Introduction to the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe
Nestled in the lush landscapes of Washington State, the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe is a vibrant community rooted in rich cultural heritage and history. With a name that translates to “the place where the water is abundant” in the Salish language, the Muckleshoot people have fostered a deep connection to the land and its natural resources for centuries. Recognized as a sovereign tribe, the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe plays a pivotal role in the preservation of its cultural traditions, governance, and economic progress, contributing significantly to the local economy and community well-being.Historically, the Muckleshoot people inhabited the fertile banks of the Green River and the surrounding regions, relying on fishing, hunting, and gathering for sustenance.Their rich spiritual beliefs and practices, encapsulated in stories and oral traditions, emphasize a profound respect for nature and community. Today, the tribe actively works to revive and promote these traditions, ensuring that younger generations inherit their cultural legacy.
In addition to its cultural initiatives, the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe has also made significant strides in economic development through various enterprises, including the triumphant Muckleshoot Casino, which has become a key player in the region’s economy. The tribe continues to advocate for its rights and interests, balancing modern challenges with the preservation of their unique identity.This dedication to both cultural revitalization and economic sustainability showcases the resilience and vibrancy of the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe, making them an essential part of Washington’s diverse tapestry.
Origin Of The People
The Muckleshoot Indian Tribe, located in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States, boasts a rich and storied heritage that dates back thousands of years. This indigenous tribe is primarily associated with the Salishan-speaking peoples, who have inhabited the areas around the Puget Sound for generations. The word “Muckleshoot” is derived from the term meaning “place of the Muckles,” or “to stroll about,” highlighting their strong ties to the land.
Historically,the Muckleshoot people were known as adept fishers,hunters,and gatherers,relying heavily on the natural resources provided by their habitat,which includes rivers,forests,and abundant wildlife. Salmon fishing, in particular, played a crucial role in their culture and sustenance, with the tribe participating in seasonal runs and practicing conventional fishing methods. Alongside fish,the Muckleshoot diet featured a variety of plants,nuts,and game animals.
The Muckleshoot Indian Tribe originally formed part of the greater Puyallup Tribe and shared connections with many neighboring tribes, including the Duwamish and Suquamish. Their social structure was primarily organized into family groups or clans, with a deep sense of community and kinship. Oral traditions convey the tribe’s rich mythology and history, teaching younger generations about their ancestry, spirituality, and the importance of preserving their culture.
Throughout the 19th century, the Muckleshoot faced significant challenges due to encroaching settlers, land treaties, and the resulting marginalization of their people. Despite these adversities, the tribe has maintained its cultural identity and resilience. The Muckleshoot Indian Tribe was officially recognized by the federal government in 1971, which paved the way for renewed self-governance and economic development.
Today, the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe actively promotes its cultural heritage through various initiative programs, such as language revitalization, traditional arts, and community events. Their commitment to preserving their language, traditions, and history continues to thrive, making the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe a vital part of the broader story of indigenous peoples in the Pacific Northwest.
Tribal Homelands
The Muckleshoot Indian Tribe,situated in Washington State,has ancient ties to an extensive territory that encompasses parts of the Puget Sound region. Their traditional homelands include the lush valleys and rich forests, which span from the shores of the Green River to the foothills of the Cascade Mountains. This territory, known for its abundant natural resources, provided the tribe with crucial sustenance from salmon-rich rivers, wild game, and edible plants.
The tribe’s ancestral lands are characterized by a rich tapestry of ecosystems, which not only supported the Muckleshoot people’s way of life but also held deep cultural and spiritual significance. The forested areas offered materials for shelter and tools, while the rivers were vital for fishing and transportation. Salmon, in particular, holds a sacred place in Muckleshoot traditions, symbolizing not only a primary food source but also a connection to ancestral practices and community gatherings.
Today, the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe works to protect and preserve their traditional homelands, ensuring that future generations have access to the resources that have sustained them for centuries. Through environmental stewardship initiatives and collaborations with local governments, the tribe aims to restore habitats and promote lasting practices. This commitment to land conservation reinforces their identity and cultural heritage, highlighting the deep bond between the Muckleshoot people and their traditional territory.
Interactions With Settlers
The Muckleshoot Indian Tribe, located in what is now Washington State, has a rich history of interactions with settlers that encompassed both positive and negative experiences. The arrival of European settlers in the 19th century brought significant changes to the region, affecting the tribe’s traditional way of life.
One of the more positive aspects of interaction was economic engagement. As settlers established farms and industries, the Muckleshoot Tribe found opportunities for trade. They were able to exchange their traditional goods, such as fish and berries, for agricultural products introduced by settlers. This interaction allowed the Muckleshoot people to supplement their diets and engage in commerce, leading to a degree of financial prosperity in certain periods.
On the flip side, the encroachment of settlers led to significant challenges for the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe. The influx of settlers resulted in the loss of ancestral lands due to treaties that were frequently enough signed under duress or misunderstood by tribal leaders. The Treaty of Medicine Creek in 1854,in particular,is a pivotal example. While the Muckleshoot were assured rights to their lands,the realities of settler expansion meant that they gradually lost access to vital resources such as hunting grounds and fishing sites,creating conflicts that would last for generations.
Culturally, the arrival of settlers also forced the Muckleshoot people to navigate a rapidly changing social landscape. While some members of the tribe adapted by embracing new ways of life, others resisted, leading to a cultural clash. This resistance to assimilation was often met with hostility, leading to misunderstandings and tensions. On occasion, the tribe faced violence as settlers encroached on their territory, intensifying the struggle for survival and autonomy.
Efforts at reconciliation and partnership have been made over the decades,with the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe actively engaging in collaborations to foster mutual understanding and respect. This interplay between cooperation and conflict highlights the complex nature of interactions with settlers. The Muckleshoot Tribe continues to assert its sovereignty, ensuring that the rich cultural traditions endure in the face of historical adversity.
Most Notable Events In Their Tribal History
The Muckleshoot Indian Tribe, located in the Pacific Northwest, has a rich and dynamic history marked by significant events that have shaped their identity and sovereignty.One of the most notable moments in their tribal history occurred in the mid-1850s when they participated in the signing of treaties with the U.S. government. The Medicine Creek Treaty of 1854 was a pivotal agreement, granting the tribe reserved lands and fishing rights, yet it also set the stage for future conflicts regarding land and resources.
In the years that followed, the Muckleshoot faced numerous challenges, including loss of land and forced assimilation into European American culture. However,their resilience shone through during the 1970s when they began to reclaim their rights. A landmark event was the legal battle against the state of Washington for fishing rights, culminating in the 1974 U.S. District Court decision in U.S. v. Washington, which affirmed their treaty rights and allowed for the restoration of their fishery.
The 1990s marked another significant turning point as the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe established the Muckleshoot Casino in 1995. This venture not only provided economic opportunities but also became a hallmark of their self-sufficiency and a means to reinvest in their community, funding educational and cultural programs.
Recently, the Muckleshoot have engaged in environmental stewardship initiatives to protect their ancestral lands and waters. The tribe’s commitment to sustainability and activism is evident in their involvement in advocacy for the preservation of the Cedar River watershed and salmon habitat.
Throughout their history, the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe has demonstrated an unwavering commitment to their cultural heritage and sovereignty, navigating complex social, legal, and economic landscapes while striving to ensure a vibrant future for generations to come.
Where Are Their Tribal Lands Now And How Were They Established
The Muckleshoot Indian Tribe is primarily located in Auburn, Washington, on a portion of their ancestral lands in the Pacific Northwest. Their tribal lands encompass about 4,800 acres, a significant part of which is situated near the confluence of the White River and the Green River. This area is rich in resources and holds historical and cultural significance for the tribe.The establishment of Muckleshoot tribal lands can be traced back to treaties made in the 19th century. In 1855, the Treaty of Point Elliott was signed, initially designated to provide a reservation for several tribes, including the Muckleshoot. Unfortunately,the tribe faced challenges regarding their land rights,experiencing loss of territory through various legal and political maneuvers over the years.
It wasn’t until the 1970s that the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe regained federal recognition, which marked a turning point for their community. The tribe’s lands were officially re-established as a federal trust in 1996, allowing them to self-govern and pursue economic development initiatives. Today, the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe operates several enterprises, including gaming, hospitality, and retail, contributing to both tribal sovereignty and the local economy.
By navigating the complexities of historical treaties and modern legal frameworks, the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe has preserved its cultural heritage and is actively engaged in protecting its lands for future generations. The tribe’s commitment to environmental stewardship and cultural revitalization showcases their deep connection to the land, reflecting a promise to honor both their past and their future.
Modern Concerns Of The Tribe
The Muckleshoot Indian Tribe, located in Washington State, faces a range of modern concerns that reflect both traditional values and contemporary challenges. Environmental sustainability is a significant issue for the tribe, as they strive to protect their natural resources, which are integral to their cultural heritage and economy. The tribe actively engages in habitat restoration projects, notably in the Puget Sound area, to safeguard salmon runs and other critical ecosystems that hold cultural and economic importance.
Economic development, while essential, comes with its own set of challenges.The Muckleshoot Tribe has successfully established enterprises such as gaming, hospitality, and retail operations, which generate revenue for community programs and services. Though, balancing economic growth with the preservation of cultural identity is a delicate endeavor. The tribe is committed to fostering business initiatives that align with their values and long-term objectives, ensuring that revenue generation does not compromise their heritage.Education is another area of focus for the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe. They prioritize educational programs that promote cultural learning, language preservation, and higher education opportunities for tribal members. Initiatives aimed at improving educational outcomes have become essential in bridging generational knowledge gaps and ensuring youth connect with their cultural roots while also thriving in modern society.Health and wellness represent vital concerns as well. Access to healthcare services,addressing public health issues,and promoting mental health programs are critical components of the tribe’s community planning. The Muckleshoot Tribe has developed health initiatives specifically tailored to their community, striving to provide comprehensive care that respects their cultural values.
Social justice and political advocacy are increasingly significant for the Muckleshoot Tribe as they navigate the complexities of sovereignty and tribal governance. The tribe actively participates in regional and national dialogues regarding Indigenous rights, land use, and resource management. Ensuring that their voices are heard in legislative matters is vital for protecting their interests and sovereignty, particularly in an era of changing policies that can impact tribal lands and resources.
the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe is dedicated to addressing these modern concerns while upholding their cultural traditions and preserving their identity for future generations.Through sustainable practices, economic development, education, health initiatives, and advocacy, they continue to navigate the challenges of contemporary society while maintaining a strong connection to their past.
Events And Other Social And Political Activities
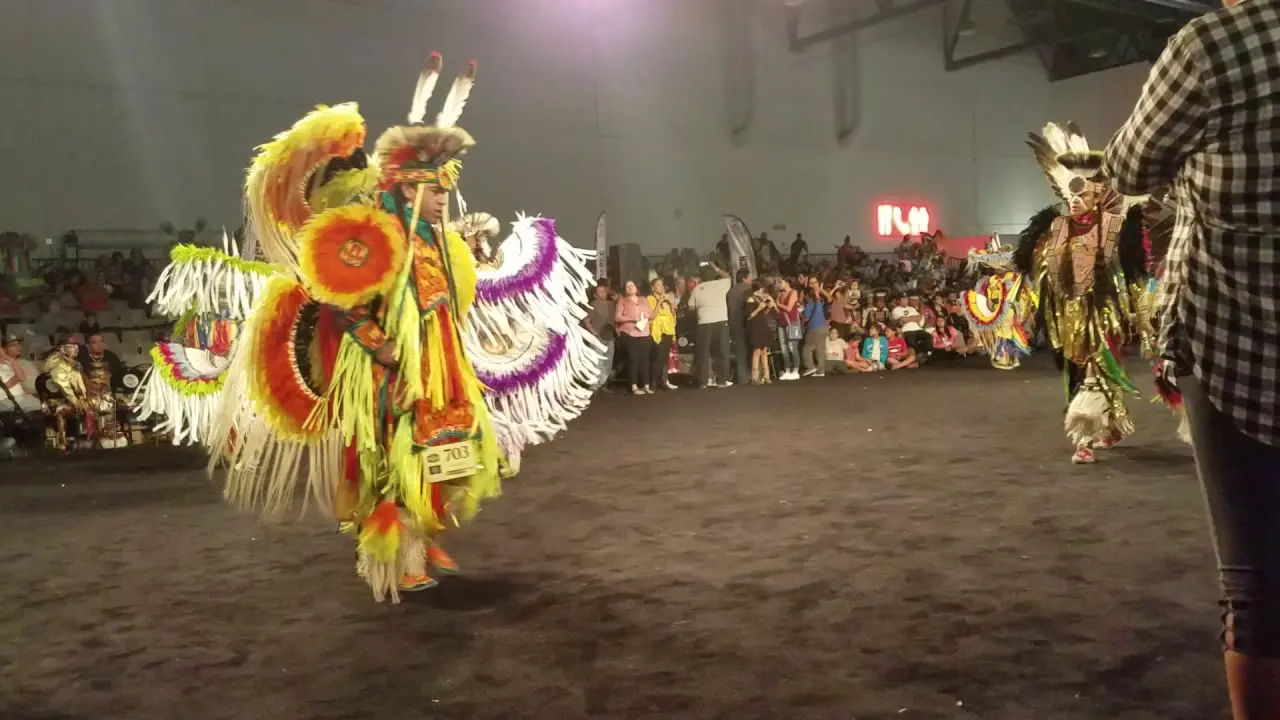
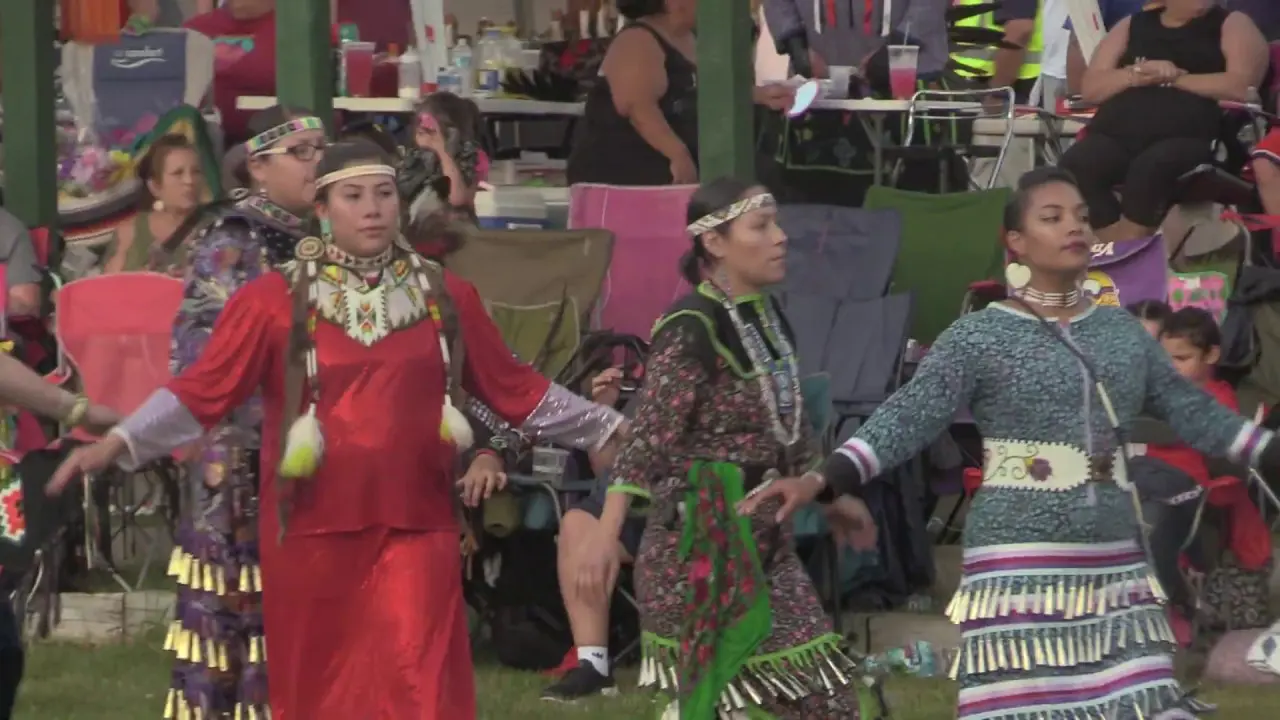
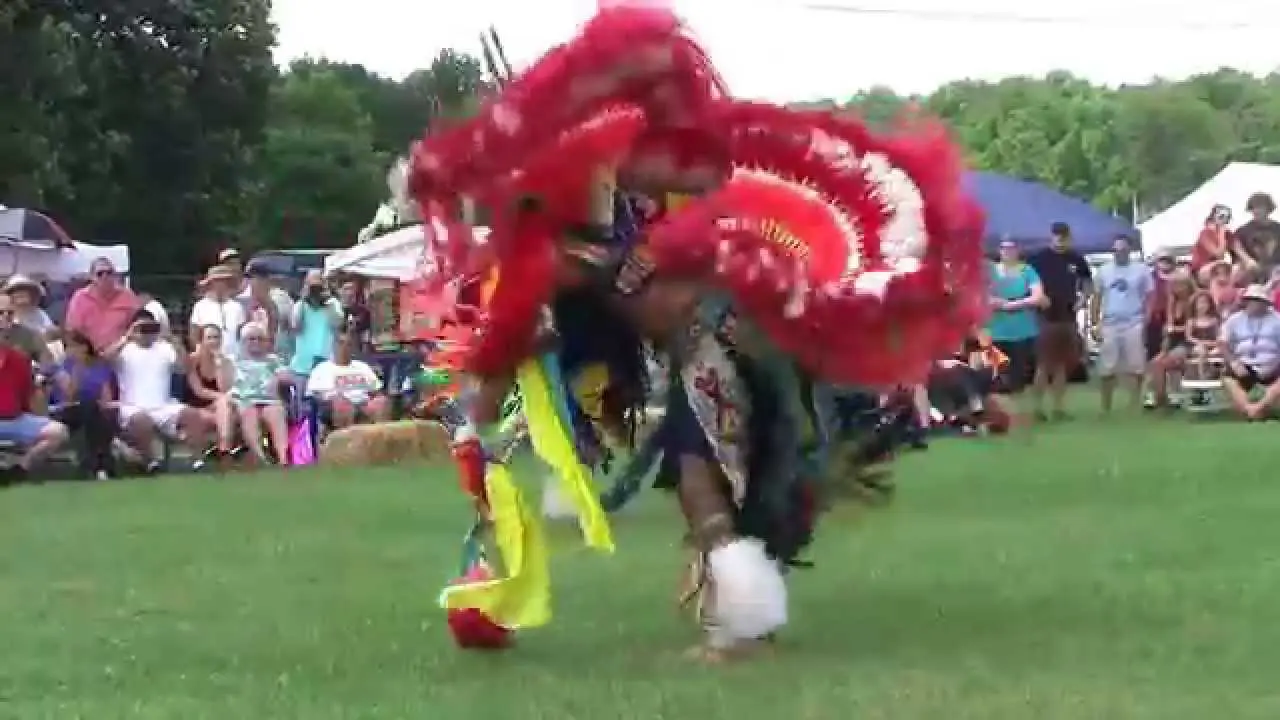
The Muckleshoot Indian Tribe, located in Washington state, actively engages in a range of cultural, social, and political activities that reflect its rich heritage and community values.The tribe hosts traditional events such as the annual Muckleshoot Tribal Days, which celebrate indigenous culture through powwows, art exhibits, and performances of Native American dance and music. This gathering not only showcases the tribe’s cultural traditions but also fosters unity among community members and encourages participation from local residents and visitors.
Along with cultural festivities, the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe is involved in various social initiatives aimed at improving the quality of life for its members. Programs focused on health and wellness, education, and economic development are essential aspects of their community engagement.The tribe operates a number of health clinics and educational scholarships promoting higher education for tribal youth, highlighting the importance of academic achievement and well-being.
On the political front, the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe advocates for the rights and recognition of Native American sovereignty, engaging in critical discussions about land use, environmental protection, and treaty rights.The tribe collaborates with local governments, non-profit organizations, and other tribes to address issues such as water rights, habitat conservation, and sustainable development practices. Through active participation in regional councils and national organizations, the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe works to amplify its voice in key decision-making processes affecting both tribal members and the broader community.
Fundraising events are also pivotal in the tribe’s social calendar, with proceeds often directed towards community projects and scholarships. Engaging the younger generation through sports leagues, mentorship programs, and cultural workshops ensures that the tribe’s traditions are passed down, preserving their unique identity while fostering pride and leadership among the youth.
Together,these events and initiatives showcase the Muckleshoot Indian Tribe’s commitment to cultural preservation,social responsibility,and political advocacy,solidifying its role as a vibrant and essential part of the wider Washington community.