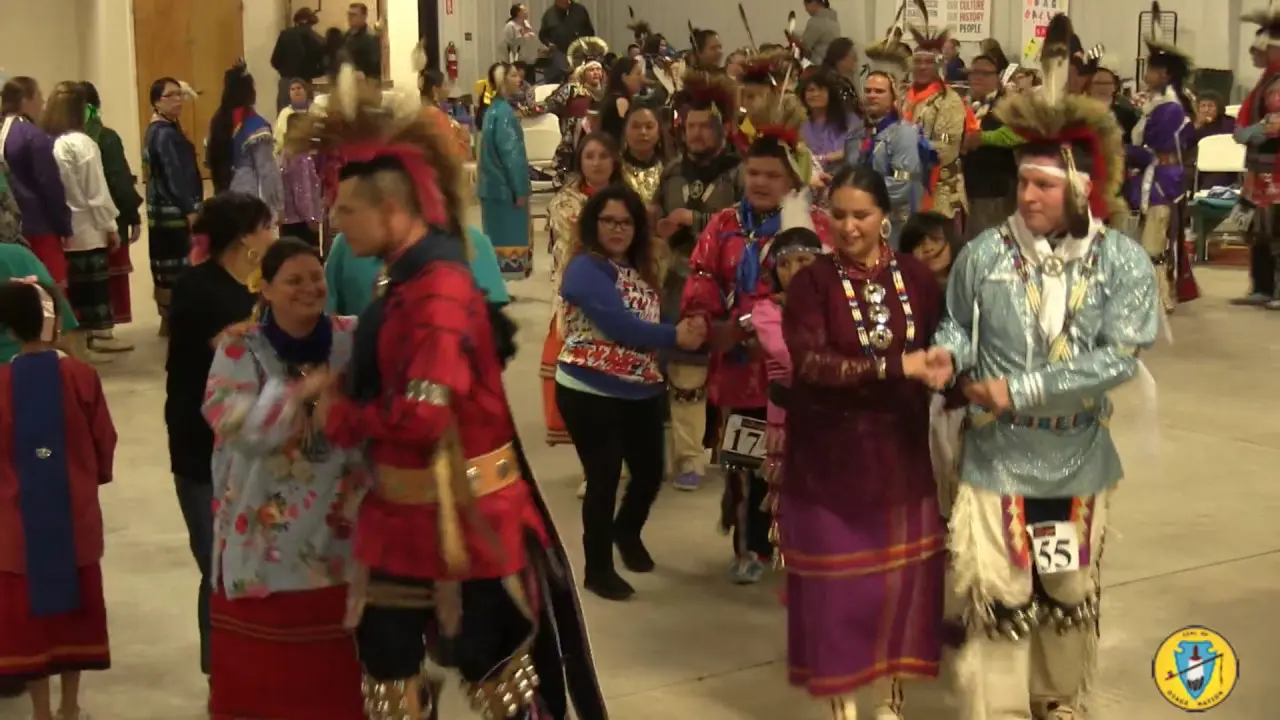
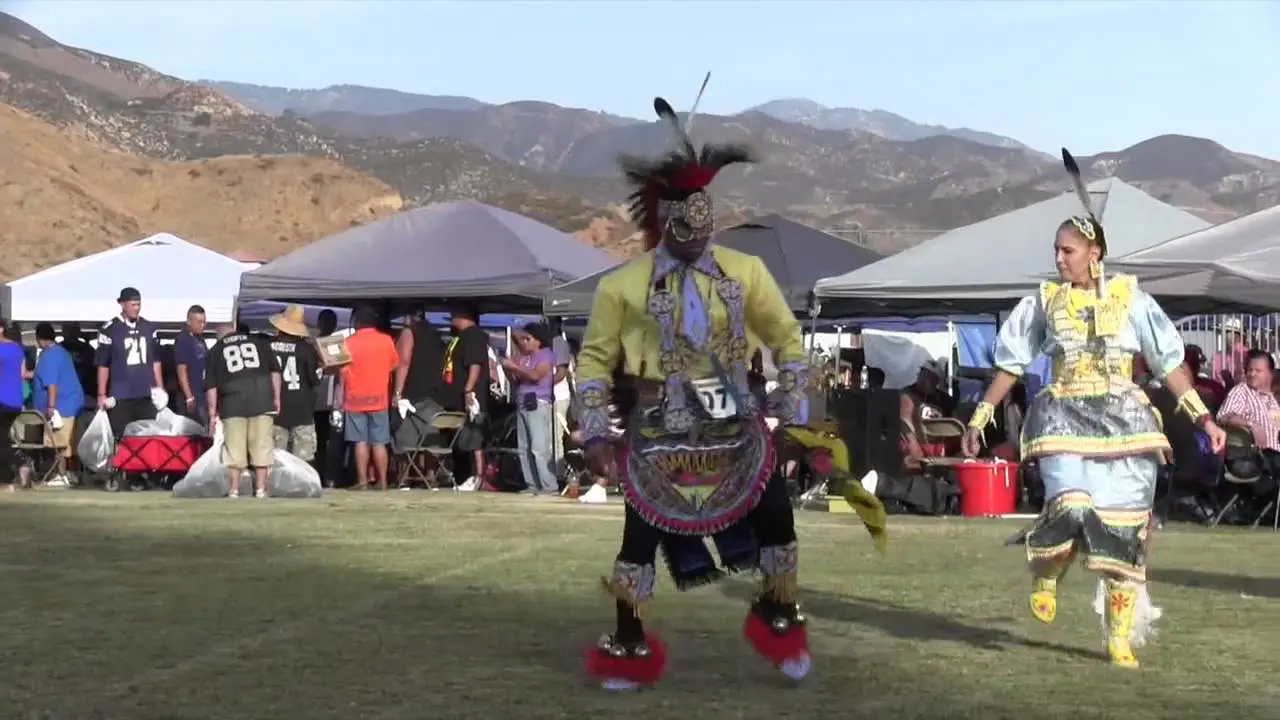
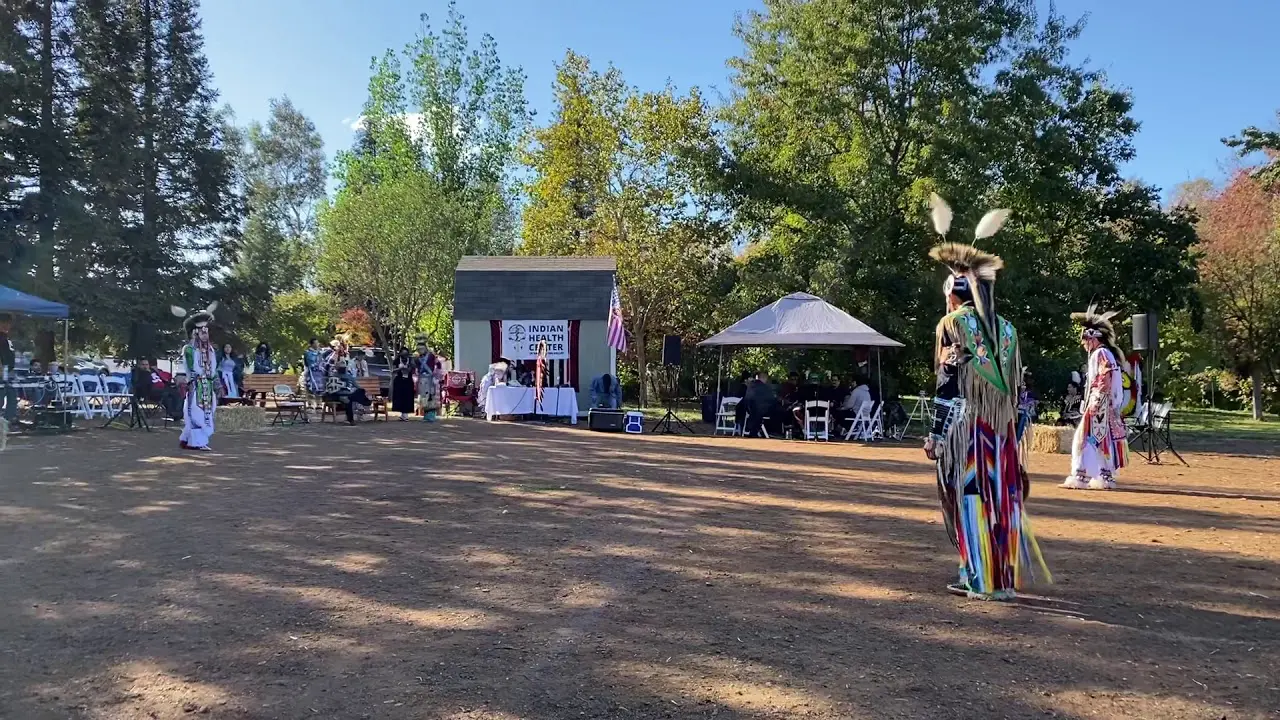
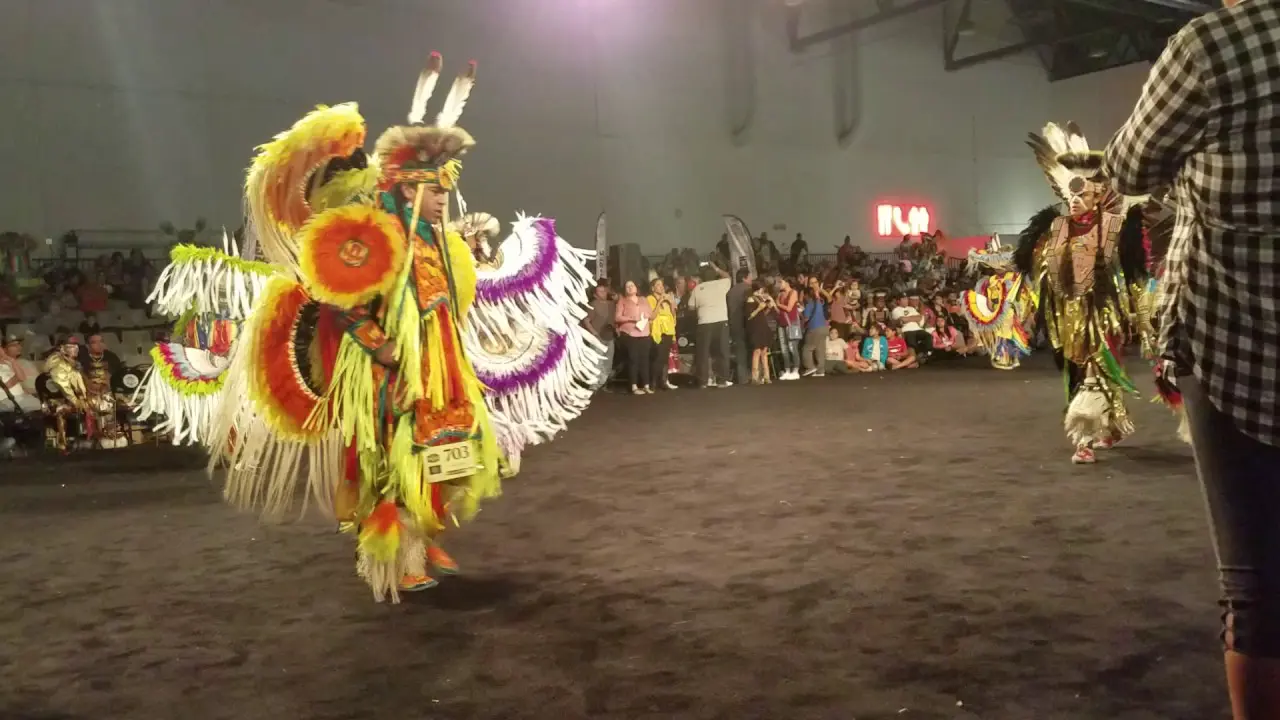
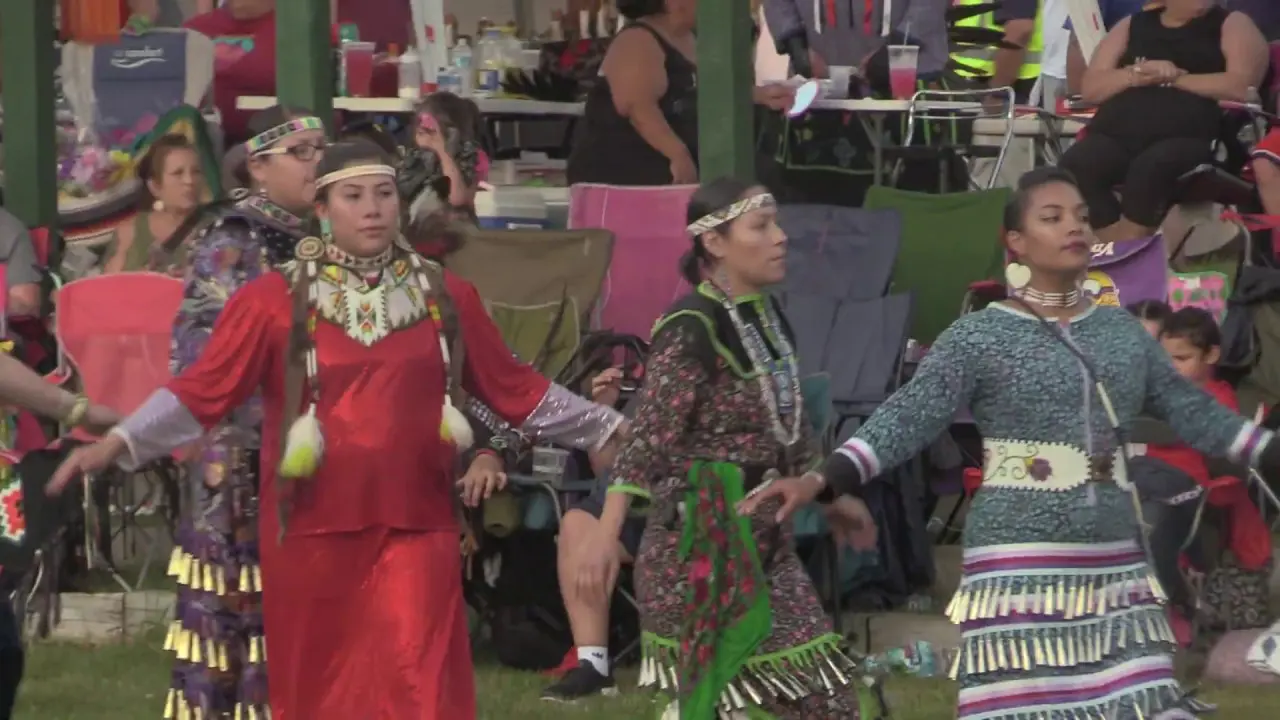
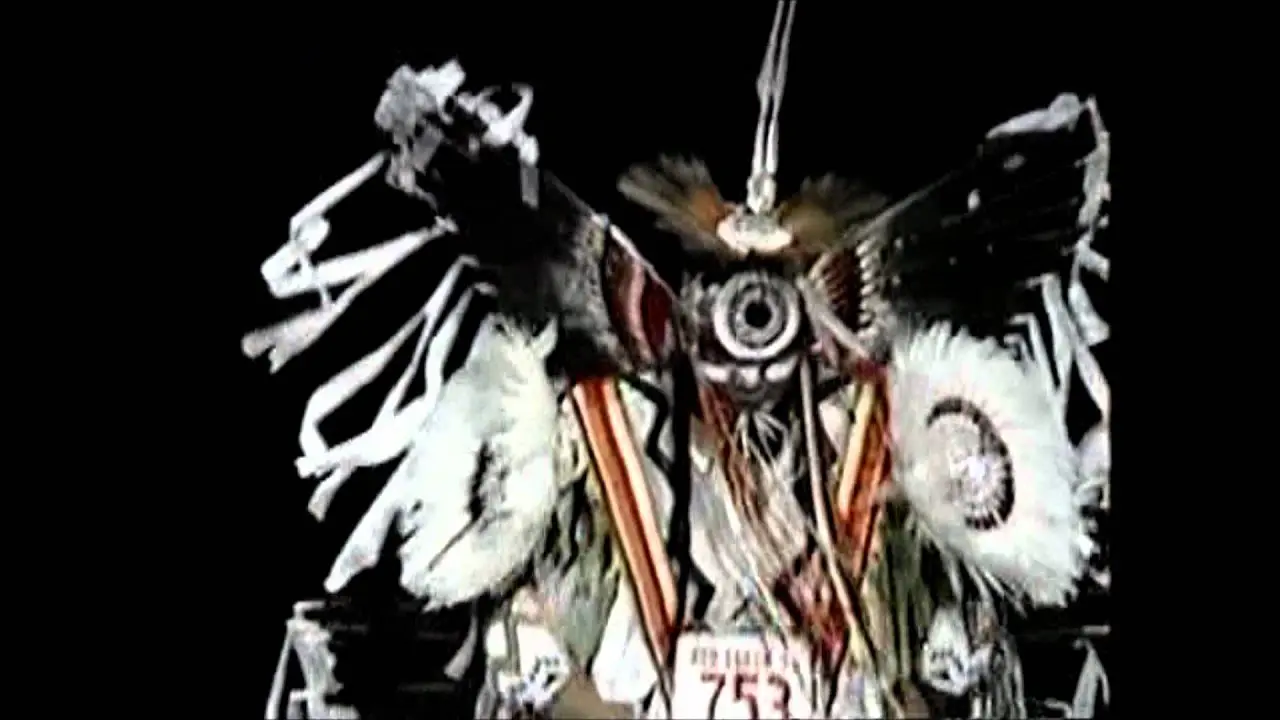
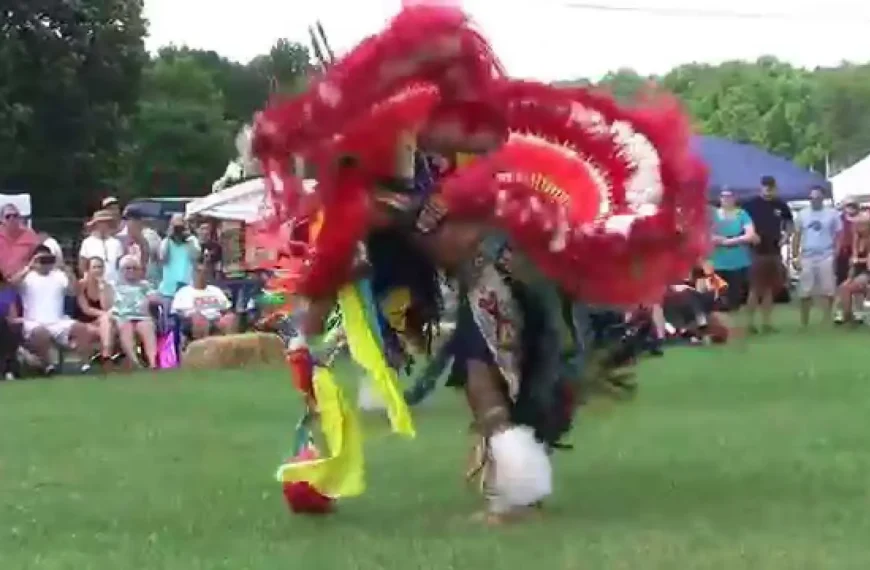
Cultural revitalization has been another crucial aspect of the tribe’s history. The Manzanita Band has worked diligently to pass down traditional practices, languages, and customs to younger generations. Engagements like annual powwows, cultural events, and educational workshops highlight their commitment to preserving the Diegueno heritage, helping to strengthen community ties and foster a sense of identity.
In recent years, the Manzanita Band has focused on addressing contemporary issues such as environmental stewardship and social justice. Collaborating with other tribes and association,they advocate for policy changes that protect indigenous rights and the environment. The tribe’s activism underscores their ongoing commitment to not only preserving their heritage but also ensuring the welfare of their community and the natural landscapes that hold cultural significance.
The Manzanita Band of Diegueno Mission Indians continues to navigate the complexities of modern society while honoring their historical roots. The resilience displayed through various challenges and achievements illustrates the tribe’s enduring spirit and dedication to sustaining their cultural identity for future generations.
Where Are Their Tribal Lands Now And How Were They Established
The Manzanita Band of Diegueno Mission Indians is primarily located on the Manzanita Reservation in Southern California,specifically within San Diego County. This reservation was established in 1978, primarily to serve the needs and rights of the tribe, following a tumultuous history marked by displacement and land loss. The Manzanita Reservation encompasses approximately 110 acres of land nestled in the scenic foothills of the Cuyamaca Mountains, providing a space for the tribe to preserve their cultural heritage and promote community wellbeing.
The establishment of the Manzanita Reservation followed years of advocacy and struggle by the Manzanita Band to secure their ancestral lands. Before the establishment of the reservation, the Diegueno people faced significant challenges due to colonization and government policies that systematically eroded their land base. The Indian Reorganization Act of 1934 played a pivotal role in this narrative by allowing tribes to re-establish some degree of self-governance and regain control over their lands. Though,it wasn’t until the late 20th century that the Manzanita Band was officially recognized by the federal government,which paved the way for the creation of their reservation.
Today, the Manzanita Band is actively restoring their traditional lands, creating economic opportunities, and fostering a vibrant cultural resurgence. Tribal lands not only serve as a physical home for the tribe but also as a cultural sanctuary,where members can connect with their heritage and community. The Manzanita Reservation continues to play a crucial role in the preservation of Diegueno traditions, languages, and practices, empowering future generations to thrive in a world that continues to change around them.
Modern Concerns Of The Tribe
The Manzanita Band of Diegueno Mission Indians faces a range of modern concerns that impact their community and cultural preservation. One significant issue is the preservation of their lands and natural resources. As development pressures increase in California, the Manzanita Reservation is at risk from urban encroachment, which threatens traditional practices and sacred sites. The tribe actively engages in land management efforts to safeguard these areas and to ensure sustainable use of their natural resources.
Economic development is another pressing concern. While the tribe has explored various economic initiatives,including gaming and tourism,balancing financial growth with cultural integrity remains challenging. The tribe seeks to create job opportunities that respect traditional values and foster community well-being. Initiatives aimed at promoting local arts and crafts have gained traction, empowering tribal members to share their cultural heritage while generating income.
Education and youth engagement are vital areas of focus for the Manzanita Band.The tribe prioritizes educational programs that not only support academic achievement but also impart cultural knowledge and language revitalization. By encouraging the younger generation to learn about their history and traditions, the tribe aims to foster a stronger sense of identity and connection to their heritage.
Health care access is another critical issue. The community faces challenges related to health disparities and the need for culturally appropriate care. The Manzanita Band is actively working to improve health services by collaborating with various organizations to address mental health, substance abuse, and overall wellness among tribal members. Furthermore, initiatives promoting traditional diets and lifestyles are essential in combatting health issues prevalent in Indigenous populations.
Climate change poses a growing threat to the Manzanita Reservation, as altered weather patterns disrupt traditional hunting, gathering, and agricultural practices.The tribe is increasingly engaging in climate resilience strategies, focusing on adaptation methods that allow them to sustain their livelihoods and protect their environment. Through educational outreach and partnerships with environmental organizations, the Manzanita Band seeks to advocate for policies that protect their land and cultural heritage for future generations.
the modern concerns of the Manzanita Band of Diegueno Mission Indians encompass land preservation, economic development, education, health care, and climate change. By addressing these challenges, the tribe can work towards a sustainable future while maintaining their rich cultural legacy.
Events And Other Social And Political Activities
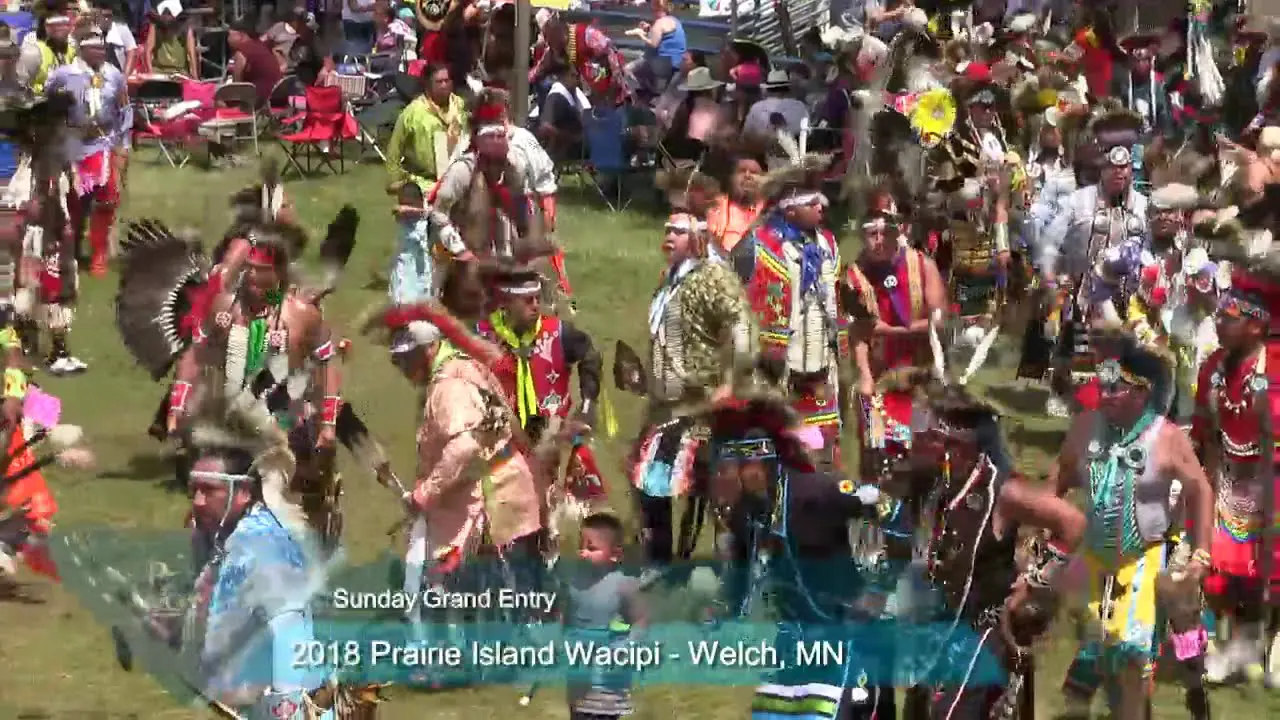
The Manzanita Band of Diegueno Mission Indians, located on the Manzanita Reservation in California, actively engages in a variety of social and political activities that reflect their rich cultural heritage and commitment to community development. Central to their events is the annual Manzanita Pow Wow, which not only celebrates Native American culture through traditional dance, music, and crafts but also serves as a vital platform for cultural exchange and education. This gathering attracts attendees from various tribal nations and beyond, fostering connections and understanding within and outside the Native American community.
In addition to cultural celebrations, the Manzanita Band is involved in advocacy initiatives that address social issues affecting Indigenous peoples. They participate in state and national discussions regarding Native American rights,land sovereignty,and environmental protection. Through partnerships with other tribes and organizations, the Manzanita Band works to amplify their voice on policies related to tribal sovereignty and resource management, ensuring their members’ perspectives are represented in legislative processes.
Community health and wellness programs are another focus for the Manzanita Band.The tribe organizes health fairs, workshops, and fitness events aimed at promoting well-being among their members.These programs frequently enough include traditional practices alongside modern health approaches, highlighting the integration of Native American traditions in contemporary health care.
Educational initiatives are also a priority for the Manzanita Band. They provide scholarships and tutoring programs for tribal youth, designed to encourage higher education while instilling pride in their Indigenous identity. Collaborations with local schools and educational institutions help raise awareness of Native American history and culture among the broader community, fostering respect and understanding.
The Manzanita Band is also actively engaged in environmental stewardship efforts, recognizing the importance of preserving their ancestral lands. Their involvement in environmental advocacy includes organizing clean-up events, habitat restoration projects, and educational seminars on sustainability. By promoting environmental awareness, they aim to protect the natural resources that are vital to their culture and livelihood.Through these diverse social and political activities, the Manzanita Band of Diegueno Mission Indians not only strengthens their community but also enriches the cultural tapestry of California’s Native American landscape. Their commitment to preserving traditions while addressing contemporary challenges underscores their resilience and dedication to future generations.