Introduction to the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma
The Apache Tribe of Oklahoma is a vibrant community with deep roots in history and culture. Residing primarily in the southwestern region of the state, this tribe is a testament to resilience and strength, having preserved their rich heritage amidst centuries of change. With a proud lineage that traces back to the great apache warriors, the tribe has embraced modernity while honoring traditional customs and practices.Established in 1936, the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma was formally recognized by the United States government, paving the way for significant cultural and economic development. The tribe is composed of several bands,each bringing unique traditions and perspectives that contribute to the tribe’s dynamic identity.Through various programs and initiatives, the apache Tribe actively engages in preserving their language, arts, and spiritual practices, ensuring that future generations continue to celebrate their legacy.
As a sovereign nation, the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma plays a crucial role in the local economy, operating accomplished enterprises and generating opportunities for community growth. Their initiatives range from tourism and hospitality to agriculture and crafting, all reflecting the unique spirit of the Apache people.
In exploring the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma, one uncovers not just a history of endurance but also a continuing story of cultural revitalization, community empowerment, and a deep commitment to the land they cherish. join us as we delve deeper into the captivating aspects of the Apache Tribe, examining their cultural practices, past significance, and the ever-evolving narrative of this remarkable community.
origin Of The People
The Apache Tribe of Oklahoma has a rich and complex origin rooted in the broader history of the Apache people. Originally, the Apache peoples are believed to have migrated from the northern regions of North America, particularly around the Canadian Plains and the Southwest, before eventually settling in areas like present-day Oklahoma. This migration occurred over many centuries, and the Apaches’ adaptability to different environments allowed them to thrive in various landscapes, including deserts, mountains, and plains.
Linguistically, the Apache Tribe belongs to the Athabaskan language family, which connects them to other Indigenous groups across North America, including the Navajo. This linguistic connection reflects shared cultural practices and beliefs, even as different Apache groups developed distinct identities. Traditionally, the Apache people were semi-nomadic, relying on hunting, gathering, and agriculture to sustain their communities. They are known for their exceptional skills in tracking and their deep understanding of the land, which has been passed down through generations.
Throughout their history,the Apache faced numerous conflicts and challenges,particularly during the westward expansion of European settlers in the 19th century. Their resistance to encroachment and efforts to protect their ancestral lands played a significant role in shaping their identity. Despite facing adversities, including forced removals and assimilation policies, the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma has maintained its cultural heritage. Today, they continue to celebrate their traditions, language, and spirituality.
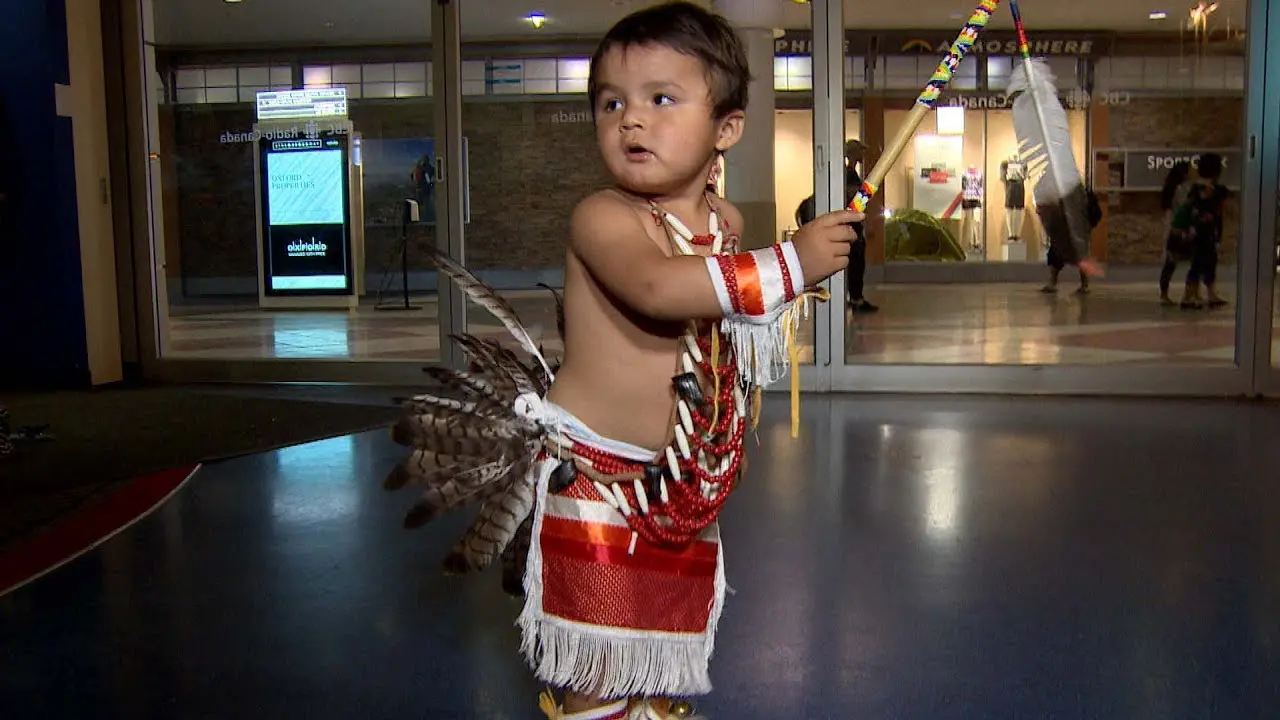
The establishment of the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma in 1970 facilitated the resurgence of their cultural practices and community engagement. With a focus on preserving their history and promoting economic development, the tribe has worked diligently to revitalize their heritage. The Apache people hold a deep sense of pride in their identity, which is celebrated through events like cultural festivals, traditional dances, and storytelling, all of which play a vital role in passing down their ancestral legacy to future generations.
Tribal Homelands
The Apache Tribe of Oklahoma, a sovereign Native American tribe, is deeply rooted in the rich cultural heritage and history synonymous with the Apache people. Their tribal homelands encompass a vast area in southeastern Oklahoma, primarily situated in the picturesque regions of McCurtain County. This unique geographical location is characterized by its rolling hills, dense forests, and vibrant rivers, all of which hold significant cultural and historical relevance to the Apache people.
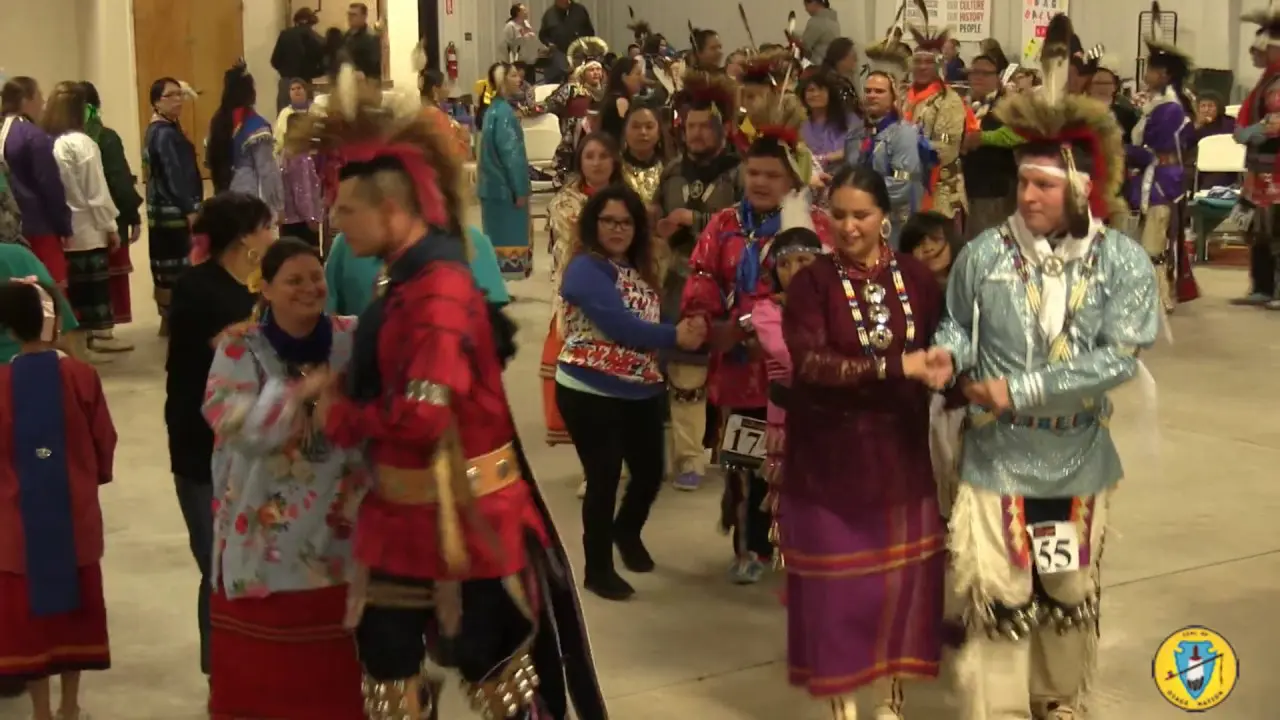
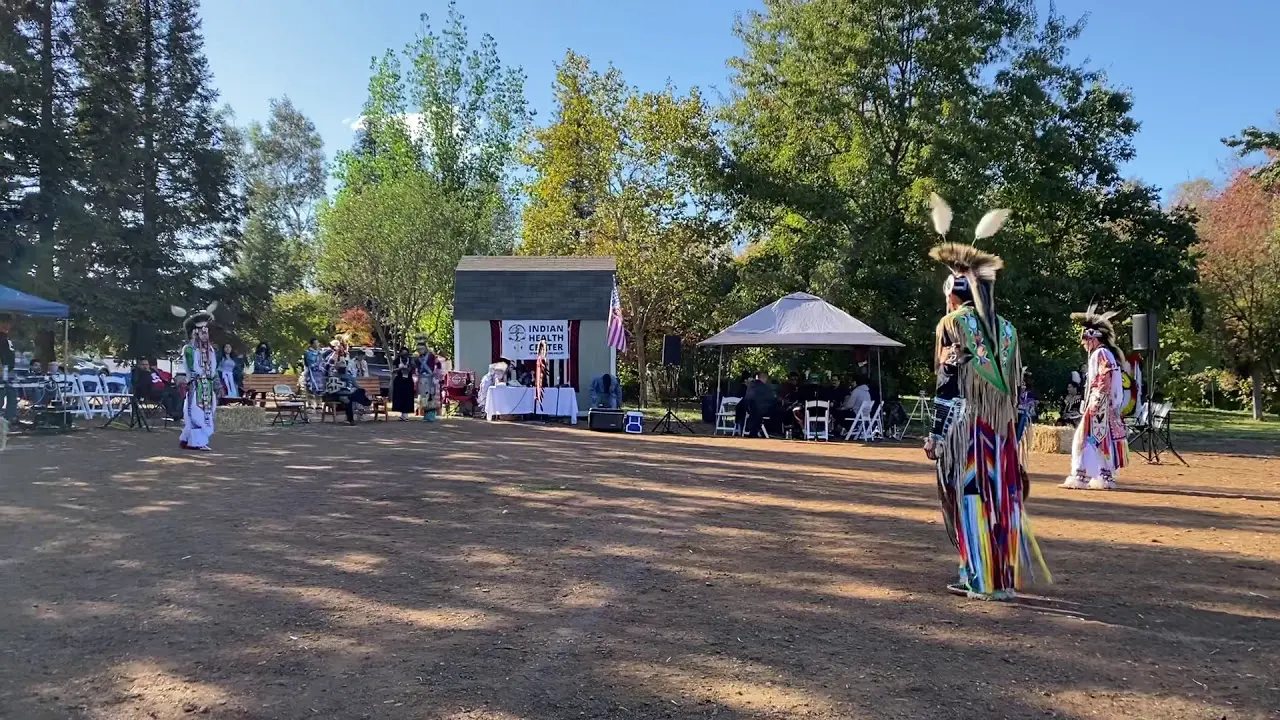
The tribal lands are primarily associated with the Kiowa, Comanche, and Apache Reservation, which was established in the late 19th century as part of the relocation and assimilation efforts enforced by the U.S. government. This region has become a symbol of resilience for the Apache Tribe, as it reflects their struggle and determination to preserve their traditional ways of life amid the challenges they faced during the colonization of North America.Today, the Apache Tribe of oklahoma holds much more than just physical territory; their homelands are a source of spiritual significance and cultural pride. The tribe continues to celebrate its traditions through various ceremonies and events, which frequently enough take place in sacred locations across their lands. Among these are the annual Apache Tribal Powwow and various community gatherings that highlight traditional music, dance, and storytelling, fostering a strong sense of unity among tribe members.
In recent years, the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma has focused on revitalizing their cultural heritage by investing in educational programs and initiatives aimed at teaching younger generations about their unique language, customs, and history. By promoting language preservation and cultural education, the tribe ensures that their connection to their ancestral homelands endures through time, enabling future generations to appreciate and uphold their rich Apache heritage.
The landscape of the Apache Tribe’s homelands also offers ample opportunities for eco-tourism and cultural exploration. Visitors can engage in outdoor activities such as hiking, fishing, and wildlife watching, while also learning about the tribe’s historical significance and contributions to the region. By embracing both nature and culture, the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma showcases the harmonious relationship they have with their land, fostering an appreciation for the natural world that is intertwined with their identity.
the tribal homelands of the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma are not only a geographical space but a vital entity that symbolizes the tribe’s resilience, cultural richness, and deep-rooted connection to their ancestors. The preservation of their land, language, and traditions continues to play a pivotal role in defining the identity of the Apache community in Oklahoma and beyond.
Interactions with Settlers
The Apache Tribe of Oklahoma experienced a complex relationship with settlers, marked by both positive and negative interactions. initially, many settlers viewed the Native American tribes, including the Apaches, through a lens of suspicion and fear, often leading to conflicts. The Apaches were known for their fierce resistance and adeptness in guerrilla warfare, which resulted in numerous confrontations with settlers who encroached upon their ancestral lands.
On the negative side, the arrival of settlers led to significant displacement and turmoil for the Apache people. As settlers pushed westward, the Apaches found their traditional hunting grounds and living spaces encroached upon, leading to skirmishes and violence. The U.S. government’s policies, including forced relocations and broken treaties, further exacerbated tensions, creating lasting scars in the community. The infamous “Apache Wars” of the late 19th century illustrate the strain of these interactions, as the tribe fought to protect their way of life against encroaching settlers.
Conversely, there were also instances of positive interactions between the Apache Tribe and settlers.In certain specific cases, settlers and Apache people exchanged goods and knowledge. For example, the Apaches were skilled horsemen and may have shared their horseback riding techniques with early settlers, fostering a mutual respect for the land and its resources.There were rare instances where settlers and Apache families allied against common enemies or shared survival strategies during harsh winters. These cooperative experiences, even though fewer, highlighted the potential for coexistence.
Over time, the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma adapted to the changing landscape, finding ways to engage with settlers through trade, cultural exchanges, and community-building initiatives. Today, the Apache Tribe embraces its rich heritage while navigating a modern world, participating in economic development ventures that foster relationships with surrounding communities. Through education and outreach, the tribe works to ensure that their story and history are recognized, promoting cultural awareness and understanding among settlers and the broader population.
These interactions reflect the multifaceted nature of the Apache experience, capturing the struggles and resilience of a people who continue to thrive despite historical challenges.
Most Notable Events In their Tribal History
The Apache Tribe of Oklahoma has a rich history marked by resilience, culture, and significant events that have shaped its identity. One of the most notable events in Apache history is the forced relocation during the 1800s, which was part of a broader Indian removal policy enacted by the United States government. In 1861, the tribe faced harsh conditions as they were moved from their traditional lands in the Southwest to reservations in Oklahoma. This drastic change not only disrupted their way of life but also posed significant challenges in maintaining their cultural practices.
Another pivotal moment in Apache history occurred in the late 19th century with the surrender of legendary leaders such as Geronimo and cochise. Their resistance against encroachment by settlers drew national attention and underscored the fierce struggle of the Apache people. Geronimo’s eventual surrender in 1886 marked the end of an era of armed conflict, but it also initiated a complex relationship with the U.S.government that would shape future interactions.
As the 20th century unfolded, the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma faced new challenges and opportunities. The Indian Reorganization Act of 1934 played a crucial role in reviving tribal governance and culture. This legislation allowed the Apache Tribe to reorganize and establish its own government, enabling a renewed focus on cultural preservation and self-determination.
In the latter half of the 20th century, the tribe took significant steps towards economic development, establishing enterprises and promoting education to empower its community. The establishment of the Apache Tribal Economic Development fund in 1983 was instrumental in providing the necessary resources for tribal members and supports various community initiatives.
Today,the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma is committed to preserving its heritage while navigating the challenges of modern society. With ongoing efforts to promote education,cultural programs,and economic growth,the tribe continues to honor its history while looking toward a vibrant future.
Where Are Their Tribal Lands Now And How Were they Established
The Apache Tribe of Oklahoma, originally comprised of several distinct bands, has developed a rich history tied to their tribal lands, now located primarily in the southeastern region of the state. The tribe’s current lands are situated in and around the town of Anadarko, Oklahoma, where the Apache tribal headquarters can be found.This area serves as a cultural and administrative center for the community and has been a focal point for the tribe’s revitalization efforts and cultural preservation.
Establishment of these lands can be traced back to the aftermath of the Indian Wars in the late 19th century, when many Native American tribes, including the Apache, were forcibly relocated to reservations. Following numerous conflicts, the U.S. government established the Apache Reservation in 1892, which was part of the broader changes during the era of Indian assimilation policies. After decades of significant upheaval, the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma was formally recognized by the federal government in 1976, solidifying their status and lands as a sovereign entity.
Today, tribal lands support various initiatives aimed at sustainability, cultural preservation, and economic growth. the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma manages programs that focus on education, health services, and natural resource management, ensuring the well-being of its members while honoring their ancestral heritage. As the tribe moves forward,the continued commitment to preserving their traditions alongside modern advancements is crucial in shaping their identity and community cohesion.
modern Concerns Of The Tribe
The Apache Tribe of Oklahoma faces several modern concerns that reflect the challenges of balancing tradition with contemporary socio-economic demands. One of the prominent issues is the preservation of cultural heritage. As younger generations navigate a rapidly changing world, there is a critical need for initiatives that promote Apache language, customs, and traditional practices. Language revitalization programs are particularly essential,as they help to maintain the tribe’s identity and ensure that cultural knowledge is passed down through generations.
Economic development is another significant concern for the Apache Tribe. While there have been successes in establishing businesses, gaming enterprises, and tourism initiatives, lasting economic growth remains a priority. The tribe is actively exploring diverse revenue streams,including renewable energy projects,agricultural ventures,and technology-based businesses,to create jobs and enhance the local economy. However, balancing economic initiatives while honoring traditional values poses an ongoing challenge.
Healthcare access and wellness are also critical areas of focus for the Apache people. Like many Indigenous communities, the tribe grapples with varying health challenges, including higher rates of chronic diseases and mental health issues. Improving access to quality healthcare services, mental health support, and nutritional programs is essential for enhancing the overall well-being of tribe members.
Environmental stewardship comes to the forefront as well,particularly with the increasing impacts of climate change.The Apache Tribe is invested in protecting their natural resources and sacred lands. Concerns over land use,water rights,and environmental degradation necessitate active engagement in policy discussions and collaborations that promote sustainable practices.
Additionally,the tribe is voicing concerns about legal and political issues affecting Native American sovereignty. issues such as jurisdiction, land use rights, and federal policies continue to influence the tribe’s ability to govern itself and protect its interests. Advocacy for stronger legal protections and representation is crucial in addressing these concerns.
the modern challenges faced by the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma underscore the complexities of maintaining cultural integrity while pursuing socio-economic advancements. The tribe’s commitment to addressing these issues demonstrates resilience and adaptability in an ever-evolving landscape.
Events And other Social And Political Activities
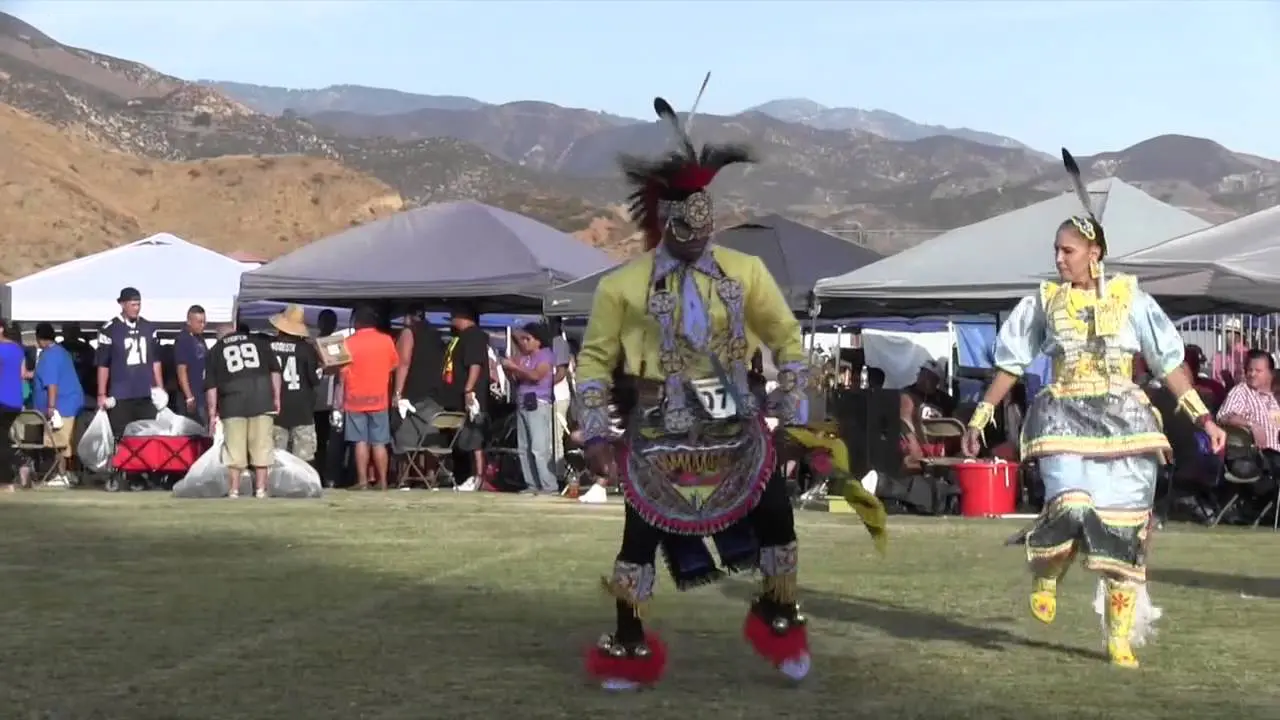
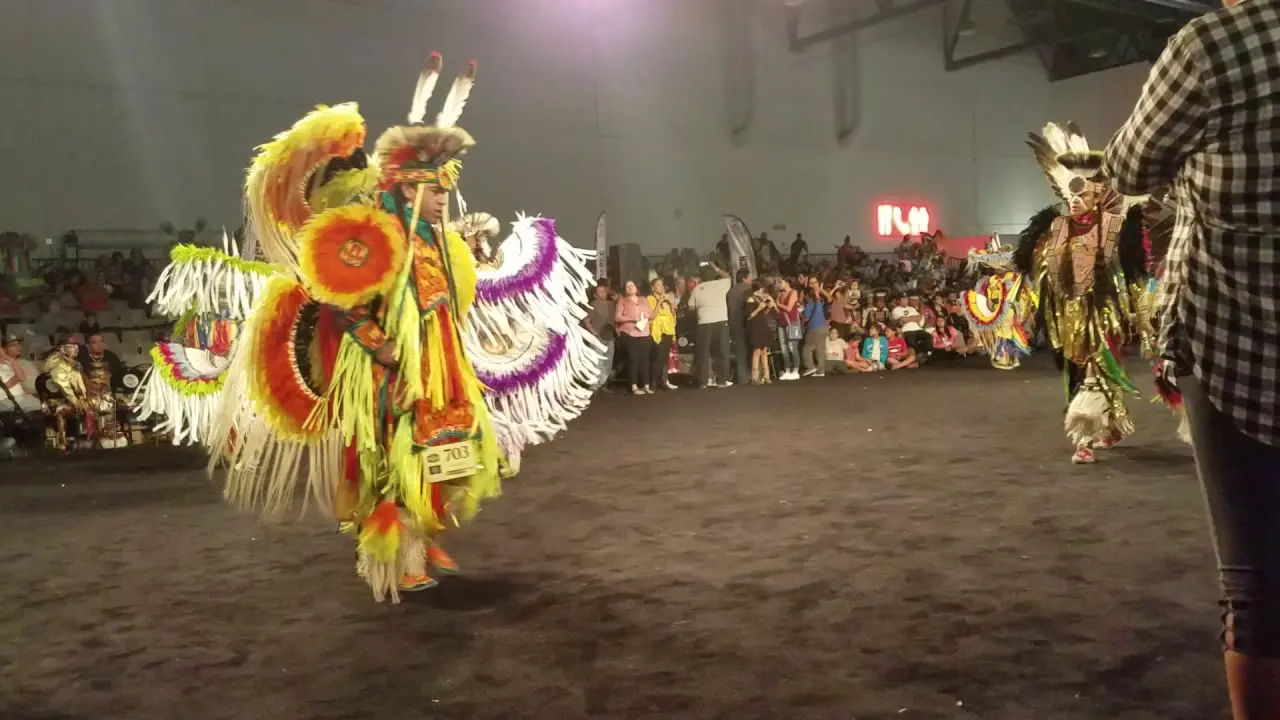
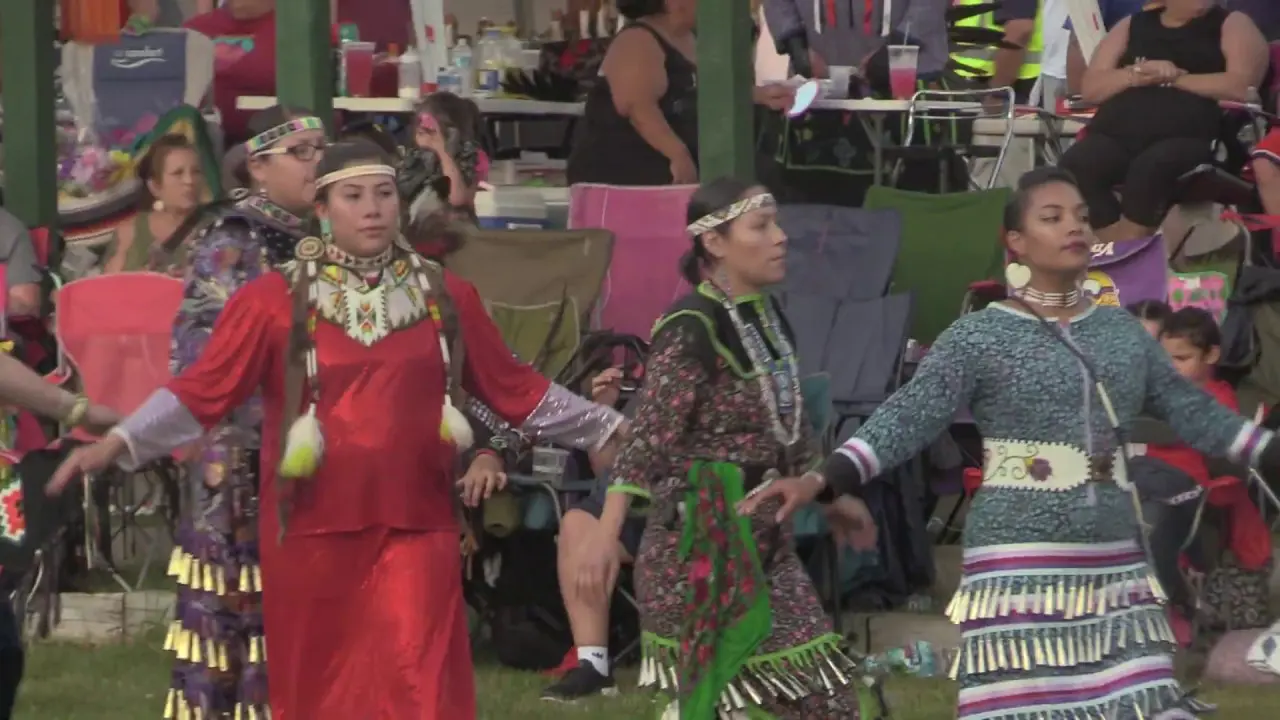
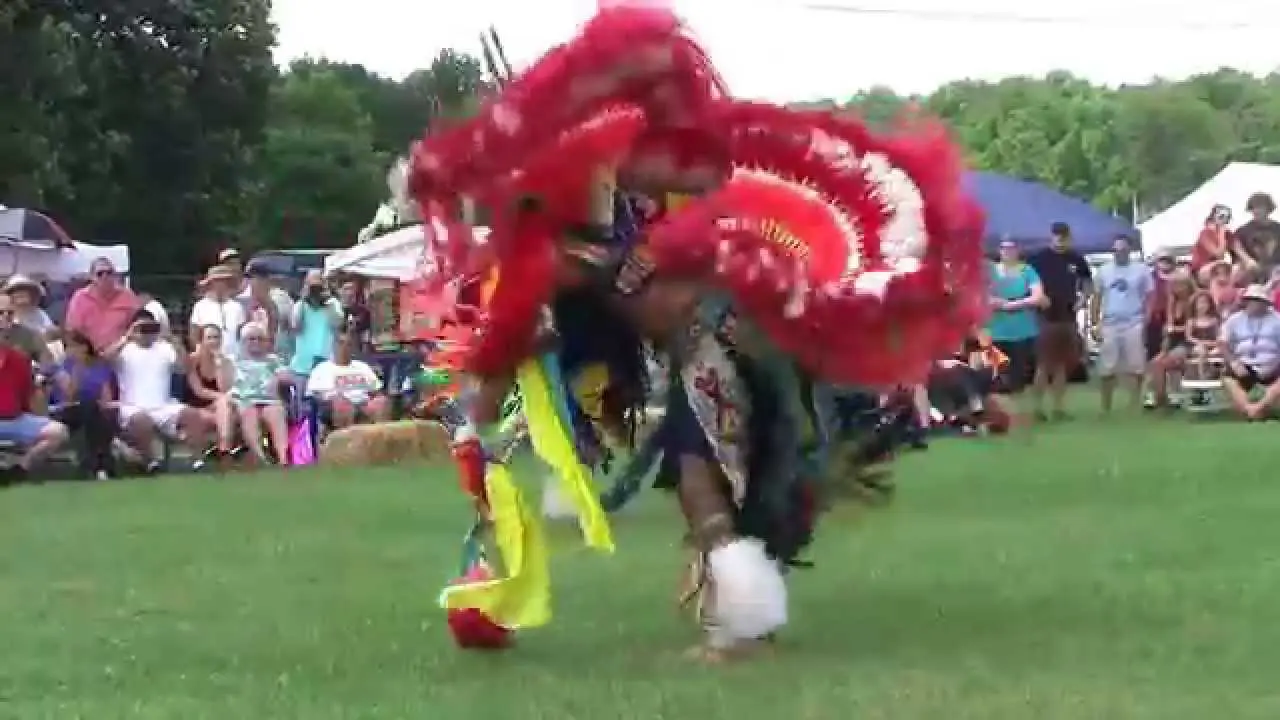
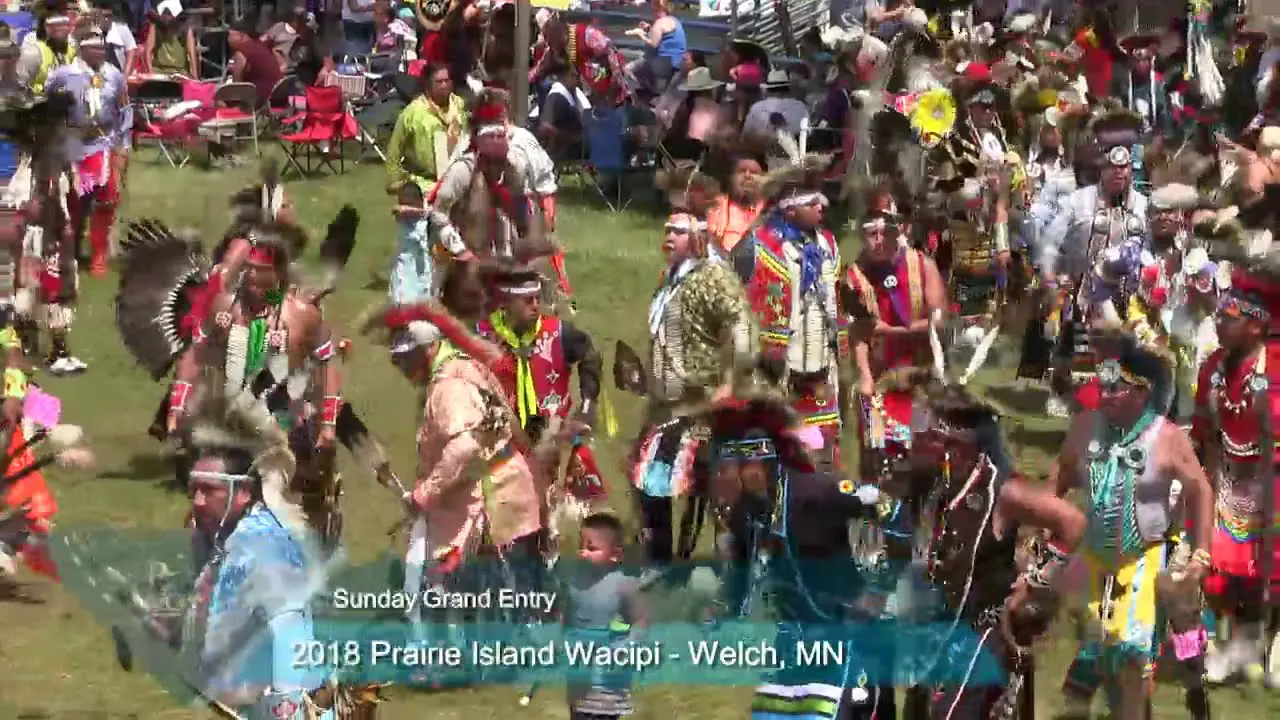
The Apache Tribe of Oklahoma actively engages in various cultural, social, and political activities that reflect their rich heritage and community spirit. Throughout the year, the tribe hosts numerous events that not only celebrate Apache traditions but also foster unity among tribal members and the broader community. One significant event is the annual Apache Tribal fair and Rodeo, which showcases rodeo competitions, traditional Apache dances, crafts, and local cuisine. This event brings together families,friends,and visitors,allowing them to experience the vibrant culture of the Apache people while participating in fun and engaging activities.
Along with cultural events, the Apache Tribe prioritizes education and awareness through initiatives like the Tribal Youth Leadership Academy. This program empowers young members by instilling leadership skills, cultural pride, and a greater understanding of tribal governance. Participants engage in workshops, discussions, and mentorship opportunities that give them the tools to become active participants in their community and beyond.
Political activities also play a vital role in the tribe’s efforts to advocate for their rights and interests. The Apache Tribe of Oklahoma frequently enough collaborates with other tribes to address common issues, such as land rights, healthcare access, and environmental protection. Through participation in regional and national gatherings, tribe leaders actively voice concerns and advocate for federal support and recognition of tribal sovereignty.
Moreover, the tribe emphasizes economic development initiatives, such as the Apache Gaming Enterprise, which not only enhances financial stability but also creates job opportunities for tribal members. the revenues generated from these enterprises are reinvested into community programs, education, and healthcare, ensuring that the future generations of the Apache Tribe thrive.the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma’s social and political activities are rooted in cultural celebration, youth empowerment, advocacy for rights, and economic sustainability. Their commitment to preserving their heritage while actively engaging with modern societal challenges showcases a forward-thinking approach that ensures the vibrancy and resilience of the Apache community.