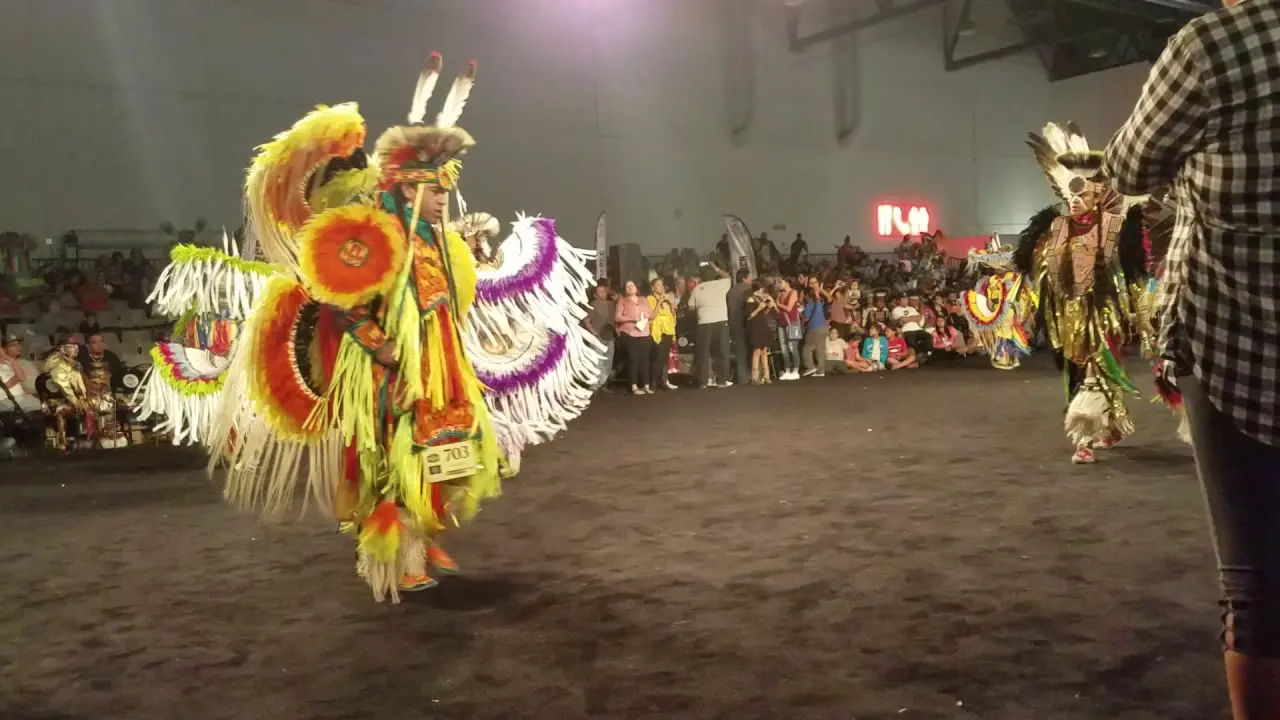
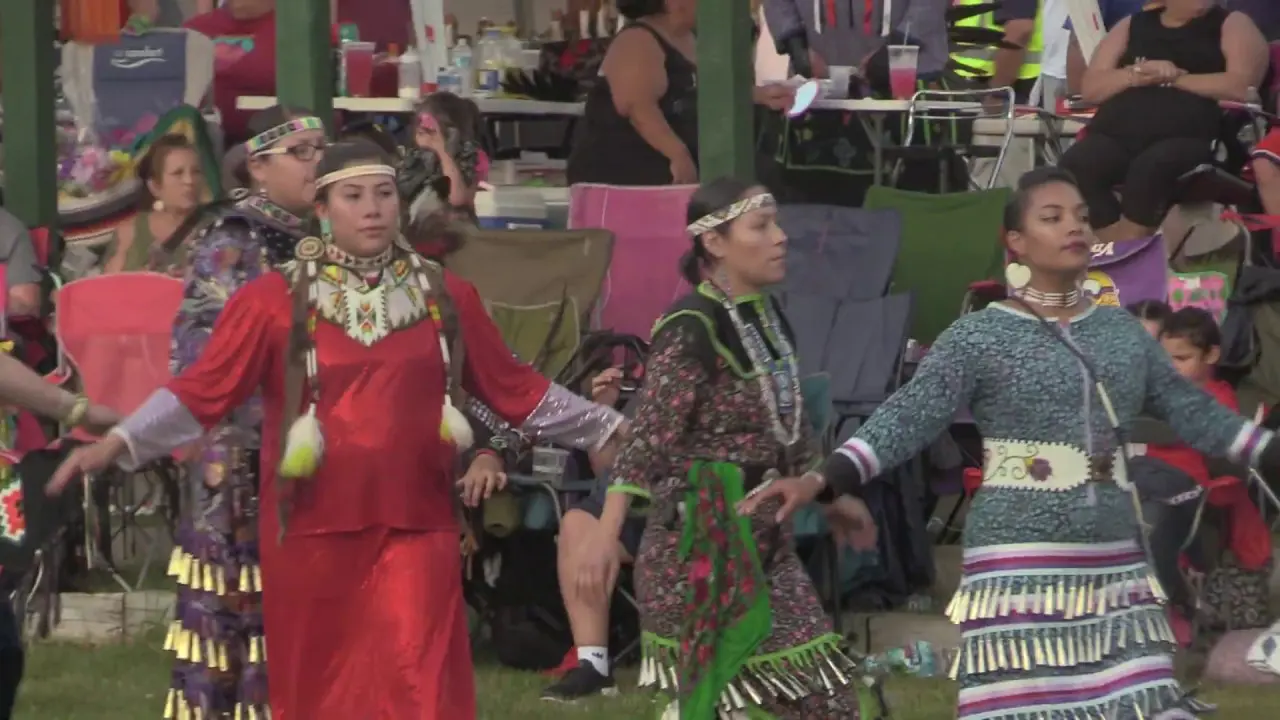
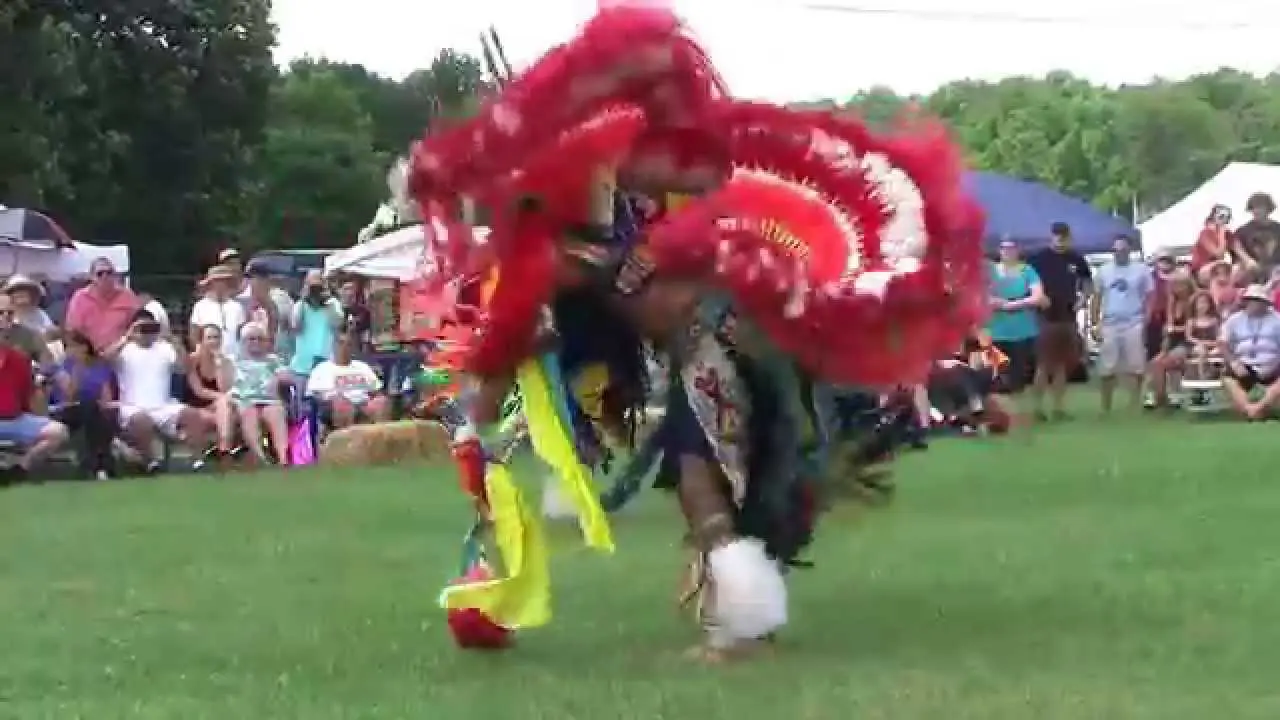
Introduction to the Bear River Band of the Rohnerville Rancheria
Nestled in the picturesque landscapes of Northern California, the Bear River Band of the Rohnerville Rancheria is a vibrant tribe with a rich cultural heritage and deep ancient roots. This federally recognized Native American tribe, comprised mainly of the Wiyot people, is located in Humboldt County, where the breathtaking natural surroundings and lush environments tell the story of a legacy that dates back thousands of years.
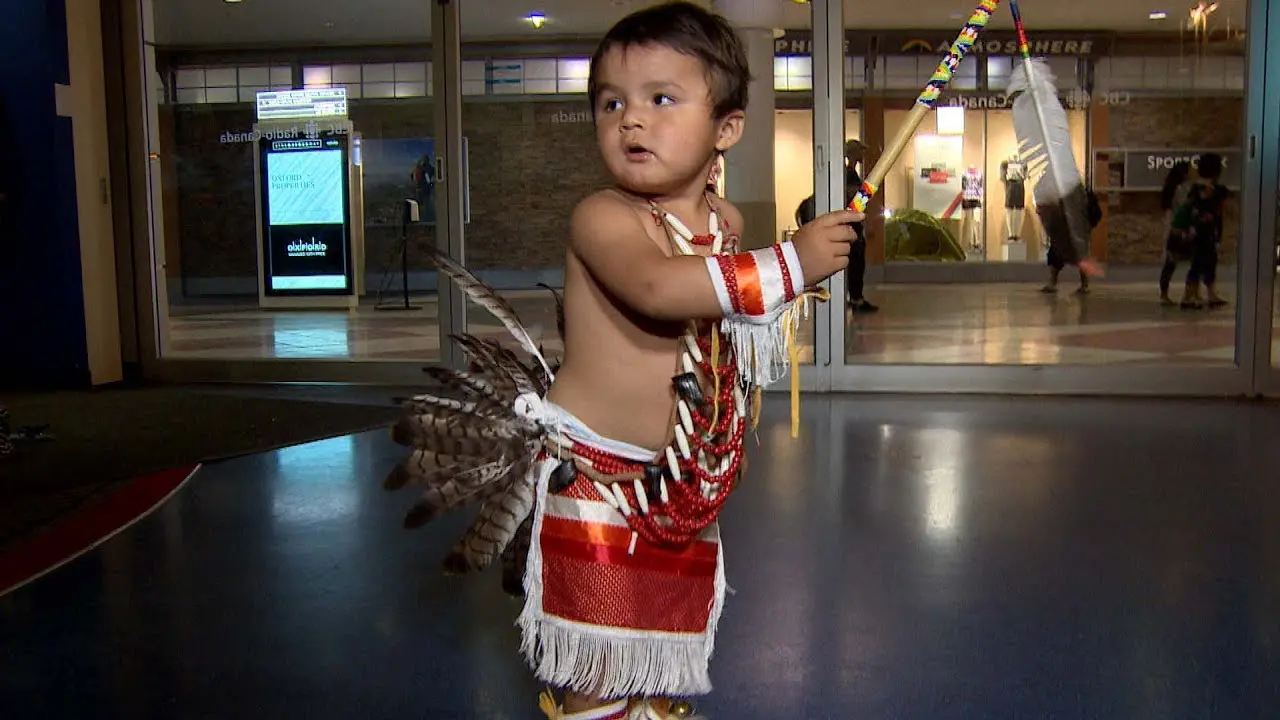
The Bear River Band is dedicated to preserving and celebrating their unique traditions, language, and music, which have been passed down through generations. With a strong emphasis on community, the tribe is actively involved in various initiatives aimed at promoting economic progress, education, and environmental stewardship. The Rancheria serves as a vital hub for tribal members, fostering a sense of belonging while also engaging with the broader community.
The Bear River Band of the Rohnerville Rancheria is not just a tribal government; it is a living testament to resilience and cultural revival. Through their commitment to sovereignty and self-determination, the tribe continues to navigate contemporary challenges while honoring their ancestral legacy. whether exploring their rich history or engaging in modern tribal life, visitors and community members alike are welcomed into a world that celebrates the enduring spirit of the Bear River Band, making it a remarkable part of California’s diverse cultural tapestry.
Origin Of The People
The Bear River Band of the Rohnerville Rancheria, located in Northern California, has a rich and complex origin story deeply rooted in the region’s cultural and historical landscape. The tribe primarily descends from the Wiyot people, who have inhabited the Humboldt Bay area for thousands of years. Traditionally, the Wiyot where skilled hunters, gatherers, and fishers, relying on the abundant natural resources of the land and waters surrounding the Eel River and Humboldt Bay.
The Bear River Band specifically emerged as a distinct community in the aftermath of the U.S. government’s westward expansion in the 19th century, which led to notable disruptions to indigenous life.the California Gold Rush and subsequent settlement brought about violence, disease, and displacement that profoundly impacted the Wiyot population. Despite these challenges, the Bear River Band persevered, maintaining their cultural identity, practices, and connections to the land.
In the late 19th century, the Rohnerville Rancheria was established as a form of reservation, allowing the Bear River Band a semblance of governance and autonomy. However, the tribe faced ongoing struggles with federal recognition and the often-adverse policies that targeted Native populations. It wasn’t until 1983 that the Bear River Band officially gained federal recognition, a significant milestone that empowered the tribe to reclaim and revitalize their cultural heritage.
Today, the Bear River Band of the rohnerville Rancheria actively works to preserve their traditions, language, and connection to the land. They engage in cultural revitalization programs, educational initiatives, and community development. The tribe’s involvement in various environmental stewardship projects reflects their commitment to protecting the natural resources that are vital to their identity and way of life. By honoring their history and looking to the future, the Bear River band continues to play a crucial role in the cultural tapestry of Northern California.
Tribal Homelands
The Bear River Band of the Rohnerville Rancheria is a federally recognized tribe located in Northern California, specifically in Humboldt County. their ancestral homelands encompass a region rich in natural resources, cultural meaning, and historical context.The territory traditionally occupied by the Bear River Band includes areas around the Eel River and it’s tributaries, which provided vital sustenance through fishing, hunting, and gathering.
This region is characterized by diverse landscapes,including lush forests,rolling hills,and fertile valleys. The tribe’s connection to the land is deeply rooted in their cultural practices, which include stewardship of the environment and a profound understanding of the local ecosystem. The Bear River Band maintained a enduring relationship with their surroundings, utilizing resources such as acorns, berries, and fish, which remain critically important to their cultural heritage today.
The tribe’s homelands are not only critical for their livelihood but also hold spiritual significance. sacred sites and traditional gathering locations pepper the landscape, embodying the tribe’s history and connection to the earth. The Bear River Band is actively involved in preserving these sites and revitalizing traditional practices, ensuring that their cultural identity remains vibrant for generations to come.
In modern times, the Bear river Band of the Rohnerville Rancheria works to promote economic development while honoring their ancestral traditions. Their tribal lands serve as a base for various initiatives aimed at community development, cultural preservation, and environmental conservation. As they navigate the complexities of contemporary life, the tribe remains committed to safeguarding their homelands and ensuring that future generations can enjoy the rich cultural tapestry woven into the land they call home.
Interactions With Settlers
The Bear River Band of the Rohnerville Rancheria, located in Northern California, has a complex history of interactions with settlers that is marked by both collaboration and conflict. These interactions have substantially shaped the tribe’s cultural and social landscape.
On the positive side, early settlers sometimes forged cooperative relationships with the Bear River Band, leading to mutual benefits. For example,some settlers recognized the agricultural knowledge and resource management skills of the tribe,particularly in areas such as fishing and foraging. This acknowledgment allowed for an exchange of ideas and practices that enriched both communities. The tribe was able to share traditional ecological knowledge that helped settlers navigate the region’s abundant natural resources, fostering a sense of respect and admiration. Moreover, certain settlers advocated for the rights and welfare of the Bear River Band, creating alliances that promoted coexistence and cultural exchange, enabling the preservation of some tribal traditions in the face of external pressures.
Conversely, negative interactions between the Bear River Band and settlers were marked by conflict, land dispossession, and cultural suppression. The arrival of settlers in the 19th century resulted in the encroachment on tribal lands, leading to significant loss of territory and traditional resources. This encroachment not only disrupted the tribe’s way of life but also forced many members into a marginalized status within their own homeland. Alongside land loss, settlers often imposed their beliefs and systems, leading to cultural assimilation efforts that sought to erase Native identities. The introduction of treaties often disregarded the tribe’s sovereignty and rights, compounding their struggles as settlers prioritized their economic advancements over the interests of the Bear River Band.
The ramifications of both positive and negative interactions continue to resonate today, as the Bear River Band of the Rohnerville Rancheria actively works to reclaim its cultural heritage while navigating the ongoing complexities of settler and tribal relations. These historical narratives are vital for understanding the present challenges and triumphs of the Bear River Band and its community in their pursuit of sovereignty, recognition, and cultural revitalization.
Most Notable Events In Their Tribal History
The Bear River Band of the Rohnerville Rancheria,a federally recognized tribe in California,has a rich and complex history marked by resilience and community solidarity. Among the most notable events in their tribal history is the formation of the Rohnerville Rancheria in 1910, which provided a legal designation for a tribal land base, allowing members to cultivate cultural practices after years of displacement and disruption.
The mid-20th century brought a significant turning point for the bear River Band, as the Indian Reorganization Act of 1934 offered tribes the opportunity to establish self-governance. The tribe began laying the groundwork for its modern governance structure, which now includes elected tribal councils and a focus on economic development.
One pivotal moment came in the 1970s with the restoration movement.A wave of activism emerged across Indian Country, leading the Bear River Band to file for recognition from the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA). This culminated in the tribe’s federal acknowledgment in 1983,allowing them to access critical resources and programs for community development and cultural preservation.
In the early 2000s, the Bear River Band made strides in enhancing their economic stability through ventures in tourism and natural resource management. The construction of the Bear River Casino, which opened in 2002, created job opportunities for tribal members and became a hub for community gatherings. Additionally, the tribe has engaged in environmental stewardship, with initiatives that protect local natural resources and traditional lands for future generations.
Throughout their history, the Bear River Band has prioritized the revitalization of their cultural heritage. Language recovery programs and traditional ceremony practices are actively supported to ensure that ancestral knowledge and traditions are passed down. The tribe’s dedication to education, health, and economic empowerment has fostered a vibrant community that honors its past while looking toward the future.
Where Are Their Tribal Lands Now And How Were They Established
The Bear River Band of the Rohnerville Rancheria is located in Northern California, primarily in Humboldt County.The tribe’s established lands are situated near the community of Loleta, encompassing approximately 72 acres.These tribal lands serve as a cultural and economic hub for the Bear River Band, allowing them to preserve their heritage and provide essential services to their members.
The establishment of the Bear River Band’s tribal lands dates back to the federal recognition of the tribe in 1983,following a long and challenging history marked by displacement and loss of territory. The Rohnerville Rancheria was established as a federal trust land, which provided the Bear River Band with the ability to govern themselves autonomously and manage their resources. This recognition came after decades of advocacy, legislation, and community persistence to reclaim their identity and rights as an indigenous people.
Today, the Bear River Band is actively involved in various initiatives aimed at economic development, environmental stewardship, and cultural revitalization on their lands. It is essential for them to engage in sustainable practices while also reclaiming traditional knowledge and customs as part of their ongoing journey of cultural renewal. The tribal lands of the Bear River Band not only represent a geographical space but also a profound connection to their ancestors and a beacon of hope for future generations.
Modern Concerns Of The Tribe
The Bear River Band of the Rohnerville Rancheria in California is a federally recognized tribe navigating a range of modern concerns that impact their community and cultural heritage. One of the primary issues facing the tribe is the preservation of their ancestral lands and natural resources. Like many indigenous communities, the Bear River Band is acutely aware of the potential threats posed by environmental degradation, climate change, and development projects that could disrupt their traditional territories.
Economic development is another significant focus for the Bear River band. The tribe is working to cultivate sustainable economic opportunities while ensuring that these initiatives align with their cultural values. This includes exploring avenues such as eco-tourism and tribal enterprises that can generate revenue without compromising their identity or environment. The challenge lies in balancing modernization with the preservation of their rich cultural heritage.
Health and wellness are also pressing concerns for community members. Access to quality healthcare services has long been an issue for many tribal nations, and the Bear River Band is no exception. Addressing health disparities, mental health support, and substance abuse prevention remains a vital aspect of their community initiatives. The tribe is actively seeking to enhance health education and advocate for resources that benefit their members.
Education and cultural revitalization are intertwined concerns for the tribe, as they strive to educate younger generations about their heritage and traditions. The Bear River Band promotes culturally relevant education through language programs, storytelling, and traditional practices. empowering youth with knowledge of their history fosters a strong sense of identity and community pride.
Furthermore, tribal governance and sovereignty remain critical discussions for the Bear River Band. Engaging in advocacy at local, state, and national levels helps ensure that their rights and interests are represented.Rebuilding relationships with non-tribal entities and addressing legal challenges related to land use and resource management are essential for safeguarding their future.
the Bear River Band of the Rohnerville Rancheria faces modern challenges including environmental preservation, economic development, healthcare access, and cultural revitalization.By addressing these concerns through a lens of sustainability and community empowerment, the tribe can work toward a resilient future that honors their past while embracing new opportunities.
Events And Other social And Political Activities
The Bear River Band of the Rohnerville Rancheria engages actively in a variety of social and political activities that reflect their commitment to preserving their culture, addressing community needs, and advocating for Indigenous rights. Through a series of annual events, the tribe fosters a sense of community not just among its members but also with surrounding communities.
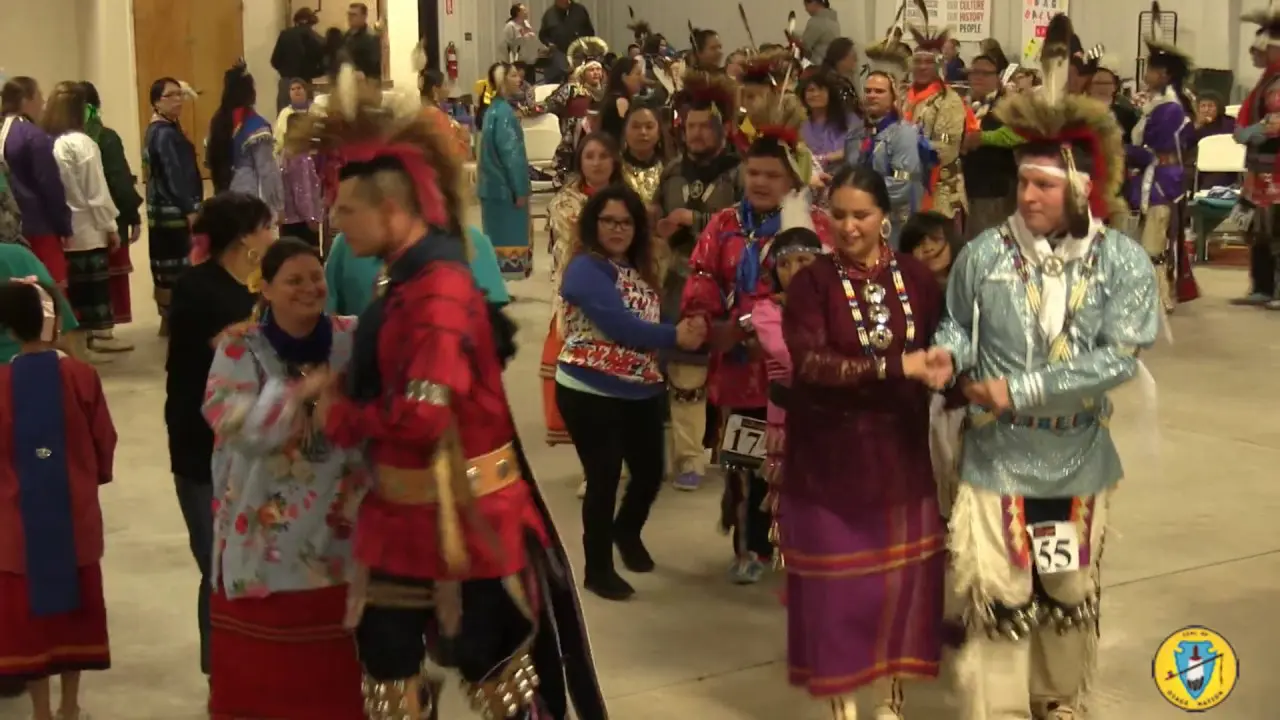
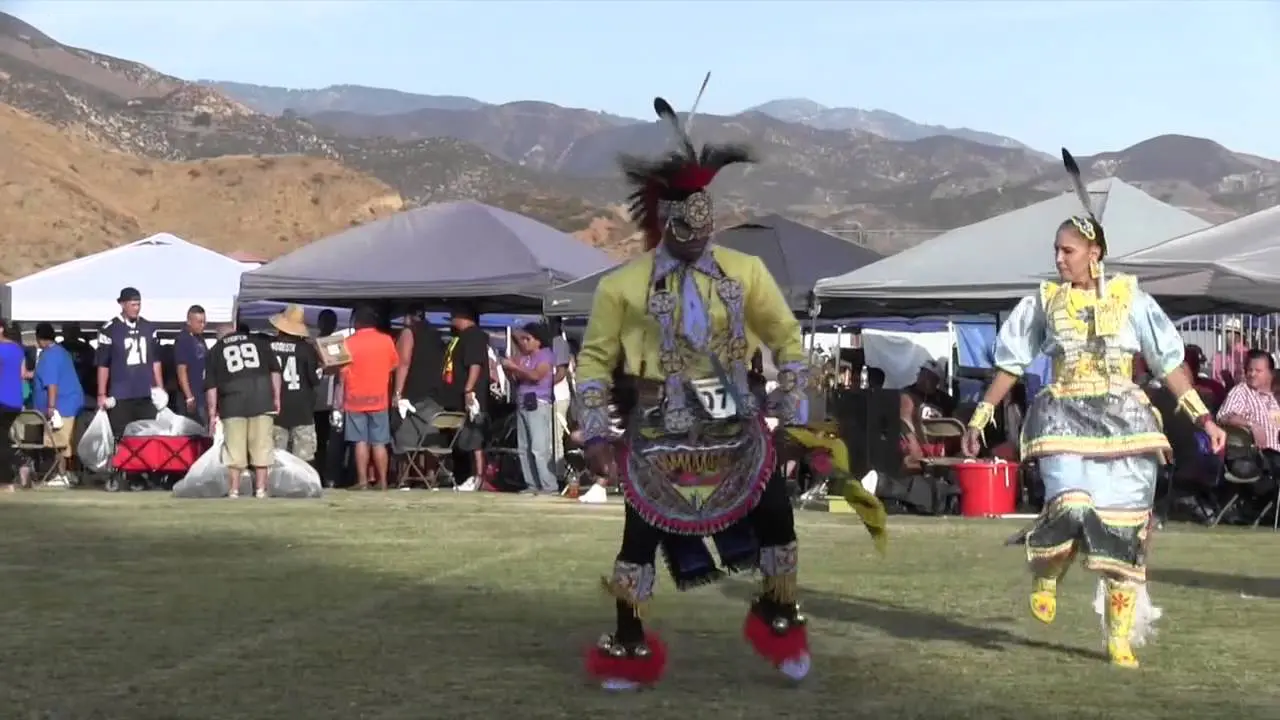
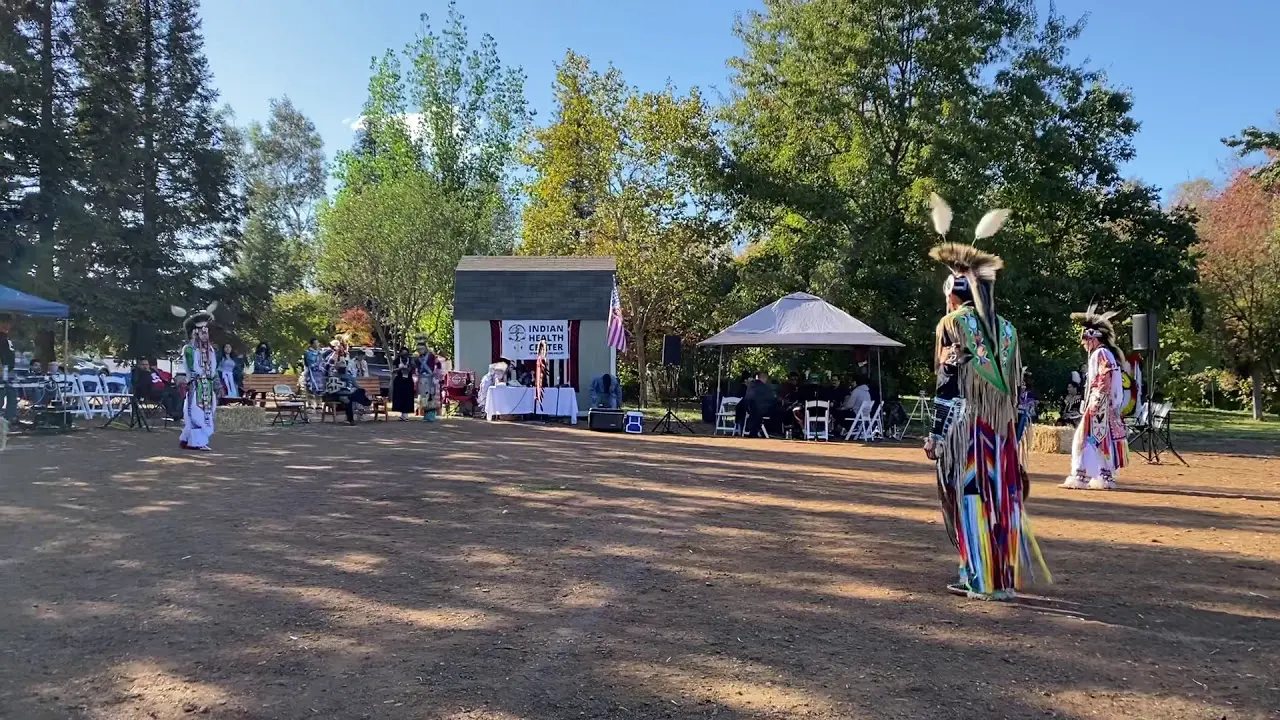
One of the key events organized by the Bear River Band is the annual Tribal Gathering, which celebrates Native American heritage through traditional music, dance, and arts and crafts. This gathering serves as an important cultural touchstone, offering educational workshops that promote awareness about Native traditions, history, and contemporary issues facing Indigenous peoples.
In addition to cultural events, the Bear River Band is involved in various political activities, advocating for policy changes that benefit both their community and the broader Native American population. The tribe actively participates in regional and state-level discussions regarding environmental protection, land rights, and healthcare access for Indigenous communities. By collaborating with other tribal governments and organizations, they work towards legislative initiatives that safeguard their rights and resources.
The Bear River band also places a strong emphasis on youth engagement. The tribe runs programs aimed at educating younger generations about their cultural heritage, political rights, and the importance of civic involvement. Through mentorship initiatives and educational scholarships, the tribe invests in the future of its members, encouraging active participation in both tribal governance and community service.
Social obligation is a cornerstone of the Bear River Band’s activities. They host community service events, such as food drives and environmental clean-up days, which not only enhance community cohesion but also promote sustainability and respect for natural ecosystems. These initiatives demonstrate the tribe’s dedication to enhancing the quality of life for both tribal members and their neighbors.By weaving together cultural pride, political advocacy, and social responsibility, the Bear River Band of the Rohnerville Rancheria exemplifies the spirit of resilience and commitment to empowerment that defines many Native American tribes today.