Introduction to the Spirit Lake Tribe: A Rich Tapestry of Culture and Resilience in North Dakota
Nestled in the heart of North Dakota, the Spirit Lake Tribe—known as the Sisseton-Wahpeton Oyate—boasts a storied history and vibrant cultural heritage that continues to thrive today. With roots tracing back to the Dakota Sioux, this Native American tribe is not just a community but a testament to resilience, identity, and an enduring connection to the land. Spanning across the picturesque Spirit Lake Reservation, the tribe encompasses a diverse population dedicated to preserving its traditions while navigating the modern world.
The tribe’s history is a rich tapestry woven with tales of survival, adaptation, and strength in the face of adversity. From their ancestral lands along the shores of Spirit Lake to their ongoing struggles for sovereignty and self-determination, the Spirit Lake Tribe represents a powerful narrative of perseverance. Their commitment to cultural preservation, language revitalization, and education reflects a strong desire to pass down traditions to future generations.
As modern challenges continue to unfold, the Spirit Lake Tribe stands at the forefront of innovation and sustainability, working to ensure a prosperous future for its members. Through community initiatives, economic advancement, and cultural events, the tribe not only honors its past but also embraces the opportunities of the present, making it a unique and vibrant part of North Dakota’s heritage. Whether it’s celebrating powwows, preserving conventional crafts, or advocating for social justice, the Spirit Lake Tribe embodies the spirit of unity and hope while keeping its rich cultural identity alive.
Origin Of The People
The Spirit Lake Tribe,known as the Sioux or Dakota Nation,is located in North Dakota and is comprised primarily of the Sisseton and Wahpeton bands of the Dakota people. The origins of the Spirit Lake Tribe can be traced back to the larger Sioux Nation, which historically inhabited the northern plains of North America. The Sioux Nation is made up of three major divisions: the Dakota, Nakota, and Lakota. Each group carries its distinct dialect and cultural practices,but they share a common ancestry and ancient narrative.
Traditionally, the Dakota people were nomadic, relying on hunting, fishing, and gathering for sustenance.They were deeply connected to the land, viewing it as sacred and integral to their identity. The Missouri River,which flows near the Spirit Lake Nation,provided a vital resource for fishing and transportation,making it central to the tribe’s way of life. The Spirit Lake area was rich in resources, allowing the Dakota people to thrive before the arrival of European settlers in the 19th century.
As European settlers moved westward, tensions escalated between Native American tribes and settlers. In the 1860s, forced relocations and assimilation policies severely impacted the Spirit Lake Tribe, leading to significant loss of their land and culture. In 1870, the U.S. government established a reservation for the Dakota people, which became known as the Spirit Lake Reservation. Here, the tribe faced challenges but also worked to maintain their cultural practices and traditions.
Today, the Spirit Lake Tribe is recognized as a sovereign nation and actively strives to preserve their heritage while adapting to modern society.Their historical journey—marked by resilience, cultural significance, and a deep bond with their ancestral lands—continues to shape their identity today. By participating in community initiatives and educational programs, the Spirit Lake Tribe emphasizes the importance of cultural preservation and empowerment, ensuring that their rich history remains relevant for future generations.
Tribal Homelands
The Spirit Lake Tribe, also known as the Spirit Lake Nation, is located in North Dakota and has a rich cultural history deeply connected to its traditional homelands.The Tribe’s reservation encompasses approximately 100,000 acres in the north-central part of the state, primarily within Ramsey County. This land serves not just as a home but as a sacred space for the people of the Spirit Lake Tribe, who have lived and thrived in this region for generations.
The Tribe’s territory is characterized by rolling hills, abundant lakes, and rivers, including the historic Spirit Lake, which plays a significant role in tribal identity and culture. Fishing, hunting, and gathering have long been integral to the Spirit Lake people, fostering a strong relationship with the environment. Rich in biodiversity, the natural landscapes provide a habitat for various wildlife and plant species, many of which hold cultural significance.
Historically, the Spirit Lake Tribe, part of the larger Dakota Sioux Nation, faced numerous challenges due to colonization and forced removals. Though, the Tribe has demonstrated resilience, maintaining its language, traditions, and spiritual practices. Today, the Tribe actively works to preserve its cultural heritage while engaging in contemporary economic development, including the promotion of tourism that highlights the natural beauty and historical importance of their lands.
The Spirit Lake Tribe also collaborates with local and state initiatives to enhance environmental stewardship, ensuring that their ancestral land remains a well-maintained and thriving ecosystem for future generations. By engaging in enduring practices, the Tribe emphasizes the importance of living in harmony with nature, a principle that is woven into the cultural fabric of the Spirit Lake people.
the tribal homelands of the Spirit Lake Tribe are not only a geographical space but a vital cultural landscape that embodies the Tribe’s identity and values, symbolizing their enduring connection to the land and commitment to future generations.
Interactions With Settlers
The interactions between the Spirit Lake Tribe and settlers in North Dakota reflect a complex tapestry of relationships, marked by both cooperation and conflict.Early encounters, especially in the mid to late 19th century, involved mutual assistance as settlers relied on the local tribes for knowledge about the land and resources. The Spirit Lake Tribe, known for their rich cultural heritage and deep connection to their territory, shared agricultural techniques and trade opportunities, benefiting both communities. These interactions often resulted in peaceful coexistence, where shared interests in farming and trade fostered a sense of community.
However, the arrival of settlers also led to significant tensions. The encroachment of settlers on tribal lands, driven by the demand for land for agriculture and infrastructure, created friction between the Spirit Lake Tribe and non-Native populations. This conflict intensified after the U.S. government’s policies shifted towards land allotment and assimilation, leading to the loss of traditional territories. The Dawes Act of 1887, for instance, aimed to assimilate Native Americans into American society by allotting individual plots of land, undermining communal land practices that were essential to the Spirit Lake Tribe’s way of life.
Throughout these interactions, there were notable episodes of conflict, including the Dakota War of 1862, which had far-reaching implications for Native tribes across the region. The resulting loss of life and displacement from ancestral lands marked a painful chapter in the Spirit Lake Tribe’s history.
Despite these challenges, the Spirit Lake Tribe has shown resilience, actively working to preserve their cultural identity and reclaim their rights. The tribe has successfully engaged in various initiatives aimed at fostering reconciliation and education about their rich history among settler communities.Programs highlighting the importance of Native cultural heritage and collaboration can help bridge gaps and facilitate more positive interactions between the Spirit Lake Tribe and its neighboring communities.
Today, efforts continue to promote understanding, respect, and cooperation, recognizing the dual heritage of the land. Through modern engagements, such as cultural events and educational outreach, the Spirit Lake Tribe seeks to reshape the narrative of their interactions with settlers, turning past challenges into opportunities for growth and mutual respect.
Most Notable Events In Their Tribal History
The Spirit Lake Tribe, located in North Dakota, has a rich history marked by significant events that have shaped its cultural and social landscape. One of the most notable events in their tribal history is the establishment of the Spirit Lake Reservation in 1884, which provided a designated homeland for the tribe after years of displacement and upheaval. This reservation, primarily situated in the northeastern part of North Dakota, is still home to the tribe today, encompassing more than 100,000 acres of land.
In the early 20th century, the Spirit Lake Tribe faced severe challenges, including forced assimilation policies and loss of language. In the 1920s, the government’s push towards assimilation led to the suppression of tribal culture, yet the tribe managed to hold on to its traditions.The creation of the Indian Reorganization Act in 1934 was a turning point, as it allowed the tribe to reclaim some sovereignty and self-governance, thus paving the way for renewed cultural revitalization.
The 1970s marked another critical period for the Spirit Lake Tribe,particularly with the establishment of the Spirit Lake Tribal Council. This council played a vital role in the empowerment of tribal governance and community decisions, fostering a sense of unity and leadership among members. Additionally, the mid-20th century saw the emergence of various initiatives aimed at economic development, cultural preservation, and educational programs, helping to uplift the tribe’s resilience.
One event that remains etched in the tribe’s collective memory is the tragic flooding of the reservation in 1997, caused by a severe winter storm. This disaster prompted widespread displacement and highlighted the tribe’s vulnerability to natural disasters. The aftermath led to significant recovery efforts, including federal assistance and community solidarity, which ultimately reinforced tribal identity and resilience.
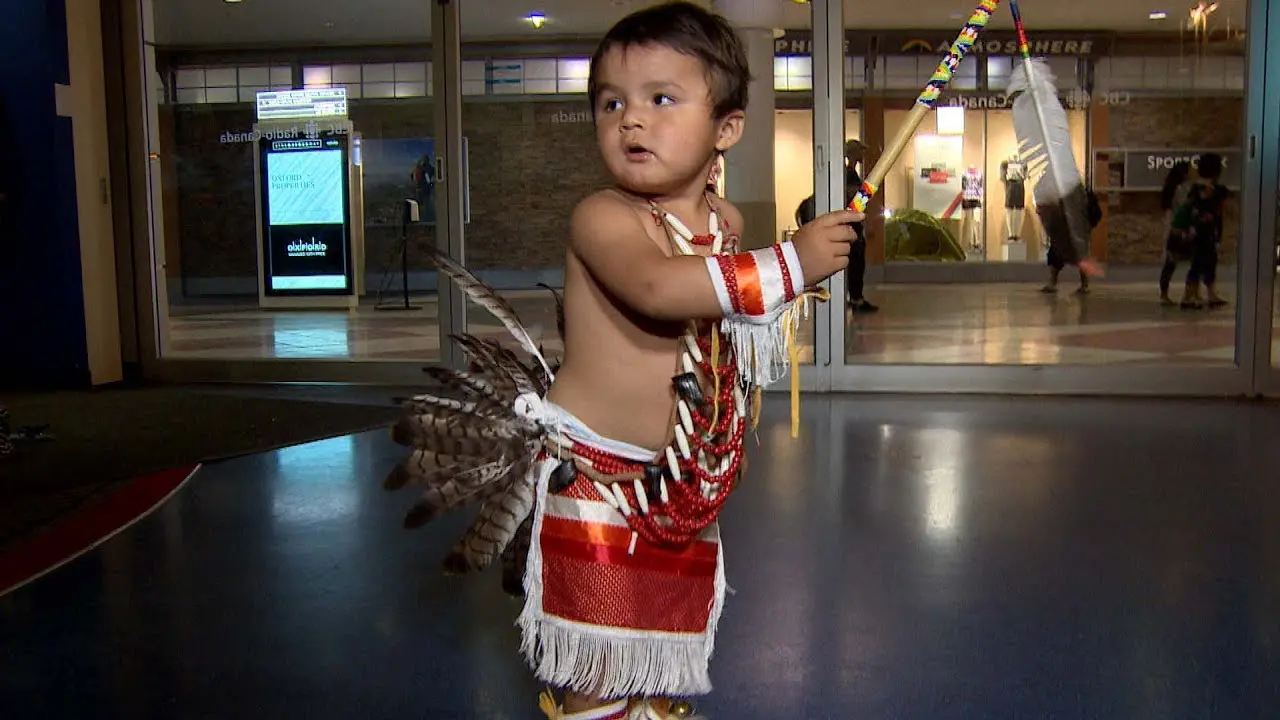
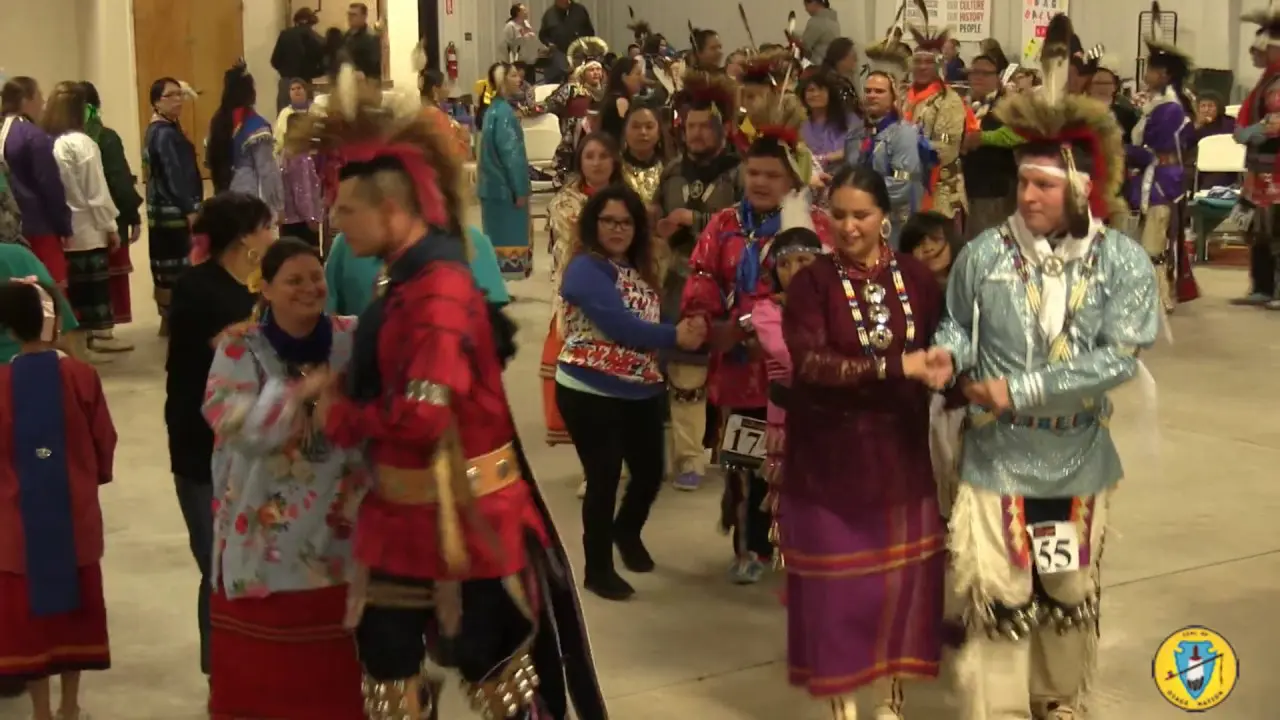
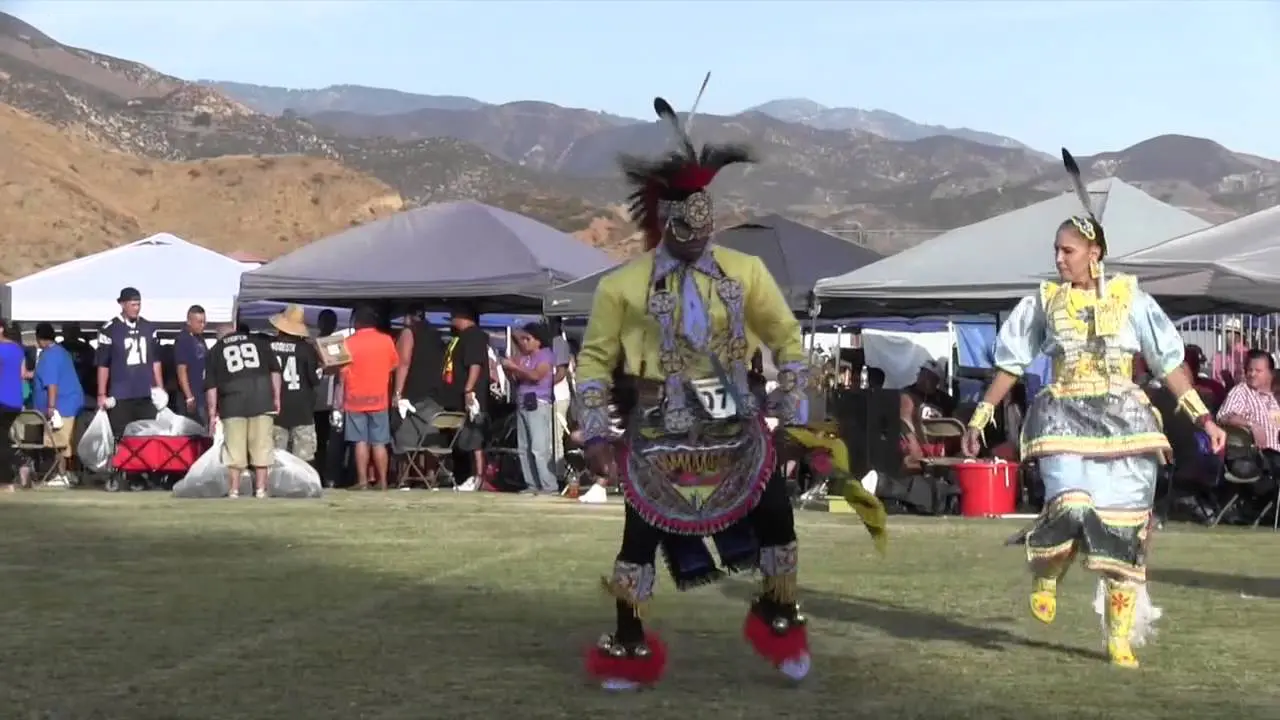
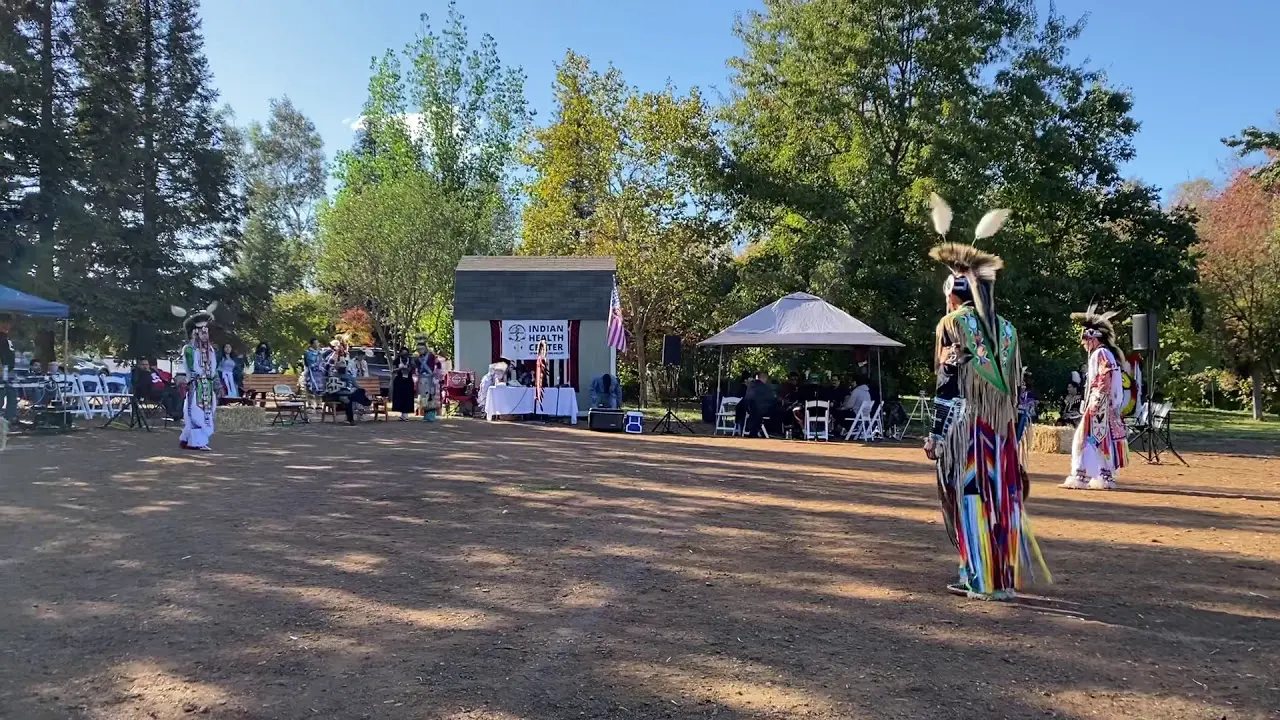
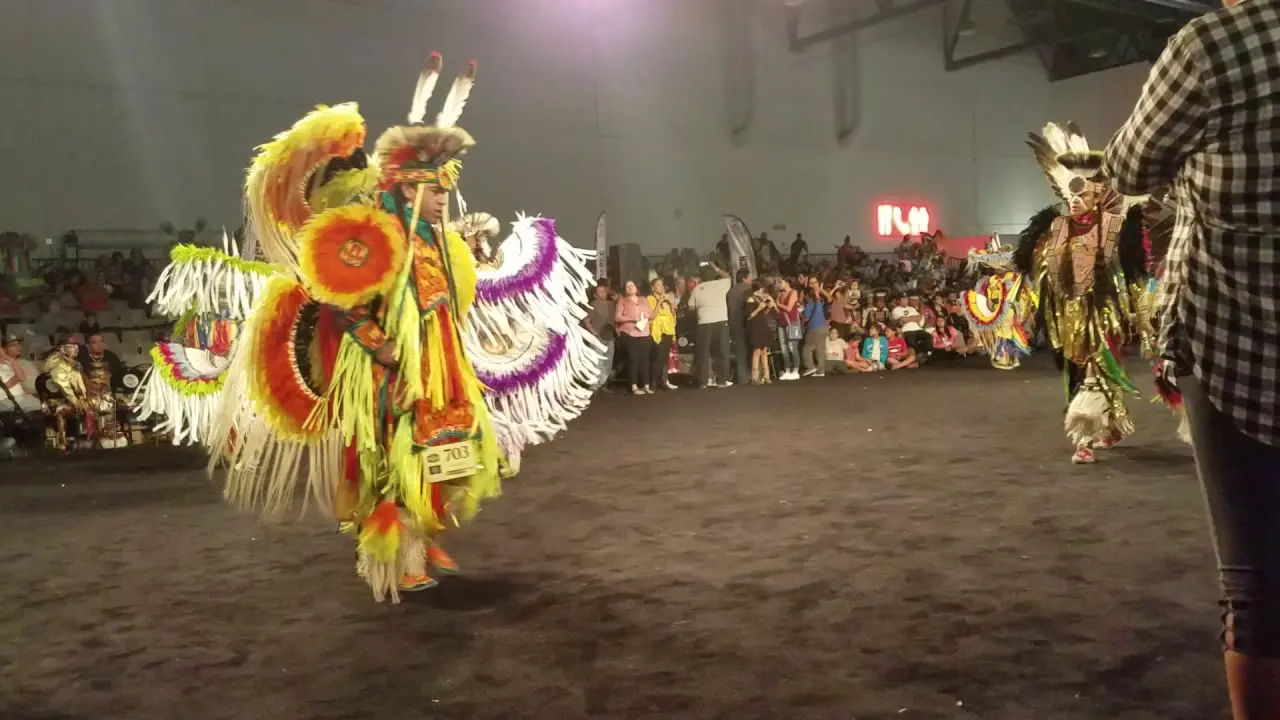
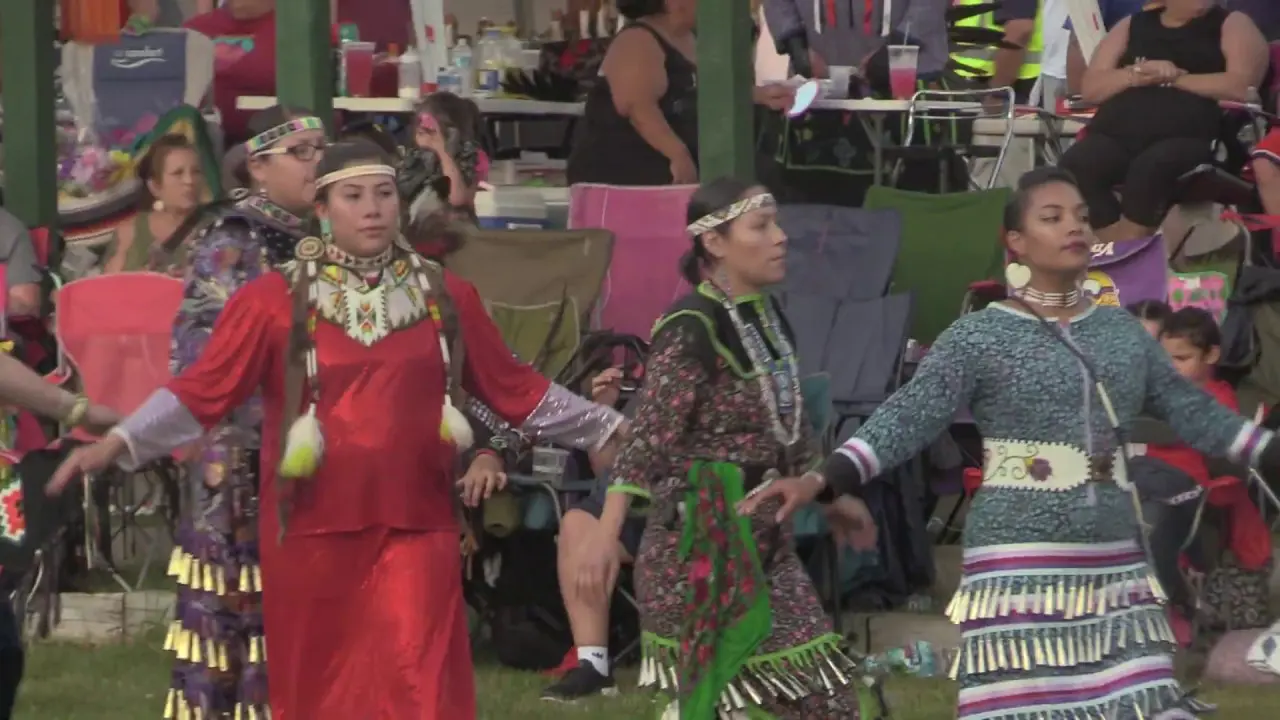
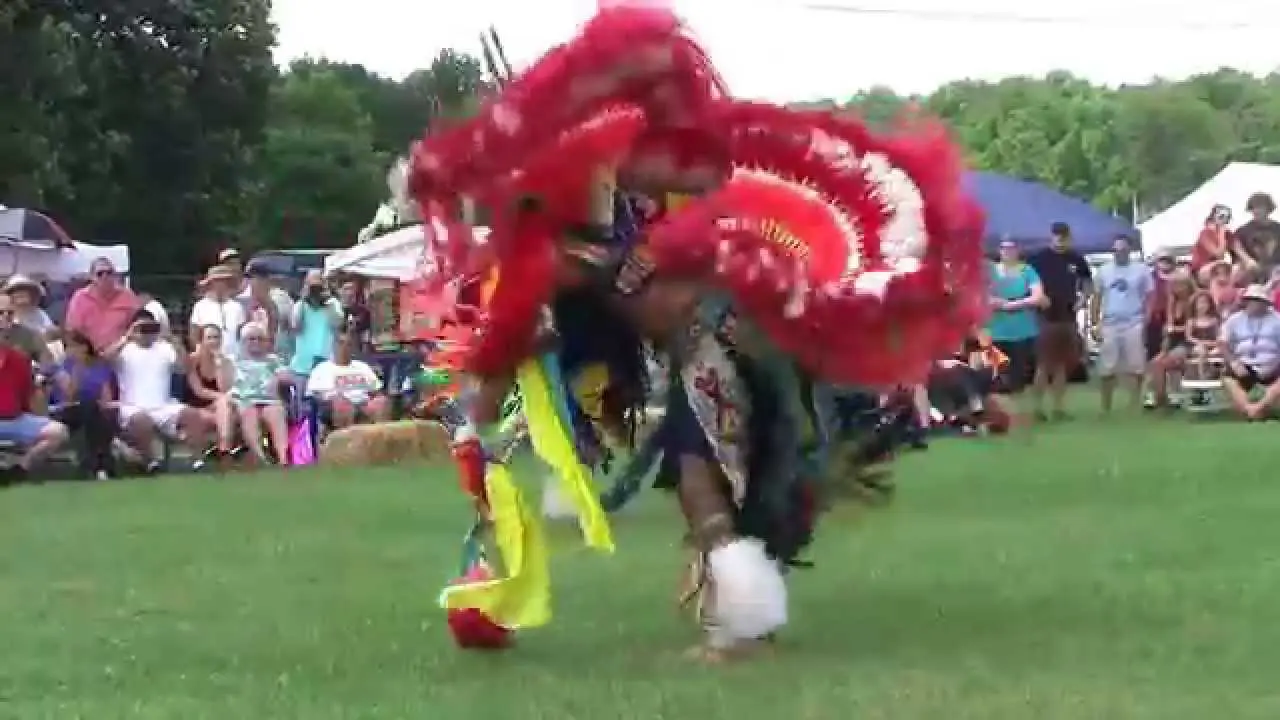
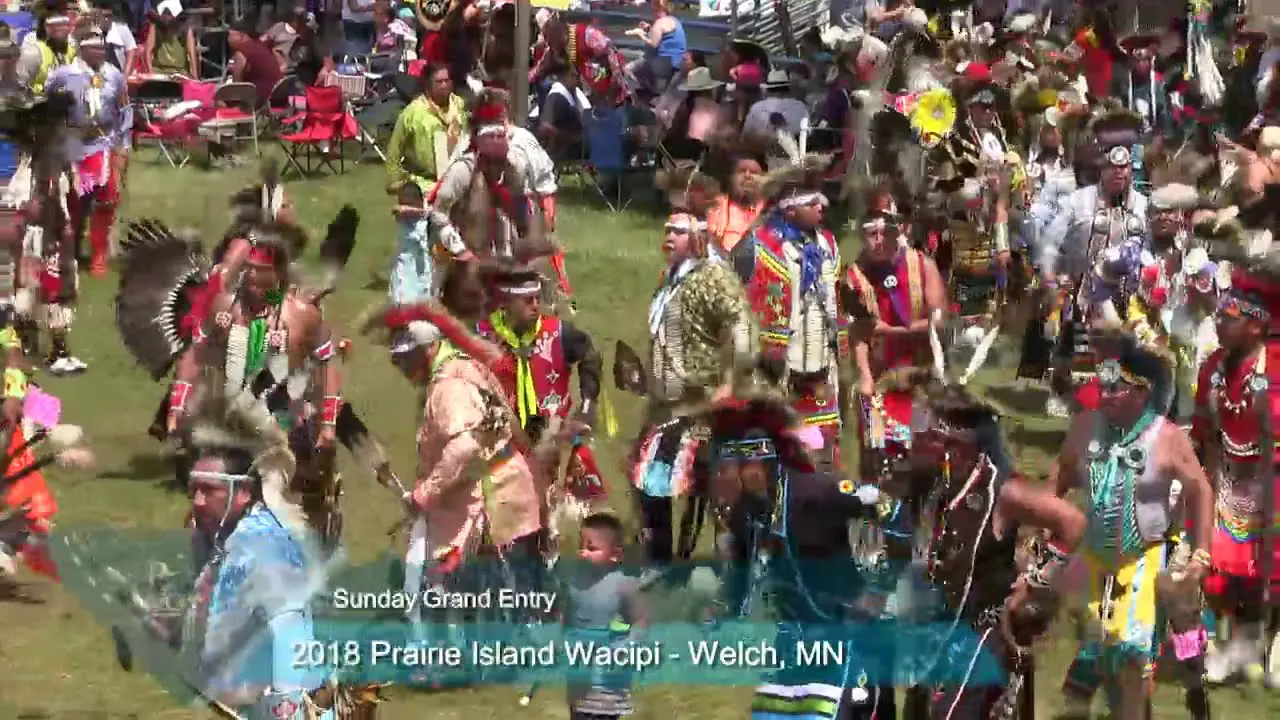
In recent years, the Spirit Lake Tribe has embraced modern development while prioritizing the preservation of their cultural heritage. The establishment of language revitalization programs and the construction of cultural centers have been pivotal in educating younger generations about their rich history. Events such as the annual powwow draw individuals from various tribes, showcasing traditional dance, music, and art while fostering intertribal relations and community pride.
Through these events and challenges, the Spirit Lake Tribe continues to celebrate its heritage and strive for a brighter future, blending tradition with progress in North Dakota. Recognizing the importance of grassroots movements, the tribe remains committed to advocating for its rights, ensuring that the voices of its members are heard and respected in the wider context of American society.
Where Are Their Tribal Lands Now And How Were They Established
The Spirit Lake Tribe, officially known as the Spirit Lake Tribe of North Dakota, is located on the Spirit Lake Indian Reservation in northeastern North Dakota. The reservation encompasses approximately 107,000 acres and is situated primarily in the counties of Benson and Ramsey. Established in the 1860s through various treaties with the United States government, the reservation was originally created to secure land for the Dakota people, also known as the Sioux Nation, who faced significant displacement due to westward expansion and colonization.
The establishment of the Spirit Lake Reservation was formalized in 1889 when the federal government recognized the tribe’s land rights. Over the decades, the reservation’s boundaries have fluctuated due to various treaties and legislative actions, including the Dawes Act of 1887, which aimed to assimilate Native Americans into American society by allotting individual parcels of land. This act led to significant loss of tribal land, but portions were retained, helping to establish the Spirit Lake Tribe’s present-day identity and jurisdiction within the region.
Today, the Spirit Lake Tribe administers its land and resources through various programs focused on cultural preservation, economic development, and social services. The tribe is committed to revitalizing their language, traditions, and community welfare. Their lands are not only home to many tribal members but also serve as a critical resource for economic development initiatives, such as agriculture, tourism, and renewable energy projects, thereby ensuring a sustainable future for future generations.
The Spirit Lake Tribe continues to assert its sovereignty and work collaboratively with federal and state governments to protect its interests, enhance its community’s quality of life, and preserve the rich heritage and traditions of the Dakota people.
Modern Concerns Of The Tribe
The Spirit Lake Tribe, located in North Dakota, faces several modern concerns that reflect both their historical struggles and contemporary challenges. One prominent issue is economic development, as the tribe seeks to enhance its financial independence while preserving its cultural heritage. The tribe is actively working on diversifying its economy, focusing on initiatives such as tribal enterprises and eco-tourism, which can bolster job creation and community welfare.
Another critical concern is the preservation of language and culture. The Spirit Lake Tribe, home to the Dakota language, is diligently working to revitalize its linguistic heritage among younger generations. Educational programs and cultural workshops aim to instill a sense of identity and pride in tribal members, ensuring that traditions and languages endure despite external pressures.
Health care access is also a significant issue for the Spirit Lake Tribe.Many members contend with high rates of diabetes, substance abuse, and mental health challenges.The tribe strives to improve health services by integrating culturally sensitive care and expanding preventative health programs aimed at addressing these pressing health concerns.
Furthermore, the Spirit Lake Tribe is deeply involved in environmental protection efforts. The tribe acknowledges that safeguarding natural resources is crucial for future generations. Issues such as water quality, land management, and climate change are prioritized, as these factors directly affect their way of life, agriculture, and fishing rights.political advocacy remains a vital concern. The Spirit Lake Tribe actively engages with federal and state governments to ensure that tribal sovereignty is respected and that they have a voice in policy decisions impacting their community. This includes addressing issues related to treaty rights, land use, and financial support for tribal programs, crucial for maintaining their autonomy and quality of life.
These modern concerns reflect the Spirit Lake Tribe’s ongoing commitment to cultural preservation, economic self-sufficiency, health betterment, environmental stewardship, and political advocacy, illustrating their resilience and determination to thrive in a rapidly changing world.
Events And Other Social And Political Activities
The Spirit Lake Tribe, located in North Dakota, actively engages in a variety of events and social and political activities that not only enrich their community but also promote cultural heritage and advocacy. Key events include the annual Spirit Lake Nation Powwow, which celebrates traditional dance, art, and music, attracting visitors from across the region. This vibrant gathering showcases the tribe’s rich history and provides a platform for cultural exchange.
In addition to cultural celebrations, the Spirit Lake Tribe is involved in various educational initiatives aimed at empowering its youth. Programs focusing on language preservation,such as the Lakota language classes,not only enhance the community’s connection to its heritage but also foster pride among the younger generation.
Politically, the tribe is active in advocacy on issues such as sovereignty, environmental protection, and social justice.Leaders from the Spirit Lake Tribe regularly participate in national conferences and legislative discussions to voice their concerns and promote tribal rights. The tribe works closely with state and federal agencies to address pressing issues like health care access and education funding, ensuring that the needs of its members are prioritized.
Furthermore, the Spirit Lake Tribe frequently hosts workshops and forums that encourage civic engagement among community members. Topics range from economic development to renewable energy initiatives, reflecting a commitment to both cultural sustainability and contemporary challenges. This focus on active participation helps empower community members to take an active role in shaping their future.
the Spirit Lake Tribe emphasizes the importance of community cohesion through shared events and active political participation,demonstrating a robust commitment to cultural preservation and advocacy. By fostering an environment of engagement and solidarity, the tribe ensures its voice is heard on both local and national stages.