Introduction to the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma
The Caddo Nation of Oklahoma is a vibrant and culturally rich Native American tribe that continues to thrive in the heart of the Southern Plains. with a history that dates back hundreds of years, the Caddo people are known for their distinctive pottery, intricate ceremonial traditions, and a profound connection to their ancestral lands. Originally from the regions that now encompass Texas, Arkansas, and Louisiana, the Caddo Nation has overcome numerous challenges through resilience and determination. Today, they are located in southwestern Oklahoma, where they actively preserve their cultural heritage while also adapting to the modern world.
The Caddo Nation operates with a government structure that reflects their commitment to community and cultural preservation, and they engage in a variety of economic ventures to support their tribal members. This includes initiatives in gaming, tourism, agriculture, and education, all designed to enhance the quality of life for Caddo families. As stewards of their unique language, traditions, and values, the tribe continues to educate both its members and the broader public about their rich history and contributions to American culture.
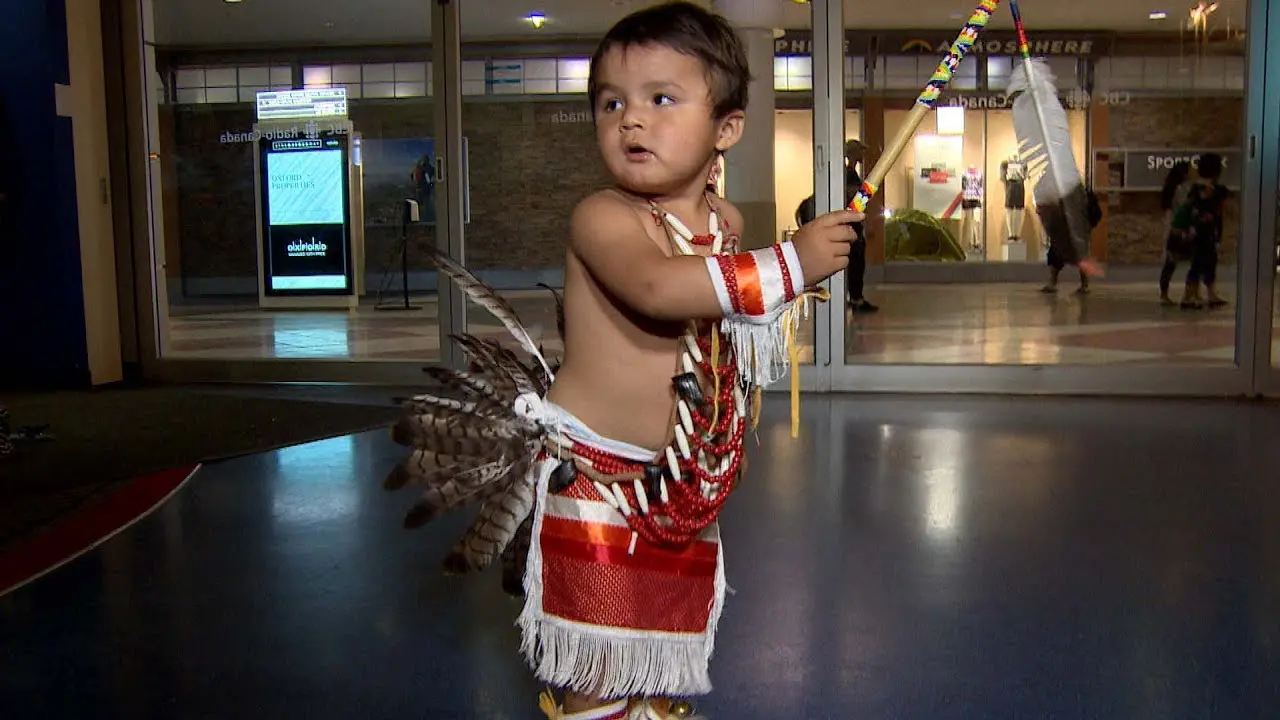
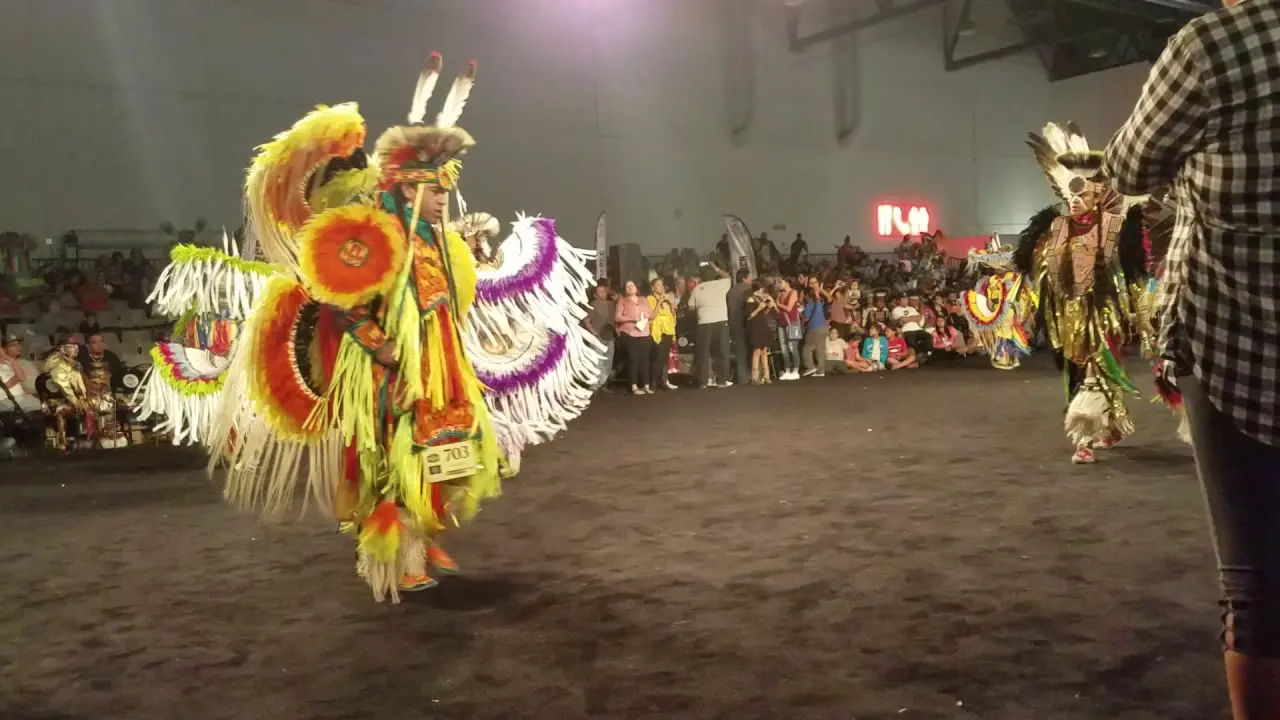
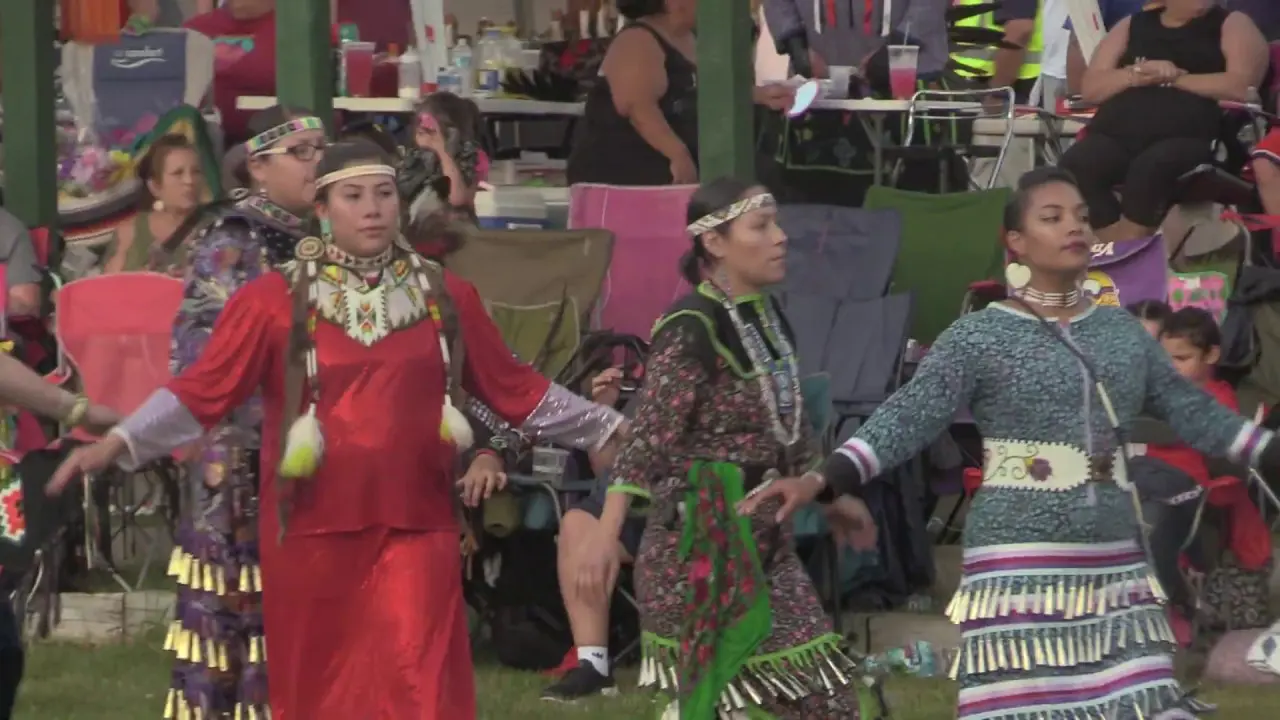
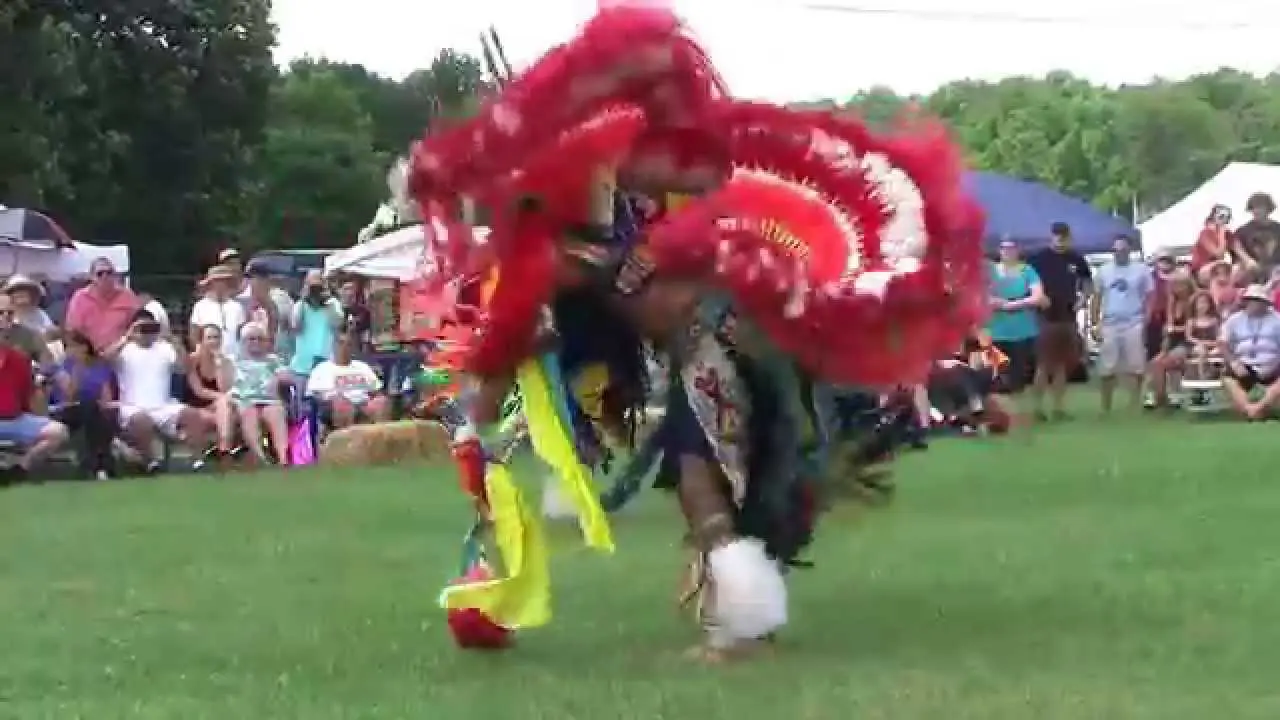
Visitors to the Caddo Nation can explore various cultural events and festivals that showcase traditional music, dance, and crafts, offering an immersive experience that celebrates their heritage. The tribe’s efforts to maintain their identity in a rapidly changing world are commendable, reflecting a deep respect for their past while looking toward a shining and hopeful future. As the Caddo Nation moves forward, they remain steadfast in their dedication to their community, culture, and the environment, ensuring that the spirit of their ancestors lives on for generations to come.
Origin Of The People
The Caddo Nation of Oklahoma traces its origins to a vibrant and sophisticated society that flourished in the southern Great Plains region, including parts of present-day Texas, Louisiana, Arkansas, and Oklahoma, long before european contact. Archaeological evidence suggests that the Caddo people have inhabited this area for thousands of years, developing a complex culture characterized by advanced agricultural practices, intricate pottery, and elaborate mound-building.The caddo people were organized into various confederacies and clans, each with distinct social structures, languages, and customs. Their settlement patterns were primarily agricultural, with maize (corn) being a staple crop that supported their population. The Caddo cultivated a diverse range of crops, including beans and squash, and practiced lasting hunting and gathering, allowing them to thrive in a variety of ecosystems.
Caddo traditions are steeped in spirituality and connection to the land. The tribe’s creation stories and oral histories emphasize their relationship with the natural world, highlighting their reverence for the earth and its resources. A matrilineal society,the Caddo valued the role of women in decision-making and community leadership,which was reflected in their governance systems.
As European settlers moved into the region in the 17th and 18th centuries, the Caddo Nation faced significant challenges, including land displacement and cultural disruption. Despite these adversities, the Caddo people adapted, maintaining their identity and cultural practices.The establishment of the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma in the 19th century further solidified their resilience and commitment to preserving their heritage.
Today, the Caddo Nation actively participates in cultural revitalization efforts, emphasizing the importance of language preservation, traditional crafts, and community events that celebrate their rich history. Their story is a testament to their enduring spirit and an affirmation of their place within the broader narrative of Native American history in the United States.
Tribal Homelands
The Caddo Nation of Oklahoma’s tribal homelands are steeped in a rich cultural heritage and a deep connection to the land. The Caddo people originally inhabited parts of what are now East texas, Western Louisiana, and Southern Arkansas before relocation to Oklahoma during the 19th century. Today, the Caddo Nation is primarily based in Caddo County, Oklahoma, where they continue to preserve their unique traditions and cultural identity.
The Caddo Nation encompasses approximately 5,000 acres of land, crucial for not only revitalizing their community and economy but also for maintaining their cultural practices. This territory serves as the heart of their heritage, where historical sites, ceremonial grounds, and community centers honor ancestral ties. The Caddo Nation is committed to reclaiming their history and fostering cultural education among younger generations, ensuring that their language, art, and traditions thrive.
Efforts to restore the tribal homelands include environmental conservation and sustainable development projects, reflecting the Caddo’s deep reverence for nature and its resources. The tribe engages in agricultural practices that are aligned with traditional methods, nurturing the land that has sustained them for centuries. By promoting economic initiatives that respect their cultural landscape, the Caddo nation strives to create a balance between modern development and ancestral values.
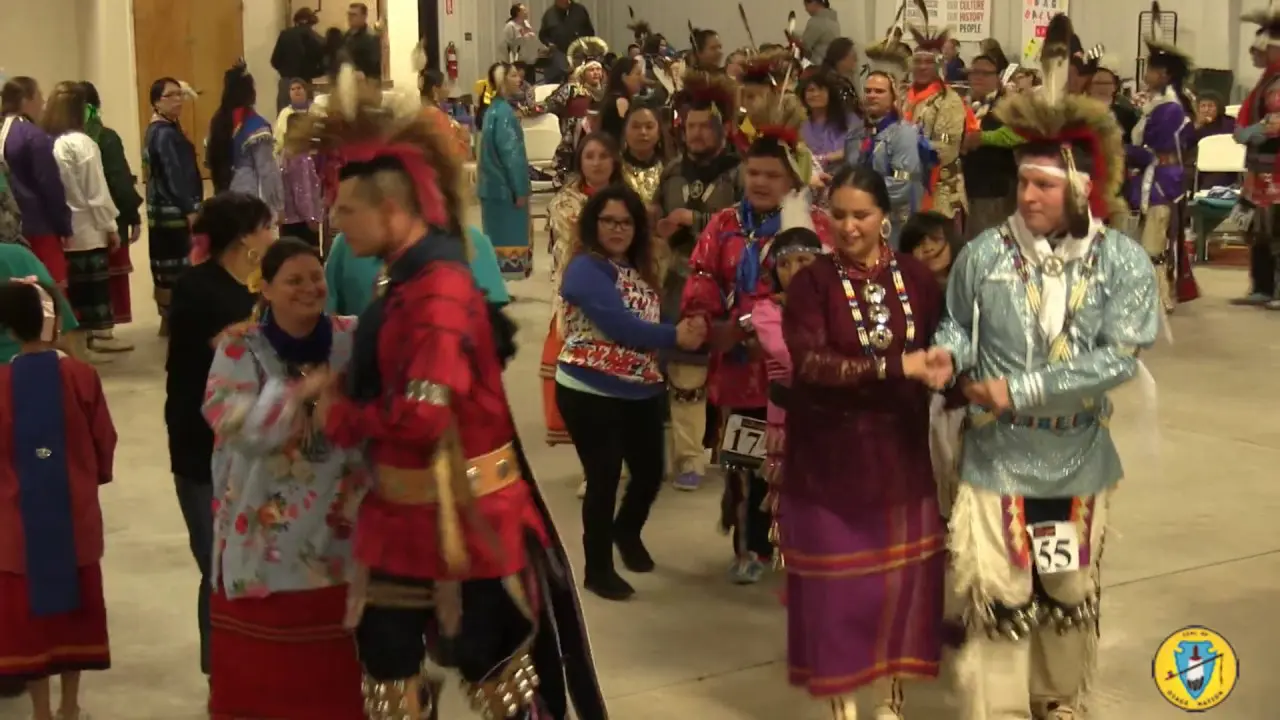
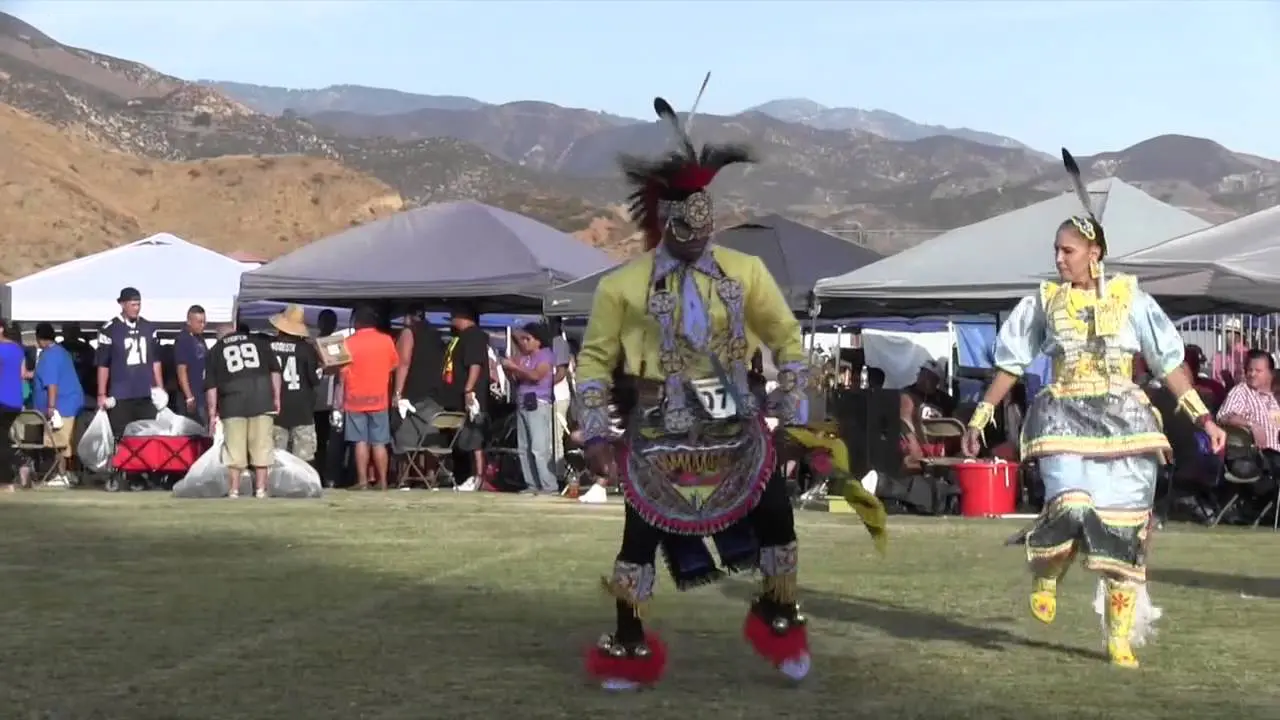
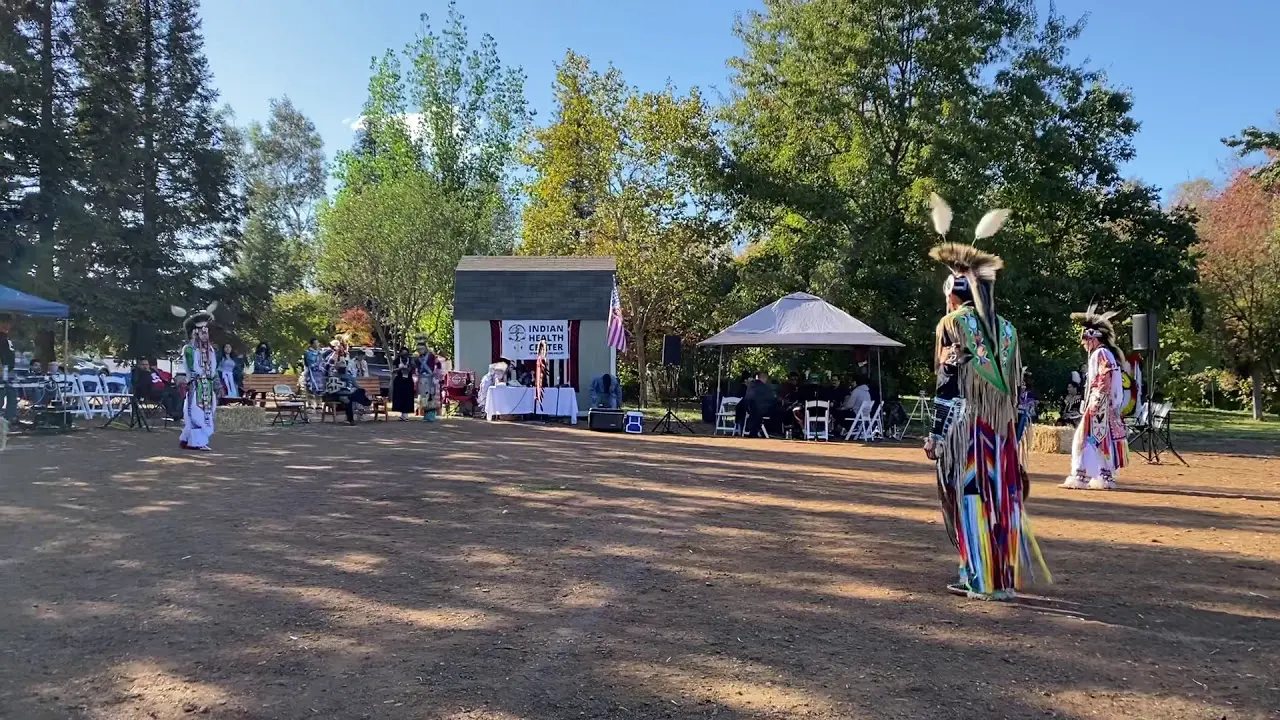
Along with land stewardship, the Caddo Nation actively participates in cultural preservation through events like the Caddo Heritage Festival, where tribal history, crafts, dance, and traditional foods are showcased. Such events not only engage tribe members but also educate the public about the Caddo Nation’s significant contributions to the cultural tapestry of Oklahoma.
By focusing on their tribal homelands in Oklahoma, the caddo Nation continues to celebrate their rich heritage while building a sustainable future, honoring the legacies of their ancestors while empowering their community.
Interactions With Settlers
Interactions between the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma and settlers have been marked by a complex tapestry of both positive and negative experiences throughout history. On the positive side, early interactions frequently enough led to mutually beneficial trade relationships. The Caddo, known for their agricultural skills and craftsmanship, engaged with settlers by exchanging goods such as maize, pottery, and handmade tools. Settlers, in turn, introduced new technologies and materials that could enhance the daily lives of the Caddo people.
Though, these interactions were not without conflict and challenges. As settlers expanded westward in search of land and resources, they encroached upon Caddo territories, leading to disputes over land ownership and usage.The introduction of European diseases also had devastating effects on the Caddo population, as they had no immunity to these illnesses, which created social and economic disruptions within their communities.In more recent times, the Caddo Nation has worked to foster stronger relations with both the government and local communities. They actively engage in cultural preservation efforts, sharing their rich heritage and traditions with those around them. This outreach has ofen led to a greater understanding and respect among settlers and newcomers, highlighting the importance of cultural exchange.Despite the historical adversities faced, the Caddo Nation has demonstrated resilience and adaptability, striving to navigate the complexities of these interactions while advocating for their rights and sovereignty.
the relationship between the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma and settlers encapsulates a broader narrative of coexistence that features moments of collaboration alongside struggles for recognition and respect. This historical dialog continues to shape the identity and future of the Caddo people in a modern context, enriching the cultural landscape of Oklahoma today.
Most Notable Events In Their Tribal History
The Caddo Nation of Oklahoma has a rich and complex history marked by significant events that have shaped their identity and culture. One of the most notable events in their tribal history is the establishment of their villages in the early 19th century. The Caddo were originally settled in the region known as the Caddo homeland, covering parts of present-day Texas, Arkansas, and Louisiana. During this time, they developed a sophisticated agriculture system based on crops like maize, beans, and squash, which provided sustenance and supported their vibrant trade networks.
The arrival of European settlers led to the forced relocation of the Caddo people. In the 1830s, the Indian Removal Act resulted in the displacement of many tribes, including the Caddo, who were moved to Indian Territory, now Oklahoma. This period was marked by hardship and loss as the Caddo faced challenges in adapting to new environments and rebuilding their communities.
A key event in the Caddo Nation’s modern history occurred in 1979 when they were federally recognized. This recognition was crucial for the Caddo people, allowing them to reclaim their sovereignty and access resources essential for the revitalization of their culture and traditions. The establishment of the caddo Nation Tribal Council has since played a vital role in governmental affairs, economic development, and cultural preservation.In addition to government recognition, the Caddo Nation has worked diligently to celebrate its heritage through events such as the Caddo Culture and Heritage Festival. This annual festival showcases traditional music, dance, art, and cuisine, bringing together Caddo people from across the nation and fostering a sense of community and pride in their cultural legacy.
The caddo Nation has also made headlines for its efforts to preserve the Caddo language,an integral part of their identity. Language revitalization programs and educational initiatives help teach young people about their linguistic heritage, ensuring that the Caddo language continues to thrive for future generations.
These events highlight the resilience and strength of the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma, reflecting their ongoing commitment to preserving their rich cultural heritage while adapting to the contemporary world. The caddo people continue to play an essential role in the tapestry of native American history, demonstrating their enduring legacy and commitment to cultural continuity.
Where Are Their Tribal Lands Now And How were They Established
The tribal lands of the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma are located primarily in the southeastern part of the state, particularly around Caddo County, where the tribe’s headquarters is situated in the city of Binger. This land embodies not only historical importance but also the spiritual and cultural heritage of the Caddo people.The current reservation encompasses approximately 7,500 acres, which serve as a vital resource for the tribe and its members.
The establishment of these tribal lands can be traced back to the aftermath of the Indian Removal Act of 1830, which forced many Native American tribes from their ancestral lands in the southeastern United States to designated territories in the West. The Caddo were relocated to what is present-day Texas and then to Oklahoma, where they settled on lands that were allocated to them through treaties.The most significant treaty was the Treaty of 1835, which gave the Caddo nation a defined territory, although it did not prevent further encroachments and reductions in land.
Throughout the years, aggressive land policies, including allotment practices in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, further diminished the Caddo’s landholdings. Though, the Caddo Nation was able to reclaim some autonomy and cultural identity through various means, including the establishment of a tribal government in the 1970s.Federal recognition in 1976 allowed the tribe to reestablish its rights over its lands and engage in economic development initiatives that benefit its members today.
The caddo Nation continues to strive toward revitalizing its cultural practices and community development. The tribe actively works to educate both its members and the public about the historical significance of its lands and the ongoing connection to the Caddo’s cultural heritage. The establishment and preservation of their lands are essential for the continuation of their traditions, language, and communal identity, ensuring that the Caddo Nation remains a vibrant part of Oklahoma’s diverse cultural tapestry.
Modern Concerns Of The Tribe
The Caddo Nation of Oklahoma, a vibrant Native American tribe with a rich cultural heritage, faces a range of modern concerns that impact its community and future. One of the most pressing issues is the preservation of their language and traditions in the face of globalization.With younger generations increasingly exposed to contemporary influences, the tribe has initiated programs aimed at language revitalization and cultural education. These efforts are crucial for maintaining their unique identity and passing down traditional practices, customs, and beliefs to the next generation.
Economic development represents another significant area of focus for the Caddo Nation. Historically reliant on agriculture and traditional practices,the tribe is exploring various economic strategies to enhance self-sufficiency and provide for its members. From investing in renewable energy projects to expanding tourism opportunities through cultural events and festivals, the Caddo Nation aims to create sustainable income sources that respect its heritage while embracing modernity.
Healthcare accessibility is also an ongoing concern. Like many indigenous communities, the Caddo Nation faces disparities in health outcomes and access to services. The tribe actively advocates for improved healthcare facilities and services, addressing issues such as diabetes, mental health, and substance abuse. Collaborations with local and federal agencies aim to enhance healthcare access and educational initiatives focused on healthy lifestyles for community members.
environmental stewardship is integral to the Caddo nation’s concerns, particularly given their historical connection to the land. Climate change poses a threat to their natural resources,which are vital for both cultural practices and economic sustainability. The Caddo Nation is engaging in efforts to create environmental initiatives that protect their lands while addressing the impacts of climate change. By promoting conservation practices and traditional ecological knowledge, the tribe continues to assert its role as a guardian of the environment.
Furthermore, legal and political sovereignty is a crucial concern for the caddo nation. Navigating the complexities of tribal sovereignty in the context of state and federal laws is an ongoing challenge. The tribe remains vigilant in protecting its rights and resources, advocating for policies that honor their sovereignty and promote their interests. Collaborative relationships with other Native American tribes and organizations enhance their advocacy efforts, providing a united front on issues affecting all Indigenous peoples.
The modern concerns of the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma highlight a commitment to cultural preservation, economic development, healthcare access, environmental stewardship, and political sovereignty. By addressing these challenges, the Caddo Nation seeks to create a sustainable and thriving community rooted in their rich history and resilience.
Events And Other Social And political Activities
The Caddo Nation of Oklahoma actively engages in various social and political activities that reflect its commitment to cultural preservation, community development, and advocacy for tribal rights. One of the key events is the annual Caddo Culture Day, where tribe members and visitors gather to celebrate traditional Caddo practices, language, and crafts. This event features lively dance performances,storytelling,and workshops on traditional pottery,enhancing awareness and appreciation of Caddo heritage.
Additionally, the Caddo Nation plays a vital role in public policy by participating in tribal government meetings and collaborating with state and federal agencies to address issues affecting Native communities. The tribe holds regular sessions to discuss health care, education, and environmental conservation, ensuring that the voices of Caddo citizens are heard in broader political discussions.
Community engagement is emphasized through various outreach programs,such as the Caddo Nation’s Youth and Family Services,which aims to empower young people with education and cultural knowledge. These initiatives not only foster a sense of identity among the youth but also promote the continuity of Caddo traditions.Moreover, the Caddo Nation organizes public forums and educational sessions on Native american rights, focusing on sovereignty, land rights, and cultural preservation.By providing platforms for dialogue, the tribe actively contributes to the understanding of critical issues facing Indigenous peoples today.
Throughout the year, the Caddo Nation collaborates with various organizations to host events like the Caddo Heritage Festival, which showcases local artists, musicians, and food vendors. This festival serves as a vital economic engine for the community and enhances local tourism, spotlighting the vibrant Caddo culture to a broader audience.
the Caddo Nation’s involvement in legislative advocacy is another significant aspect of its political activities. By engaging with elected officials and participating in national Native advocacy coalitions, the tribe works diligently to ensure that policies reflect the needs and aspirations of its members. The Caddo Nation’s commitment to social justice is evident through its consistent efforts in promoting policies that protect Indigenous rights and promote social equity.
Through these social and political engagements, the caddo Nation of Oklahoma not only preserves its rich cultural heritage but also positions itself as a proactive player in the contemporary political landscape, ensuring a thriving future for its community.