Introduction to the Three Affiliated Tribes of the Fort Berthold Reservation, North Dakota
Nestled in the picturesque landscapes of North Dakota, the Fort Berthold Reservation is home to the Three Affiliated Tribes: the Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara. Known collectively as MHA Nation, these tribes boast a rich cultural heritage and a history that dates back centuries.The Fort Berthold Reservation, located along the Missouri River, has been a vital lifeline for the tribes, providing not only sustenance but also a connection to their ancestral lands.
The Three Affiliated Tribes have endured substantial challenges throughout their history, including forced relocations and the impacts of colonization. Despite these adversities, they have maintained a strong sense of identity and community, celebrating their traditional customs, language, and art. Today, the MHA Nation is increasingly recognized not only for its resilience but also for its significant contributions to the state of North Dakota and the broader indigenous landscape.
In recent years, the Three Affiliated Tribes have made strides in economic development, including initiatives in tourism, energy, and agriculture. With a commitment to preserving their rich cultural heritage while embracing modern opportunities, the MHA Nation stands as a testament to effective tribal governance and community empowerment. Through education, cultural programs, and economic investments, the Three Affiliated Tribes continue to thrive, ensuring that the history and traditions of the Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara peoples are passed down through generations.
Join us as we delve deeper into the fascinating stories, vibrant traditions, and contemporary challenges faced by the Three Affiliated Tribes of the Fort Berthold Reservation, and discover the unique role they play in enriching the cultural tapestry of North Dakota and beyond.
Origin Of The People
The Three Affiliated Tribes of the Fort Berthold Reservation, comprising the Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation, trace their origins back thousands of years to the Missouri River Valley. These tribes have a rich cultural heritage that is deeply intertwined with their environment, showcasing a profound relationship with the land that sustains them.
The Mandan people are believed to have settled in the North Dakota region around 1250 AD, establishing agricultural practices that capitalized on the fertile floodplains along the Missouri River. Their unique earth-lodge villages, characterized by circular structures made of earth and grass, served as hubs for trade, social gatherings, and spiritual ceremonies. The Mandan were known for their advanced agricultural techniques, growing crops such as corn, beans, and squash, which formed the basis of their diet and economy.
The Hidatsa, closely related to the Mandan, migrated to the Northern Plains, joining their neighbors in the 16th century. They too built earth lodges and practiced agriculture while engaging in hunting and gathering. The Hidatsa were integral to the cultural and social fabric of the region, known for their spiritual and ceremonial practices, including the sacred Medicine Bundle, which played a significant role in their identity and traditions.
The Arikara, originally from the Great Plains, also established themselves in this region following their migration from the south. Their communities, rich in fishing and hunting practices, added to the diverse cultural mosaic of the Three Affiliated Tribes. The Arikara people possessed unique traditions and societal structures that greatly contributed to the overall identity of the confederation.
Throughout history, these tribes have faced numerous challenges, including the impacts of European colonization, forced relocations, and significant changes to their way of life. Yet, despite these adversities, the Three Affiliated Tribes have maintained their cultural integrity and resilience. Today, the tribes are united in their efforts to preserve their history, languages, and traditional practices while embracing modernity and striving for self-determination.
The Fort Berthold Reservation, established in the 1851 Treaty, serves as a testament to their enduring legacy and cultural revival. Each tribe’s unique stories and experiences contribute to the rich tapestry of the Three Affiliated Tribes,ensuring that their heritage continues to thrive for generations to come.
Tribal Homelands
The Three Affiliated Tribes, comprising the Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nations, are the original inhabitants of the Fort Berthold Reservation located in North Dakota. This sprawling land, approximately 1,000 square miles, extends along the Missouri River, offering both rich cultural heritage and diverse ecosystems.
The Mandan,known for their earth-lodge villages,historically thrived in the bottomlands of the Missouri River. Their agricultural practices were advanced, with a focus on crops like corn, beans, and squash, which they cultivated in fertile river valleys. The Hidatsa tribes, who also lived along the riverbanks, shared many cultural similarities with the Mandan. They are known for their communal farming methods and skilled craftsmanship in pottery and beadwork.
The Arikara, another vital part of the Three Affiliated Tribes, settled primarily in the river’s upper reaches and are recognized for their trade networks and unique spiritual practices. The confluence of these three tribes has resulted in a rich tapestry of traditions and cultural exchanges that still resonate today.
The Fort Berthold Reservation itself serves as a crucial habitat for various wildlife, reflecting the deep connection the tribes have with nature. The landscape includes rugged ridges, flowing rivers, and lush forests, which play a vital role in the tribes’ hunting and gathering practices. This geographic diversity supports not only cultural food sources,such as fish and game but also medicinal plants that form the backbone of traditional healing practices.
In recent years, the tribes have worked diligently to reclaim their lands and promote economic development while preserving their rich heritage. The establishment of community-led initiatives highlights the tribes’ commitment to environmental sustainability and cultural preservation. Efforts to revitalize native languages, arts, and education are in full swing, ensuring that future generations remain connected to their ancestral roots.
The Three Affiliated Tribes continue to play an essential role in the cultural mosaic of North Dakota, advocating for their rights and responsibilities toward their homelands. Through storytelling, dance, and communal gatherings, they celebrate their unique identity, which is intrinsically linked to the land of the Fort Berthold Reservation. With ongoing developments in tribal governance and community engagement, the future of the tribes looks promising as they honor their past while building towards a sustainable future.
Interactions With Settlers
Interactions between the Three Affiliated Tribes,consisting of the Mandan,Hidatsa,and Arikara Nations,and settlers in North Dakota have been marked by significant moments of both cooperation and conflict. Positive interactions primarily arose during the early years of contact in the 19th century. The tribes played a pivotal role in the fur trade, establishing fruitful relationships with European-American traders. These partnerships often facilitated cultural exchange and economic benefits for both parties. The Three Affiliated Tribes aided settlers by providing vital knowledge of the land and resources, which helped newcomers navigate the harsh environments of the northern plains.
However, as settlers continued to encroach on traditional lands, negative interactions began to surface. The arrival of more settlers led to increasing competition for resources like bison and land, culminating in heightened tensions. The implementation of policies such as the Dawes Act in 1887 further exacerbated these tensions, as it encouraged the allotment of tribal lands to individual members, often resulting in the loss of communal land and weakening tribal sovereignty.
Additionally, the construction of the Garrison Dam in the 1940s had devastating consequences for the Three Affiliated Tribes, flooding vast areas of their homeland and displacing many families.This government-led initiative, while aimed at providing hydroelectric power and flood control, disregarded the Tribes’ ancestral connections to the land, igniting profound grievances that shaped the tribe’s interactions with settler society.Today, despite the historical challenges, the Three Affiliated Tribes work to reclaim their narrative, preserving their cultural heritage and advocating for their rights. This complex relationship with settlers is a testament to the evolving dynamics of coexistence, where both historical grievances and moments of cooperation shape the ongoing story of the Three Affiliated Tribes and their interactions with the larger American society.
Most Notable Events In Their Tribal History
The Three Affiliated Tribes, comprised of the Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara nations, have a rich and complex history that has been marked by resilience and adaptation. One of the most notable events in their tribal history was the signing of the Fort Laramie Treaty in 1851. This treaty established large swaths of land for the tribes,but the changing dynamics of westward expansion soon created tensions that would challenge their sovereignty.
In the late 19th century, the tribes faced significant adversity due to the establishment of the Dawes Act in 1887, which aimed to assimilate Native peoples into Euro-American culture by allotting individual plots of land and selling off surplus land. This legislation led to considerable land loss and a dramatic reduction in their traditional ways of life.
The construction of the Garrison Dam in the 1940s was another pivotal moment in their history.The dam’s creation flooded a significant portion of the Fort Berthold Reservation, displacing many tribal members and submerging ancestral lands. This event catalyzed a broader movement for tribal sovereignty,as the tribes sought compensation and recognition for their losses,ultimately leading to the formation of the Three Affiliated Tribes’ governing structure.
Throughout the 20th century, the tribes continued to advocate for their rights and resources, culminating in the enactment of the Indian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act in 1975.This act allowed tribes to take control of their educational and public services, fostering a renewed sense of independence and identity.
Today, the Three Affiliated Tribes are actively engaged in economic development, with initiatives ranging from agriculture to energy production.They continue to celebrate their cultural heritage through art, language preservation, and traditions, ensuring that their rich history remains a vibrant part of their identity.
Where Are Their Tribal Lands Now And How Were They Established
The Three Affiliated Tribes, composed of the Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara nations, are located on the Fort Berthold Reservation in North Dakota. Established in 1870, the Fort Berthold Reservation spans approximately 1,070 square miles and is situated along the Missouri River. The tribal lands were originally set aside through treaties with the U.S. government, which recognized the sovereignty and rights of the tribes to govern themselves and maintain their cultural heritage.
The establishment of these lands was not without struggle. The tribes faced significant challenges during the mid-20th century, particularly following the construction of the Garrison Dam in the 1940s, which led to the flooding of a substantial portion of their traditional lands. Despite this loss,the Three Affiliated Tribes worked tirelessly to secure their remaining territories and enhance their economic conditions.
Today, the Fort Berthold Reservation is home to a vibrant community that actively preserves its cultural identity while fostering economic development through initiatives such as energy production, agriculture, and tourism. The tribes are also engaged in ongoing efforts to reclaim and restore their historical lands and revitalize their connection to the land and resources that are integral to their way of life.With an emphasis on sustainability and community resilience, the Three Affiliated Tribes continue to navigate the complexities of modern governance while honoring their past.
Modern Concerns Of The Tribe
The Three Affiliated Tribes, consisting of the Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara nations, face a variety of modern concerns that significantly impact their community on the Fort Berthold Reservation in North Dakota. One pressing issue is the environmental impact of oil extraction in the Bakken Formation. This booming oil industry has brought both economic opportunities and significant ecological challenges.While the influx of revenue from oil royalties has the potential to fund community initiatives and infrastructure development, it also raises concerns about pollution, land degradation, and the effects on traditional hunting and fishing grounds.Another critical concern for the Three Affiliated Tribes is the preservation of their cultural heritage and language. As younger generations become increasingly influenced by mainstream culture, efforts to revitalize Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara languages and traditions are becoming a priority. Educational programs and cultural events aimed at fostering a sense of identity and belonging among tribal members are essential in addressing this concern.
Healthcare access remains a significant issue, with tribal members often facing barriers to quality care. The healthcare infrastructure on the Fort Berthold Reservation struggles with underfunding, leading to challenges in addressing both physical and mental health needs.Substance abuse and addiction represent a substantial concern, with efforts underway to provide better support systems and prevention programs within the community.
Economic diversification is another area where the Three Affiliated Tribes are focusing their efforts. While oil revenues provide a financial boost,the volatility of the oil market poses risks to long-term economic stability.Exploring sustainable enterprises,such as tourism,agriculture,and renewable energy,allows the tribes to build a more resilient economic future that honors their heritage while meeting contemporary needs.
the Three Affiliated Tribes continue to advocate for sovereignty and self-determination, navigating complex legal and regulatory frameworks that can influence their governance and resource management decisions. By strengthening their political voice and fostering partnerships with other Indigenous and non-Indigenous entities, the tribes aim to protect their rights and ensure a vibrant future for their community on the Fort Berthold Reservation.
Events And Other Social And Political Activities
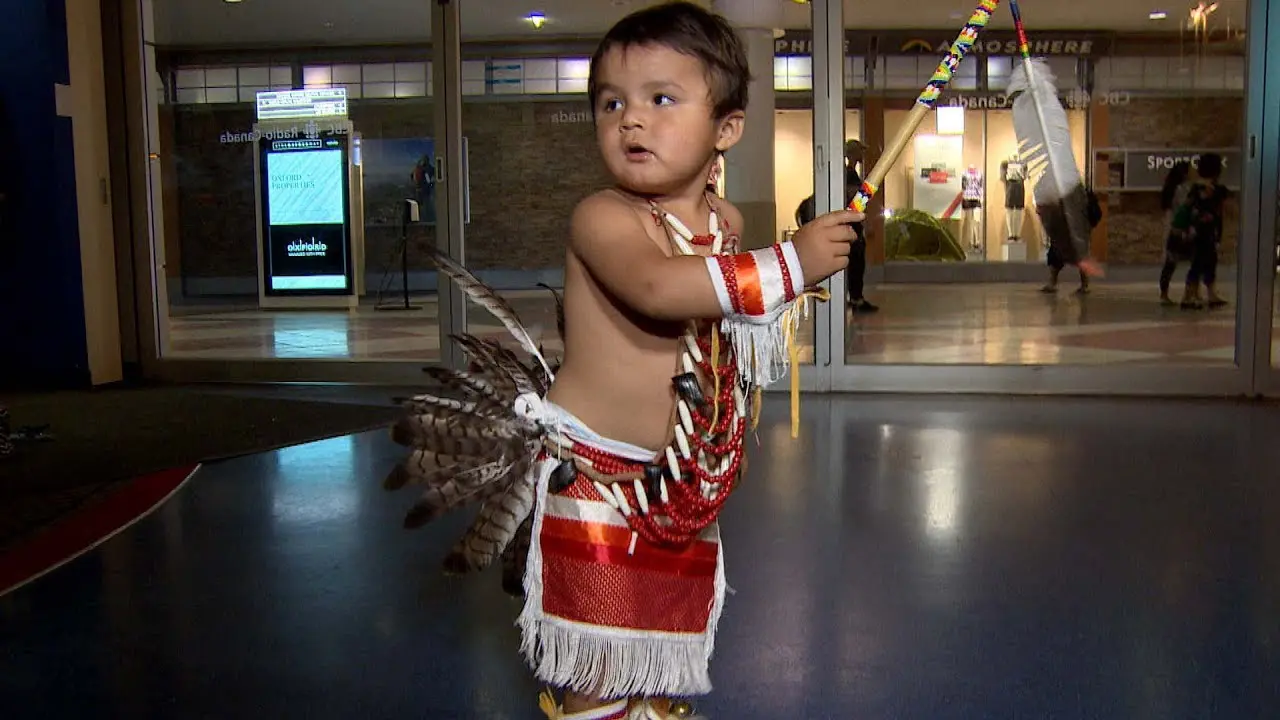
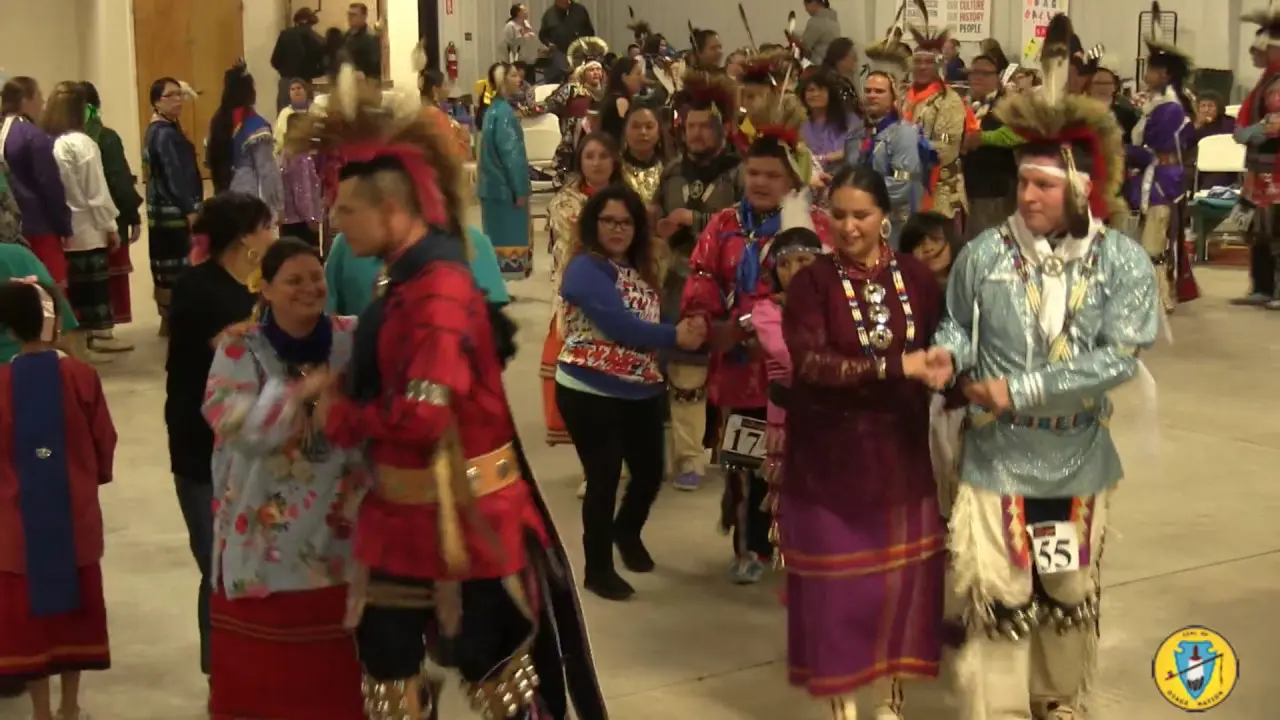
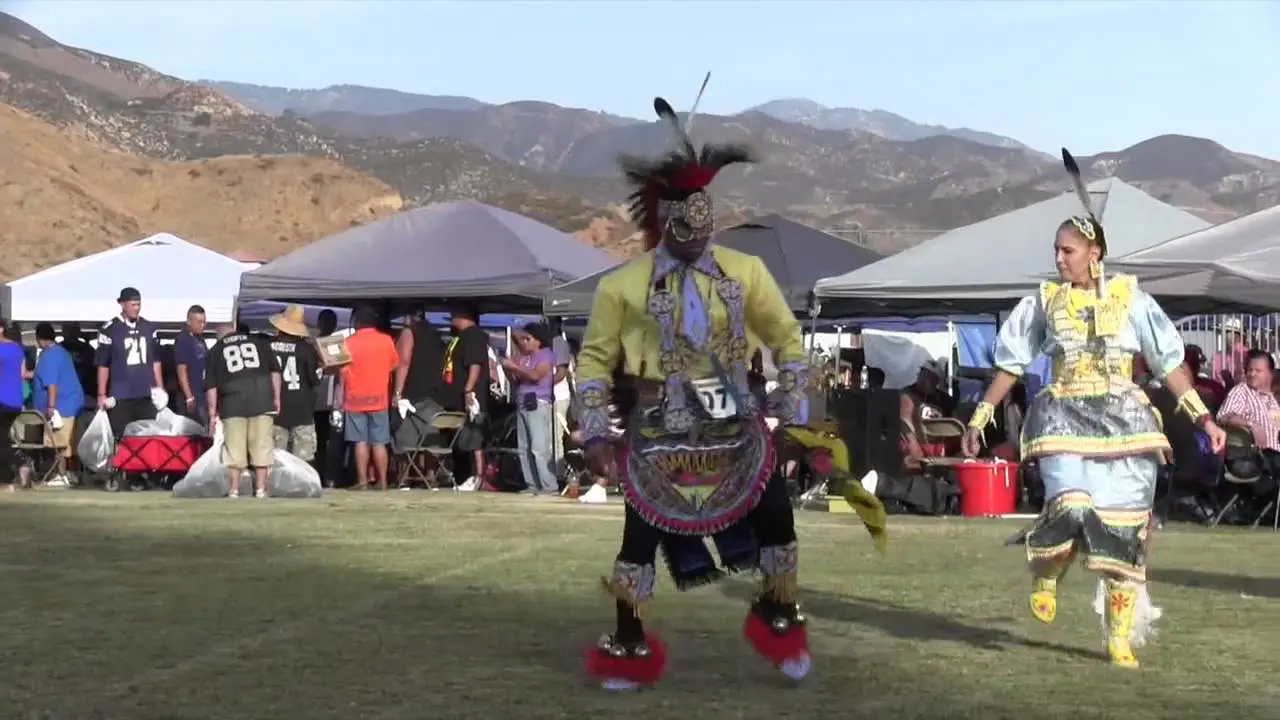
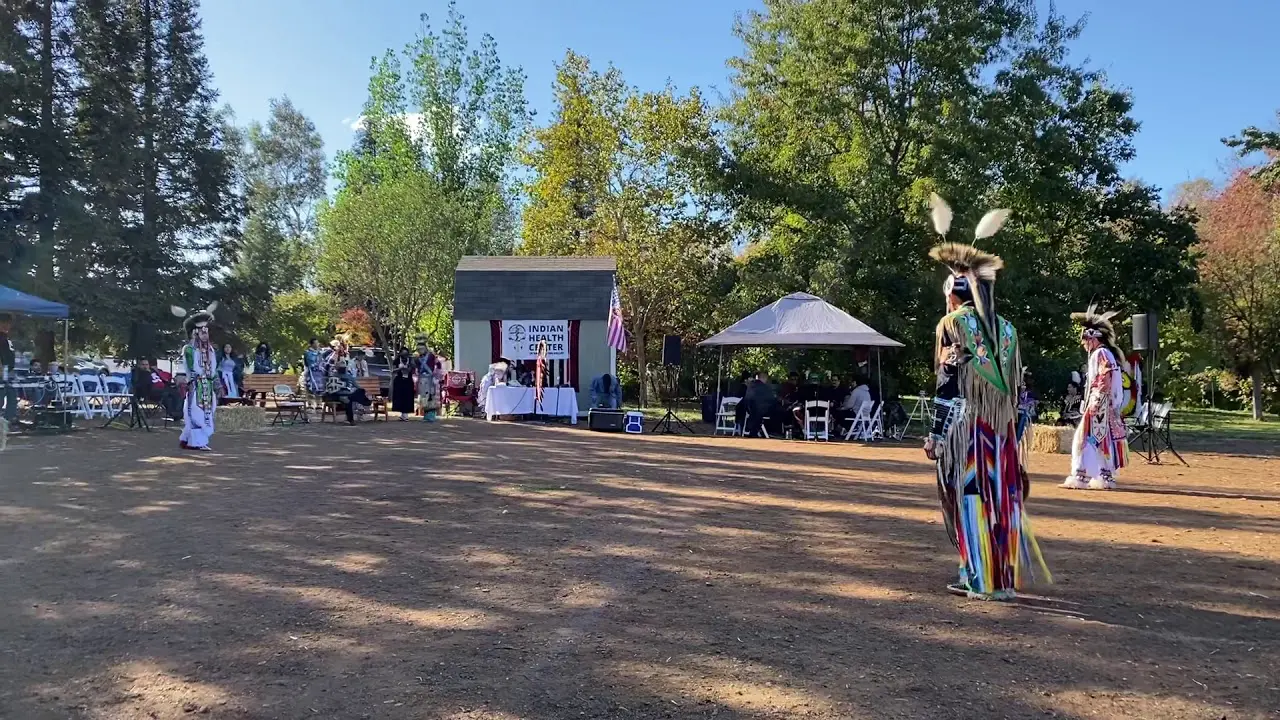
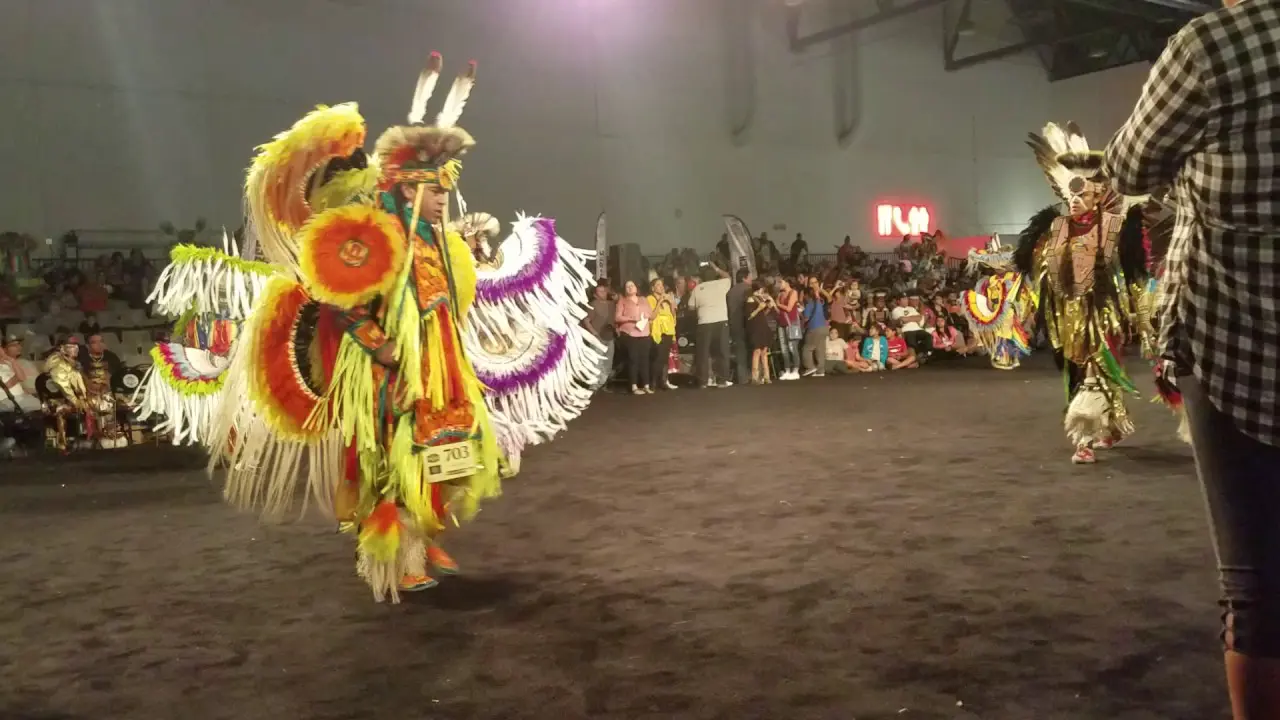
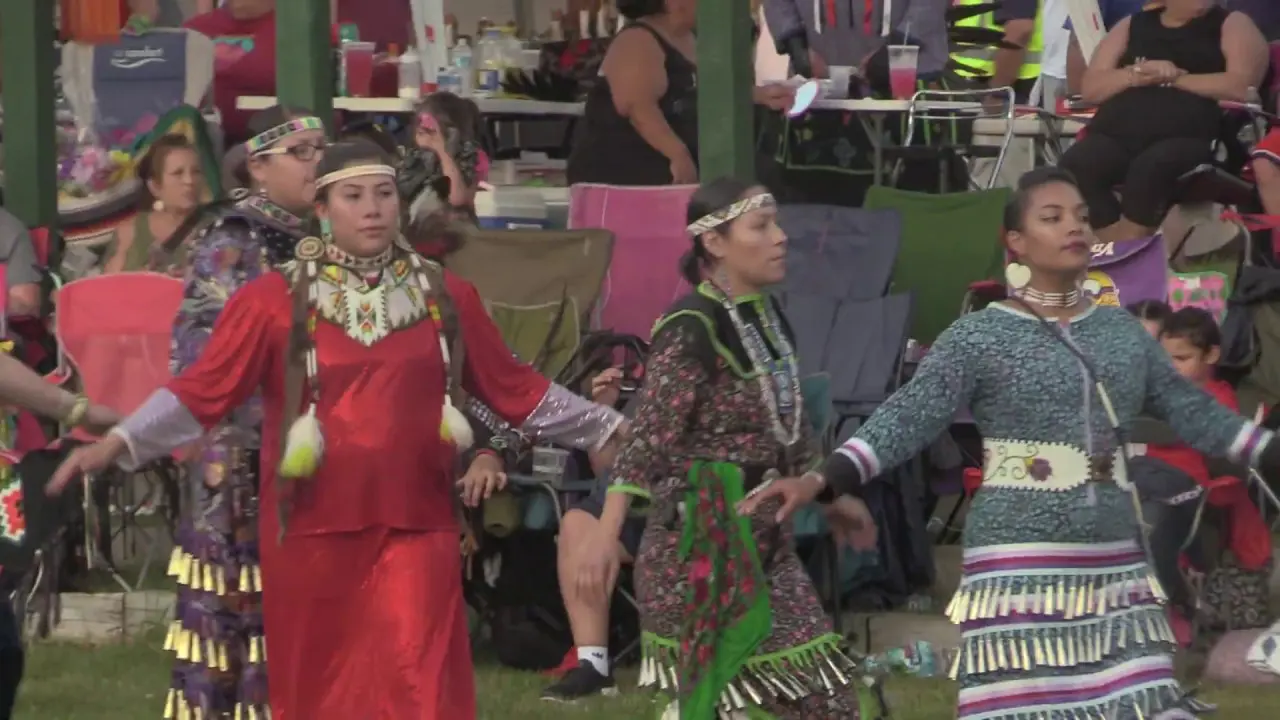
The Three Affiliated Tribes, consisting of the Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nations, are deeply engaged in both social and political activities on the Fort Berthold Reservation in North Dakota. Events like the annual Fort Berthold Day celebration showcase tribal heritage through traditional dances,art,and food,fostering a sense of community and pride among tribal members. These gatherings serve not only to celebrate cultural identity but also to reinforce social ties within the tribes.
Politically, the Three Affiliated Tribes actively advocate for their rights and sovereignty. The tribal council plays a crucial role in representing the interests of the community in negotiations with federal and state governments, particularly concerning issues like land rights, water resources, and energy development. Recent initiatives have focused on harnessing the tribe’s natural resources ethically while ensuring the preservation of their cultural heritage.
The tribes also emphasize education and youth engagement through events like the annual youth summer camp and cultural workshops, which teach younger generations about traditional practices and languages. These programs empower the youth, equipping them with skills to be future leaders and advocates for their community.
The Three Affiliated Tribes are also involved in environmental initiatives, advocating for sustainable practices in the face of challenges related to oil extraction and its impact on local ecosystems. Engaging in local and national dialogues about climate change, they strive to protect their land and resources for future generations.
Community health initiatives, including health fairs and wellness programs, reflect the tribes’ commitment to improving the well-being of their members. These events often incorporate traditional healing practices alongside modern healthcare solutions, emphasizing a holistic approach to health.the social and political landscape of the Three Affiliated Tribes is characterized by a rich array of events, advocacy efforts, and initiatives aimed at preserving cultural identity while addressing contemporary challenges. The active participation of tribal members in these activities highlights both a commitment to tradition and a vision for a sustainable future.