The Onondaga Nation, one of the original five nations of the Haudenosaunee Confederacy, holds a rich history and vibrant culture deeply intertwined with the land of central New York. Known as the “Keepers of the Fire,” the Onondaga people have served as a vital political and spiritual centre for the Iroquois Confederacy, which has played a significant role in shaping the governance and social structures of Indigenous communities in North America. With a commitment to preserving their language, traditions, and community values, the Onondaga Nation continues to thrive today.
Historically,the Onondaga Nation’s territory encompassed the Syracuse region,characterized by its lush forests,clear lakes,and strategic waterways. The tribe’s reliance on agriculture, hunting, and fishing not only highlights their enduring lifestyle but also their profound connection to the natural world. The Onondaga culture is rich in oral traditions, with stories and teachings passed down through generations, emphasizing the importance of community, respect for nature, and the interconnectedness of all living beings.
Today, the Onondaga Nation actively engages in efforts to promote cultural revitalization, environmental stewardship, and economic development. The tribe operates various enterprises, including a prosperous casino, and participates in ecological restoration projects aimed at protecting their ancestral lands.Additionally, the Onondaga Nation is a vocal advocate for Indigenous rights, sovereignty, and environmental justice, making significant contributions to discussions on climate change and natural resource management.
Through their enduring commitment to tradition and innovation,the Onondaga Nation not only honors the legacy of their ancestors but also paves the way for future generations to thrive. This introduction serves as a gateway to learning more about the Onondaga Nation’s history, culture, and contemporary initiatives, highlighting their ongoing journey toward cultural preservation and self-determination.
Origin Of The People
The Onondaga Nation, one of the principal nations of the Haudenosaunee, or Iroquois Confederacy, has a rich cultural heritage and a deep-rooted history that dates back thousands of years. According to their oral traditions, the Onondaga people originated from the area surrounding what is now known as central New York, specifically around Onondaga Lake. They refer to themselves as “Onondowaga,” which translates to “people of the hills,” reflecting their connection to the lush,hilly landscape of the region.
Historically, the Onondaga played a vital role in the formation of the Iroquois Confederacy, a refined political and social alliance that united six nations: the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, Seneca, and Tuscarora. This confederation aimed to promote peace, cooperation, and collective defense among its members. The Onondaga served as the central fire keepers of the Confederacy, signifying their importance in maintaining harmony and guiding meetings that shaped the policies and decisions of the allied nations.
The Onondaga people have a strong spiritual connection to their land, viewing it as sacred and vital to their identity. Their spiritual beliefs are closely tied to nature, emphasizing the importance of balance and respect for the earth, which is central to their traditions and practices.Additionally, the Onondaga’s matrilineal society highlights the significant roles that women play in family and community life, further enriching their cultural narrative.
As skilled hunters,fishermen,and agriculturalists,the Onondaga have historically relied on the bountiful resources of their ancestral lands,cultivating crops of corn,beans,and squash—often referred to as the Three Sisters—while also engaging in traditional practices such as fishing and hunting to sustain their communities.
Despite facing challenges over the centuries, including the impact of colonization and modern-day issues, the Onondaga Nation continues to uphold its traditions and values. The resilience of the Onondaga people is reflected in their ongoing efforts to promote cultural revitalization and language preservation, ensuring that future generations have a strong connection to their heritage.By actively participating in contemporary dialogues about sovereignty and self-determination, the Onondaga are committed to forging a meaningful path forward while honoring their past.
Tribal Homelands
The Onondaga Nation, one of the six nations of the Haudenosaunee (Iroquois) Confederacy, is located in central New York, primarily around the area of Syracuse. The tribal homelands of the Onondaga Nation are rich in cultural significance and natural resources, making them a vital part of their identity and way of life. For centuries, the Onondaga have inhabited this region, which is characterized by lush forests, lakes, and the beautiful Onondaga Lake.
Onondaga Lake holds great importance for the tribe, not only as a source of sustenance but also as a cultural touchstone. Traditionally, the lake has served as a gathering place for ceremonies and community events, reinforcing the tribe’s social cohesion and cultural heritage. The Onondaga people maintain a profound spiritual connection to the land, viewing it as a living entity that must be respected and cared for.The Onondaga Nation has taken significant steps to reclaim and restore their traditional homelands, particularly following decades of environmental degradation. Efforts to clean up Onondaga Lake, alongside preservation initiatives for their natural habitats, reflect the tribe’s commitment to fostering a sustainable relationship with the environment.These endeavors not only enhance ecological health but also support traditional practices and the community’s way of life.
Moreover,the Onondaga Nation’s governance,rooted in their historical practices,emphasizes stewardship of their land. They utilize a holistic approach to land management,integrating traditional ecological knowledge with contemporary conservation methods.This perspective allows for a balanced approach to farming,hunting,and gathering,ensuring that future generations inherit a vibrant and healthy environment.
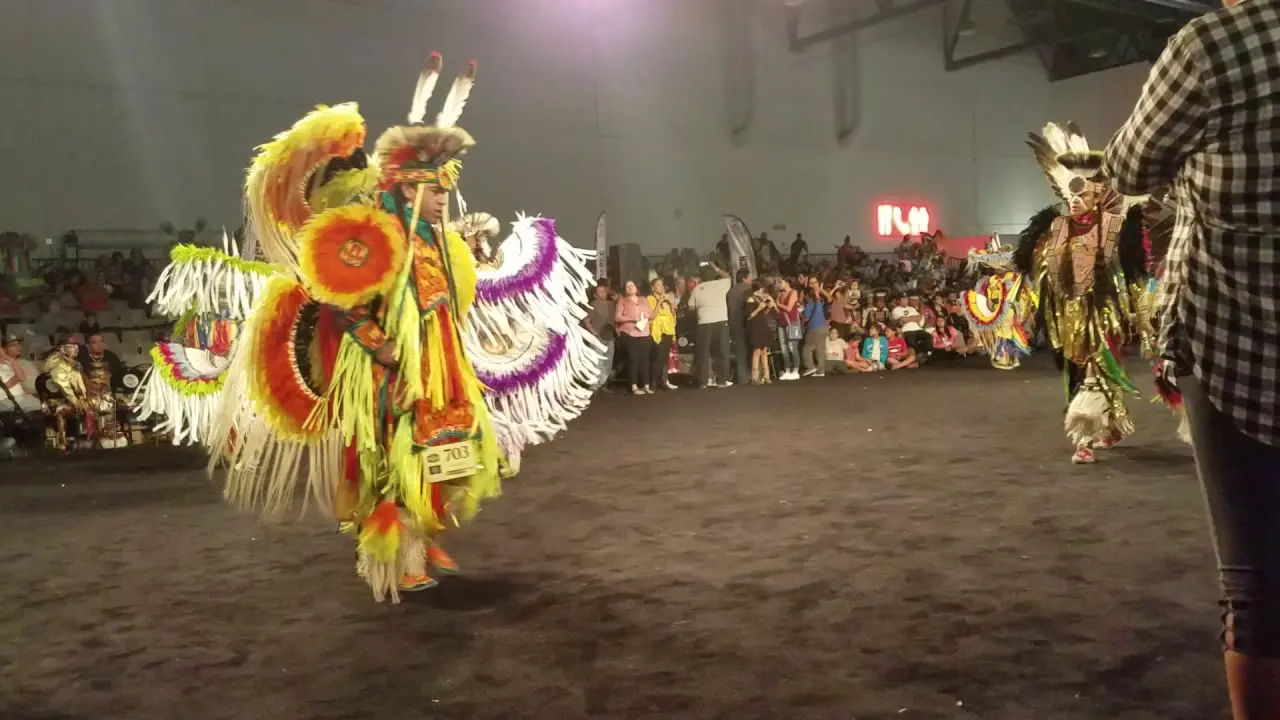
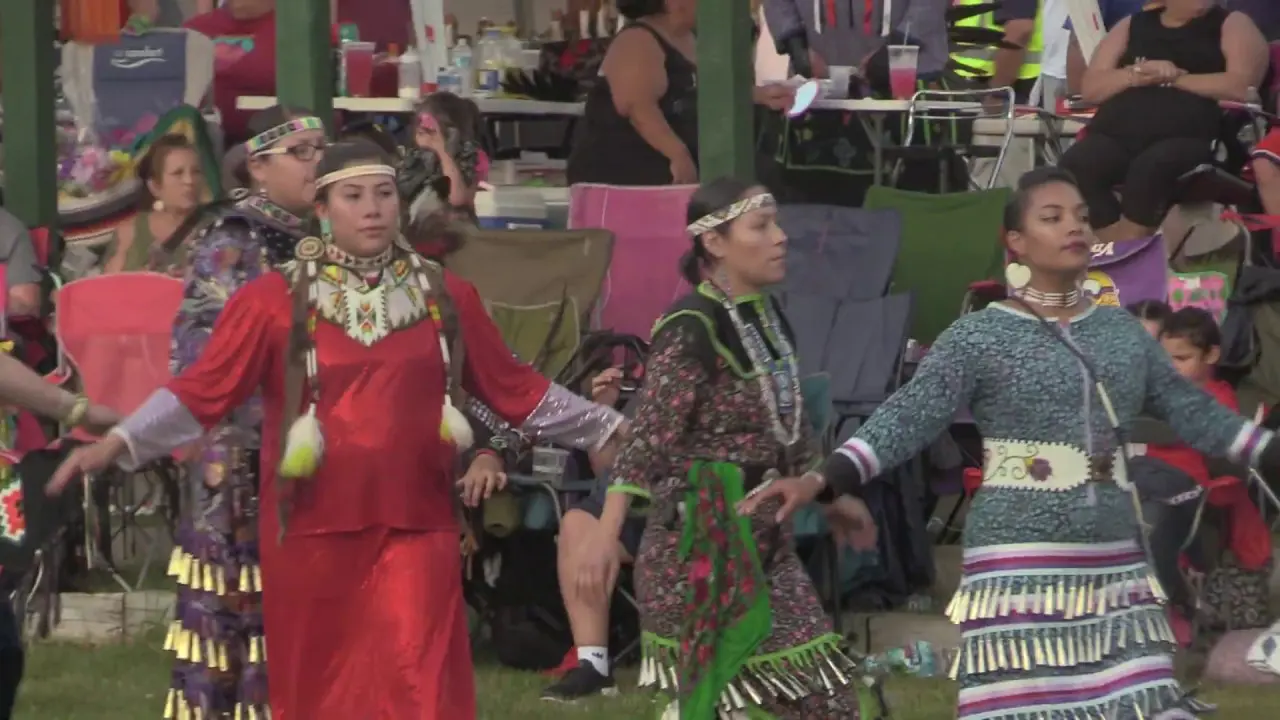
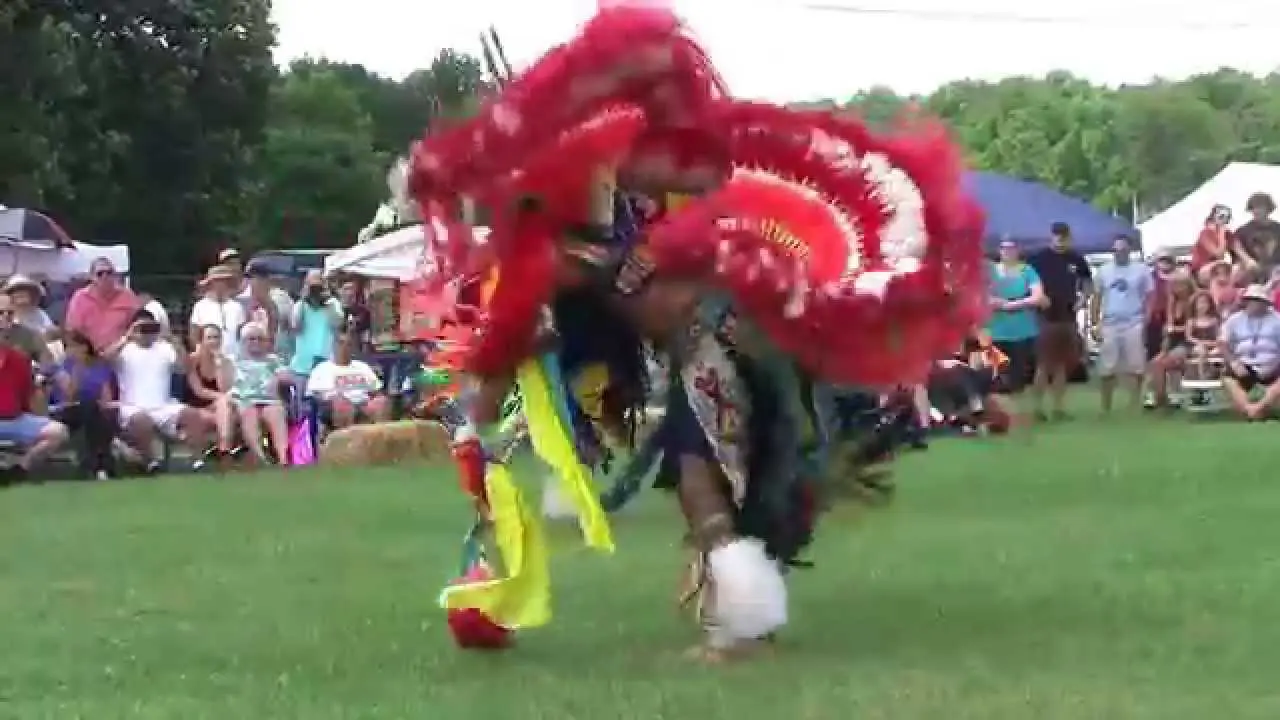
Culturally, the Onondaga Nation is known for its contributions to the arts, particularly in areas like music, dance, and storytelling. The surroundings inspire many of these cultural expressions, showcasing the tribe’s deep-rooted connection to their homelands. Festivals and events, frequently enough held in traditional sites, reflect their enduring legacy and foster a sense of community among members and visitors alike.
In recent years,the Onondaga Nation has also engaged in educational outreach,sharing their history and values with outsiders.By highlighting the significance of their homelands and the ongoing efforts to preserve them, the Onondaga Nation is not only advocating for their rights but also raising awareness about Indigenous issues in a broader context. Through these initiatives, the tribe continues to strengthen their relationship with their land and promote understanding of their culture and traditions.
Interactions With Settlers
The interactions between the Onondaga Nation and European settlers were complex and multifaceted, reflecting a range of positive and negative experiences that shaped both their histories.
One positive aspect of these interactions was the collaboration and trade between the Onondaga and settlers.The Onondaga, known for their agricultural prowess and knowledge of local resources, engaged in trade with Europeans, exchanging goods such as corn, beans, and tobacco for metal tools, firearms, and textiles. This exchange allowed the Onondaga to enhance their lifestyle and adapt new technologies, aiding them in their agricultural practices and daily lives.
Furthermore, the Onondaga played a crucial role in the political landscape of the region. As one of the Five Nations of the Iroquois Confederacy, they established alliances with various European powers. Their diplomatic skills often enabled them to negotiate treaties that preserved their lands and autonomy for some time, showcasing their agency in the face of colonial encroachment.These alliances also facilitated cultural exchanges, fostering an understanding of each other’s ways of life.
However, the interactions were not without significant negative consequences. As European settlers expanded their territories, the Onondaga faced increasing pressure on their lands. The encroachment led to land treaties that were often unfairly negotiated or coerced, resulting in the loss of traditional territories that were essential for their hunting, fishing, and farming. The infamous Treaty of Fort Stanwix in 1768 is one such example, where large swathes of Onondaga land were ceded under duress.
Moreover, the arrival of settlers brought new diseases, to which the Onondaga had little immunity. This led to devastating outbreaks that significantly reduced their population, weakening their social structure and cultural practices. The loss of life and the introduction of new challenges such as alcoholism and poverty further elaborate their interactions with settlers, leading to tensions and conflicts.
The legacy of these interactions continues to resonate today, as the Onondaga Nation strives to reclaim their rights and protect their cultural heritage. The story of the Onondaga Nation’s encounters with settlers highlights the resilience of Indigenous peoples in the face of change and the ongoing struggle for recognition and respect in a world that often overlooks their contributions and rights.
Most Notable Events In Their Tribal History
The Onondaga Nation, one of the original five nations of the Haudenosaunee (Iroquois Confederacy), boasts a rich and storied history marked by significant events that have shaped their culture and governance. One notable event in their tribal history is the formation of the Iroquois Confederacy in the late 16th century, which united the Onondaga, Mohawk, Oneida, Cayuga, Seneca, and later the Tuscarora nations. This alliance was crucial in establishing a sophisticated governance system that emphasized peace, collective decision-making, and mutual defense.
Another significant event occurred during the American Revolution when the Onondaga Nation faced intense pressure from both British and American forces. The tribe’s strategic location in central New York made them pivotal in the conflict. After the war, many Onondaga people struggled with the repercussions of their alliances, facing land dispossessions and social upheaval as they navigated their new realities.
In the 1800s, land treaties such as the Treaty of Fort Stanwix (1784) and further agreements resulted in significant land loss for the Onondaga Nation. The U.S. government frequently enough failed to honor these treaties, leading to a protracted struggle for recognition and land rights. The Onondaga’s resilience was exemplified during the Land Claim settlement initiatives starting in the 1970s, as they sought restitution for lost territories, culminating in landmark legal battles that brought national attention to Indigenous land rights.
The Onondaga Nation also gained international recognition through its involvement in environmental advocacy. In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, the Onondaga people focused on restoring their traditional lands and waters, especially in relation to pollution issues in Onondaga Lake. Their activism has highlighted the importance of indigenous stewardship of the environment, demonstrating the tribe’s ongoing commitment to protecting their heritage and natural resources.
Moreover, the establishment of the Onondaga Nation’s comprehensive government, known as the Haudenosaunee Confederacy Council, serves as a testament to their democratic traditions. The council upholds the Great Law of Peace, a foundational document that governs the Onondaga and the broader Iroquois Confederacy. This governance model has not only nurtured Onondaga culture and social cohesion but has also inspired indigenous movements globally for self-determination and natural rights.
Through these events, the Onondaga Nation demonstrates a rich legacy of resilience, governance, and environmental stewardship, underscoring the tribe’s continuing evolution and its integral role in the broader narrative of Native American history.
Where Are Their Tribal Lands Now And How Were They Established
The Onondaga Nation, one of the original tribes of the Haudenosaunee Confederacy, is primarily located near Syracuse, New York. Their lands encompass approximately 7,300 acres of territory, which is a fraction of what they once occupied before European colonization. The Onondaga’s current tribal lands were established through a combination of historical treaties, agreements, and contemporary legal battles aimed at restoring their rights and sovereignty.
The establishment of these lands has roots in a complex history of engagement with colonial powers.Initially, the Onondaga occupied vast areas of central New York, which they utilized for agriculture, hunting, and trade. Though, treaties made with colonial governments frequently enough resulted in land cessions that significantly diminished their territories.Following the American Revolution, numerous treaties further eroded their land holdings, and by the 19th century, the Onondaga were confined to a much smaller area.In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, the Onondaga Nation has worked diligently to reclaim their rights and restore their land. Legal actions, such as the landmark 1988 federal court case that affirmed their sovereignty and self-governance, have been critical in this effort. Additionally, various initiatives aimed at environmental conservation and cultural revitalization have been undertaken to reinforce their presence and connection to the land.
Today, the Onondaga Nation continues to advocate for the recognition of their historical land claims and the preservation of their cultural heritage.Their territories serve not only as a place of residence but as a living reminder of their enduring legacy and a focal point for their community’s social, political, and spiritual activities. As an inevitable result, the Onondaga Nation symbolizes resilience, striving to ensure that future generations honor and respect the land their ancestors once thrived upon.
Modern Concerns Of The Tribe
The Onondaga Nation,one of the original five nations of the Haudenosaunee Confederacy,faces a myriad of modern concerns that reflect both the unique challenges of Native American communities and the specific historical context of their sovereignty and land rights. One pressing issue is the restoration of their territorial lands. Historically, the Onondaga Nation has seen significant loss of their lands due to treaties that were often signed under duress or misrepresentation. Today, they are actively working to reclaim these lands and preserve their cultural heritage, which is intrinsically linked to their territory.
Environmental concerns also play a pivotal role in the Nation’s modern challenges. The Onondaga Lake, once a central part of their community and spirituality, has been heavily polluted over the decades. Efforts to clean and restore the lake to a condition that supports both wildlife and recreational activities are ongoing. The tribe has been vocal about ecological preservation and sustainable practices, emphasizing the importance of traditional ecological knowledge in modern environmental stewardship.
Economic development is another significant concern for the Onondaga Nation. The tribe seeks to create sustainable economic opportunities that respect their cultural values. Initiatives such as ecotourism, organic agriculture, and small business development have been explored to foster economic self-sufficiency while enhancing community welfare. Moreover, the tribe is actively involved in discussions around renewable energy projects, recognizing the need for energy independence and sustainability.
Health disparities also impact the Onondaga Nation,with increased rates of chronic illnesses and limited access to quality healthcare. Access to traditional medicine, combined with modern healthcare options, is often part of their strategy to improve community health. The tribe works toward better healthcare initiatives tailored to their cultural context, addressing both physical and mental health needs among members.
Legal and political advocacy remains crucial in addressing modern concerns. The Onondaga Nation continually engages in negotiations with federal and state governments regarding issues of treaty rights, sovereignty, and self-governance. Their efforts emphasize the importance of respecting tribal sovereignty and the need for governmental accountability in fulfilling treaty obligations.
These modern concerns highlight the Onondaga Nation’s resilience and commitment to preserving their culture, rights, and environment, as they navigate the complexities of contemporary society while honoring their rich heritage.
Events And Other Social And Political Activities
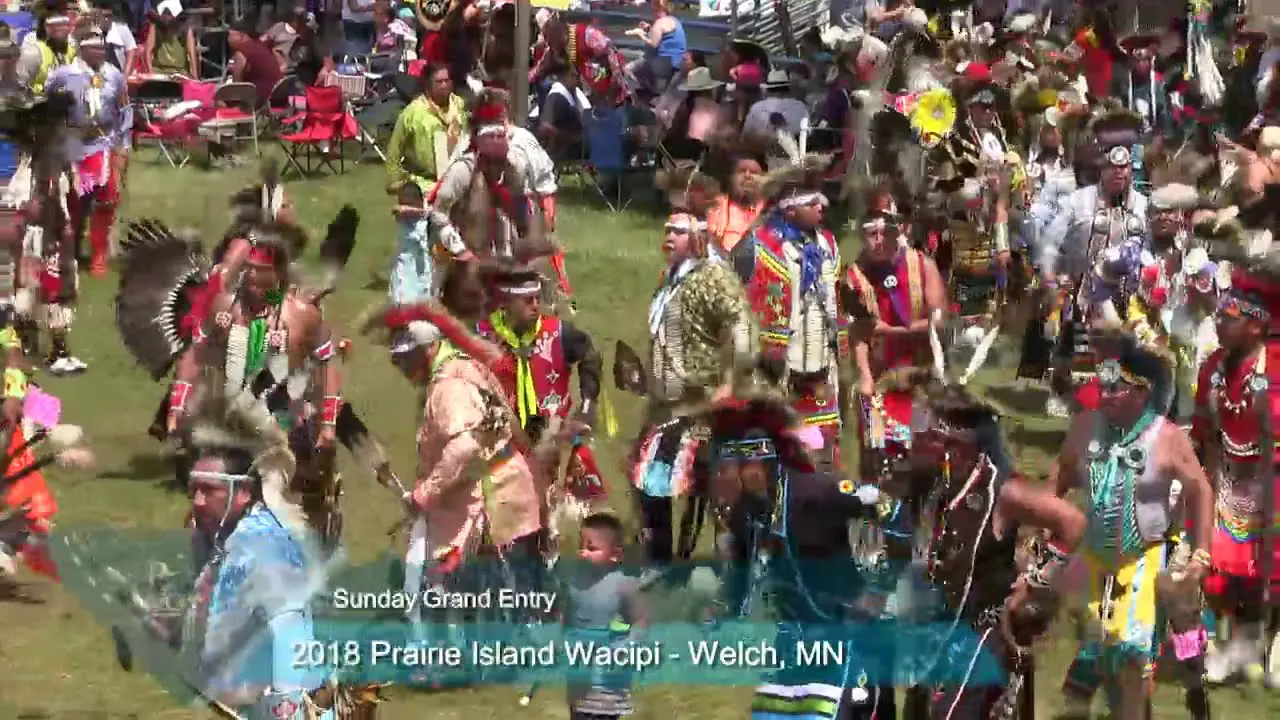
The Onondaga Nation, part of the Haudenosaunee Confederacy, is deeply engaged in numerous social and political activities that reflect its rich cultural heritage and contemporary challenges. One of the most significant events hosted by the Onondaga Nation is the annual Great Law Festivity, which commemorates the formation of the Iroquois Confederacy and emphasizes the importance of peace and unity among the Six Nations. This celebration not only attracts members from various tribes but also educates non-Natives about the Onondaga’s traditions and governance.
In terms of political activities, the Onondaga Nation actively participates in discussions surrounding land rights and environmental stewardship. The nation has been at the forefront of legal battles to reclaim ancestral lands and address the impacts of pollution from both industrial activities and legacy contamination. Their commitment to environmental justice is evident in initiatives such as the Onondaga Lake restoration project, an effort to rehabilitate one of the most polluted lakes in North America, showcasing their dedication to the health of their community and ancestral territories.
Culturally, the Onondaga Nation hosts traditional festivals, such as the summer ball games, which not only strengthen community bonds but also revive ancient sports practices. These events serve as a platform for cultural expression and education, where younger generations learn the importance of their heritage through direct participation in traditional sports and art forms.
Furthermore, the Onondaga Nation engages with broader social issues by participating in inter-tribal gatherings and collaborations with environmental activist groups. Their involvement in activism not only highlights their ongoing struggles but also contributes to regional and national dialogues on Indigenous rights and environmental protection.
The Onondaga Nation exemplifies resilience and advocacy through its various events, cultural practices, and steadfast commitment to social justice. By participating in and promoting these activities, the Onondaga Nation not only strengthens its own community but also fosters greater awareness and respect for Indigenous sovereignty and environmental stewardship.