Introduction to the Blue Lake Rancheria Tribe of California
Nestled in the serene landscapes of Northern California,the Blue Lake Rancheria is a vibrant Native American tribe with a rich cultural heritage and a deep connection to the land. Established officially in 1983, the Blue Lake Rancheria is a federally recognized tribe consisting primarily of descendants of the Wiyot people, who have inhabited the region for thousands of years.
The tribe spans a range of approximately 88 acres near the picturesque town of Blue Lake, where the lush redwood forests intermingle with the tranquil waters of the Mad River, creating a stunning backdrop for both living and community activities. The Blue Lake Rancheria is not only a steward of its ancestral lands but also a thriving economic entity, engaging in various enterprises that foster sustainability and growth, including a triumphant casino and resort that cater to both locals and tourists.
Cultural preservation is central to the tribe’s mission, as it strives to uphold customary practices, languages, and crafts that define Wiyot identity. Community engagement plays a key role in their initiatives, as the tribe actively promotes education and wellness programs for its members and the surrounding community.
As you delve deeper into the history, culture, and contributions of the Blue Lake Rancheria, you will discover a community that embodies resilience, empowerment, and a profound respect for its ancestral traditions. Whether you’re looking to learn more about their ongoing efforts in cultural preservation, economic development, or environmental sustainability, the Blue Lake Rancheria stands as a remarkable testament to the enduring spirit of Native American tribes in California.
Origin Of the People
The people of Blue Lake Rancheria, a federally recognized tribe located in Humboldt county, California, are primarily descendants of the Wiyot tribe, an Indigenous group whose ancestral territory encompasses the coastal region along the Humboldt Bay and the expansive redwood forests of northern california.The Wiyot people have a rich cultural heritage that spans thousands of years, with their origins deeply rooted in the land, waters, and ecosystems surrounding them.
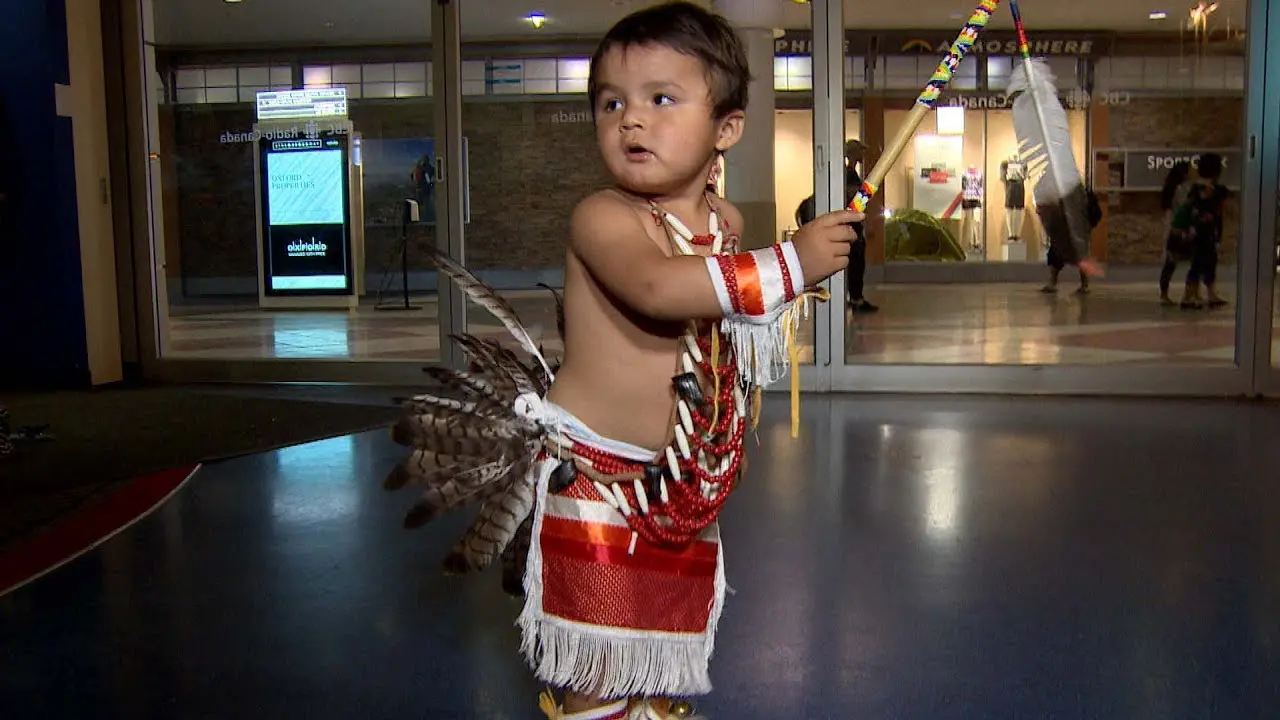
Traditionally, the Wiyot community thrived as hunter-gatherers, utilizing the diverse resources of both land and sea. their lifestyle was intricately connected to the rhythms of nature,with seasonal rounds of fishing,hunting,and gathering allowing them to live in harmony with their environment. The tribe is known for its vibrant traditions,including basket weaving,ceremonial practices,and the creation of art,which continue to be essential components of their cultural identity today.
The establishment of the Blue Lake Rancheria was a important moment in the tribe’s modern history, serving as a sanctuary for Wiyot people after a painful period of colonization and displacement.In the late 19th century, following the California Gold Rush, the Wiyot faced numerous challenges, including violence, land loss, and forced assimilation. Despite these adversities, the community persevered, reclaiming its rights and heritage over time.
The Blue Lake Rancheria formally received federal recognition in 1983, which marked a pivotal point in the tribal community’s resurgence. Today, the Blue Lake Rancheria is not only a home for Wiyot descendants but also a hub for cultural revitalization and economic development.The tribe actively engages in initiatives that promote education, community health, and environmental stewardship, ensuring that its rich history and traditions will endure for future generations.
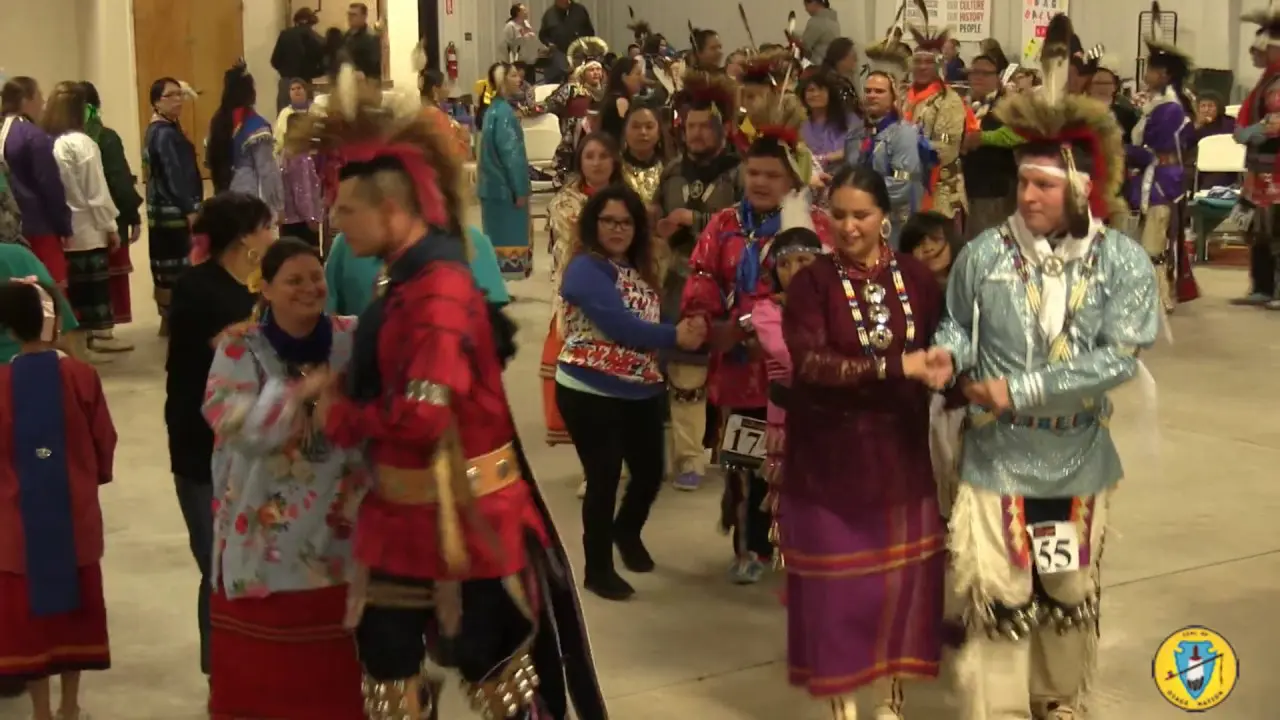
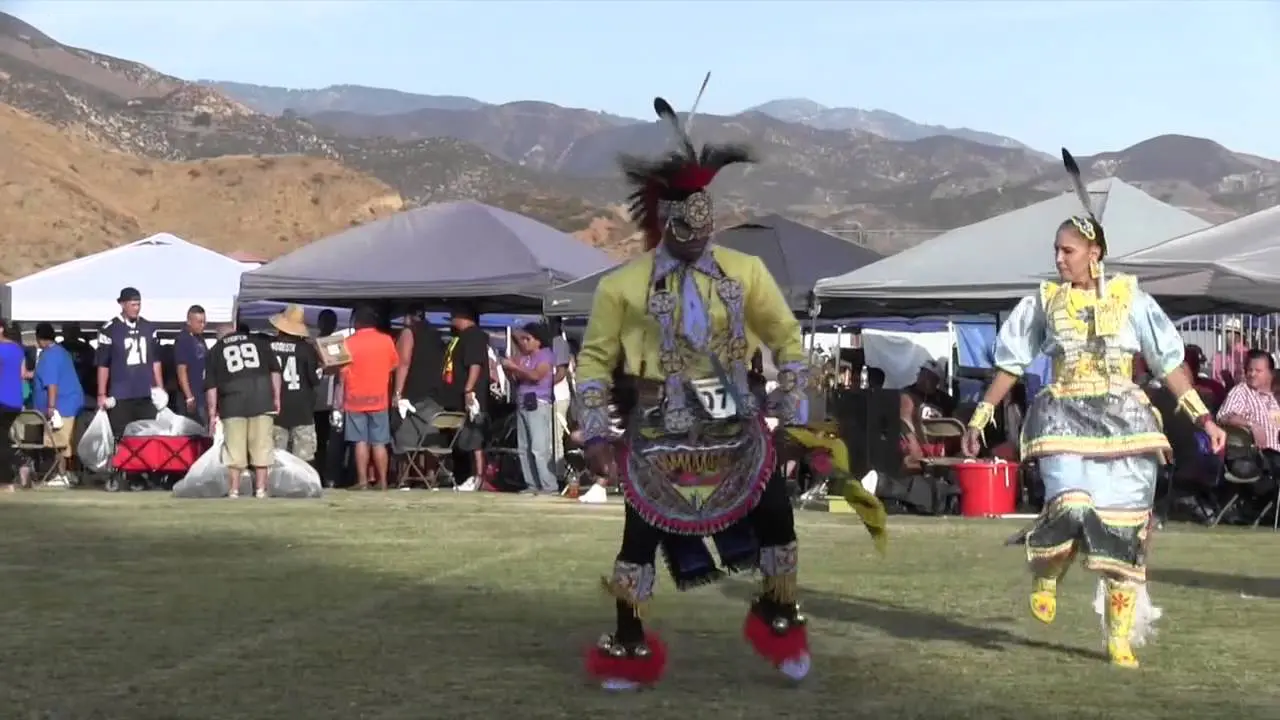
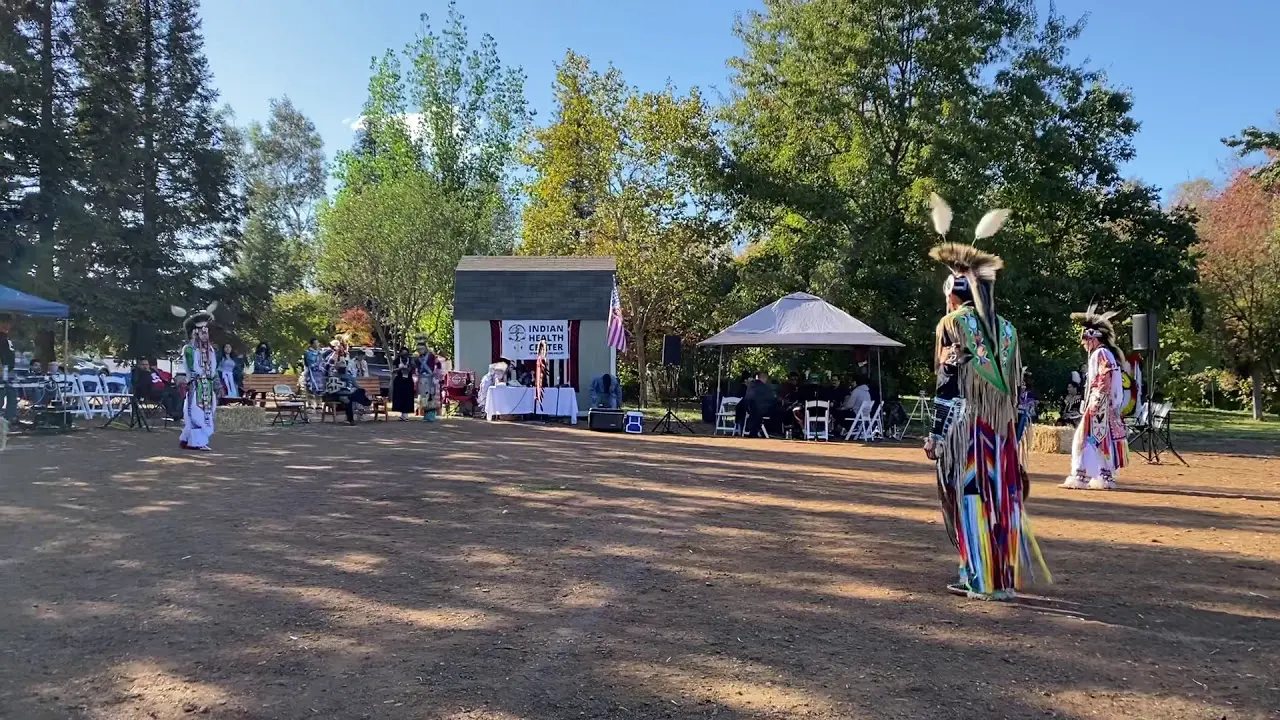
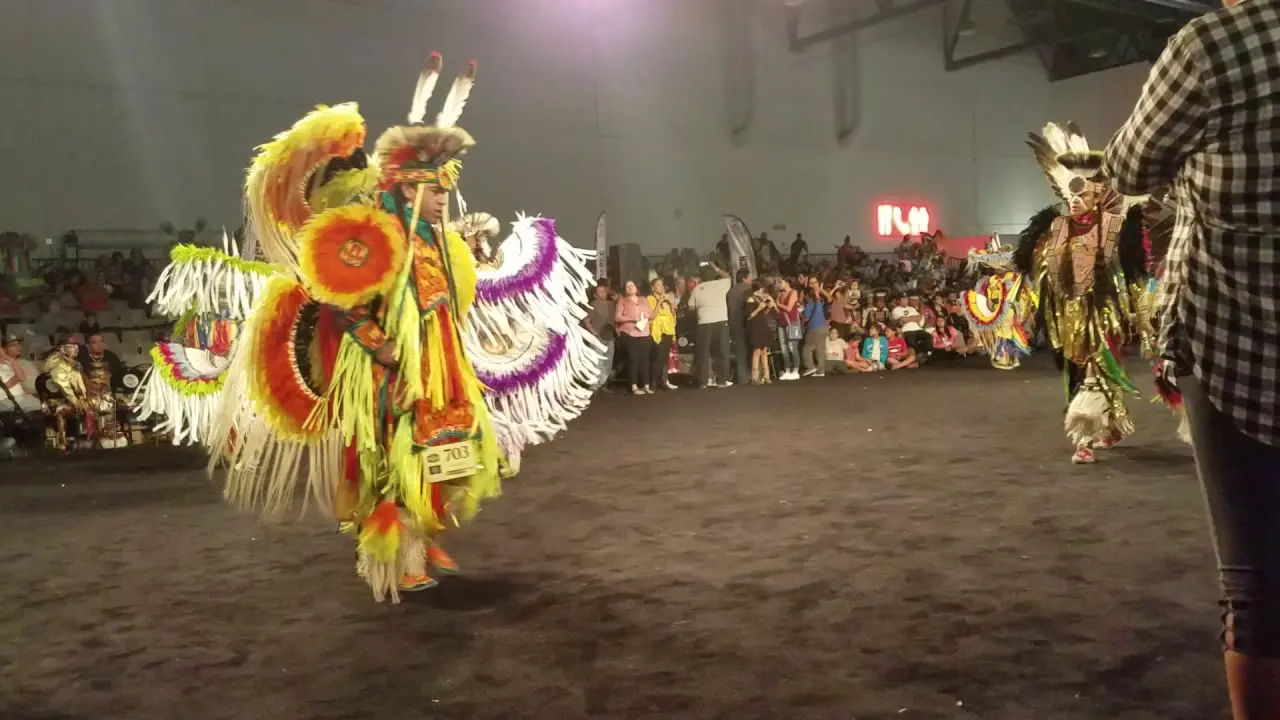
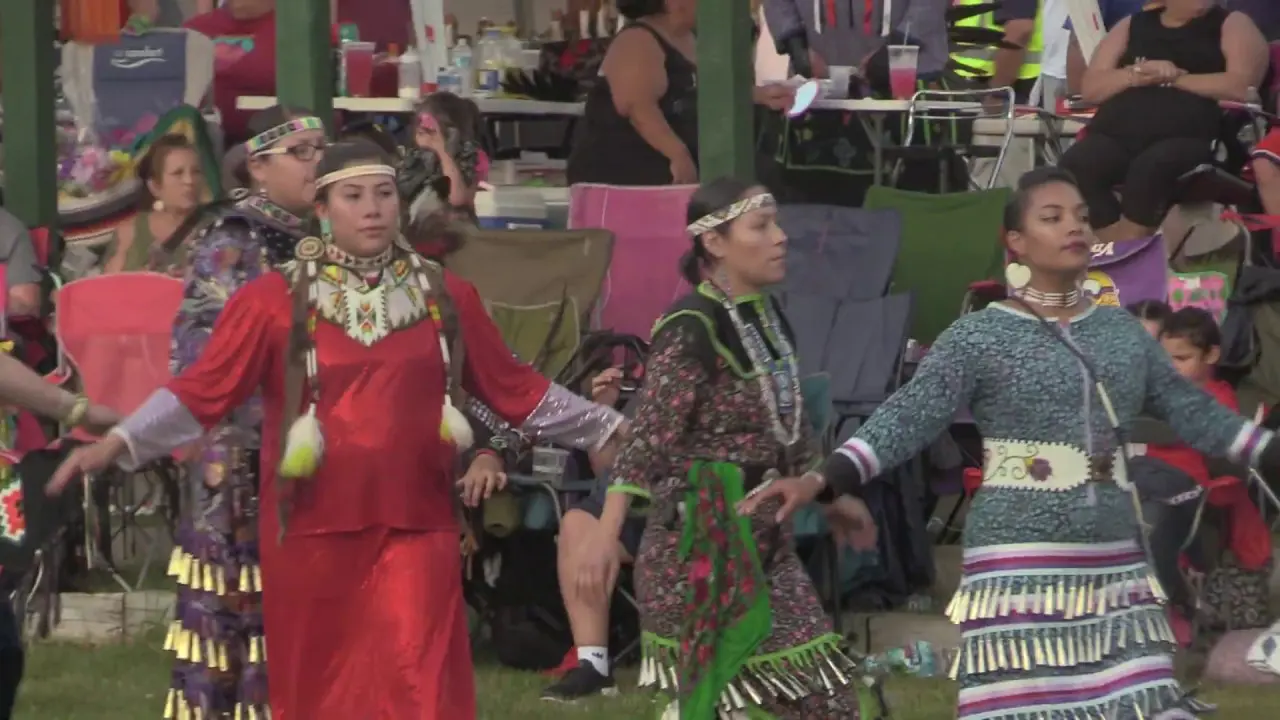
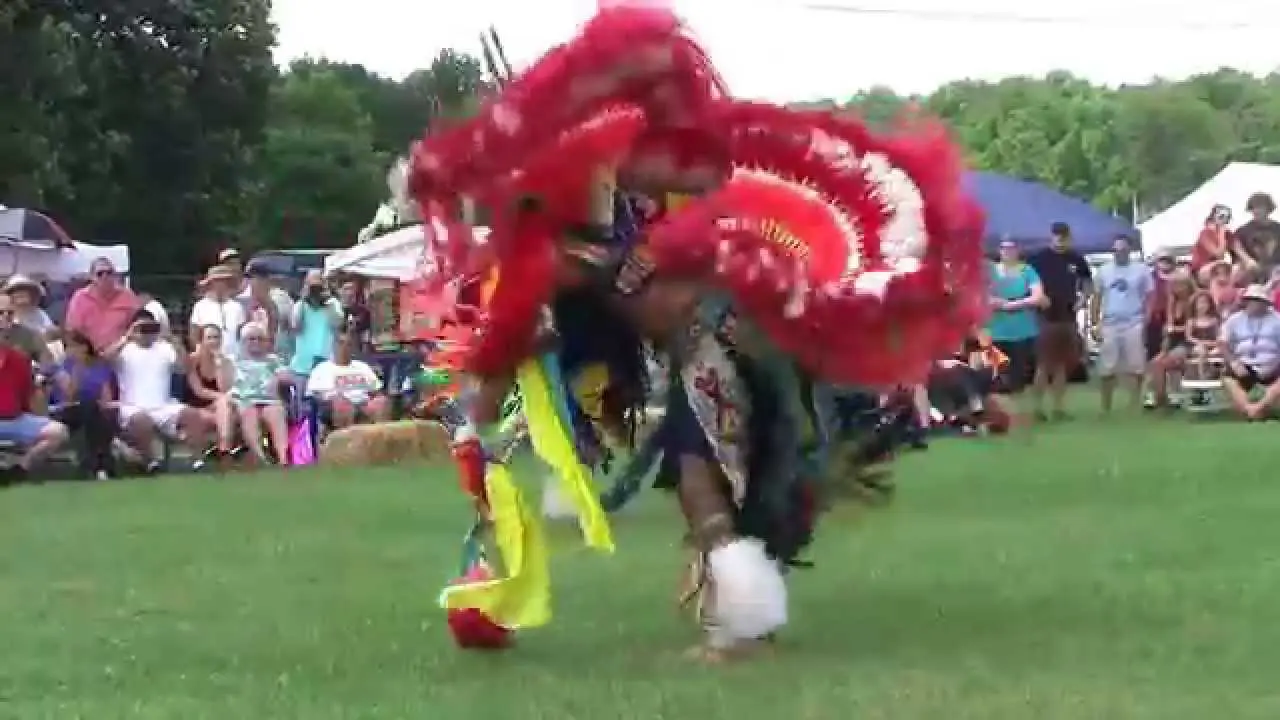
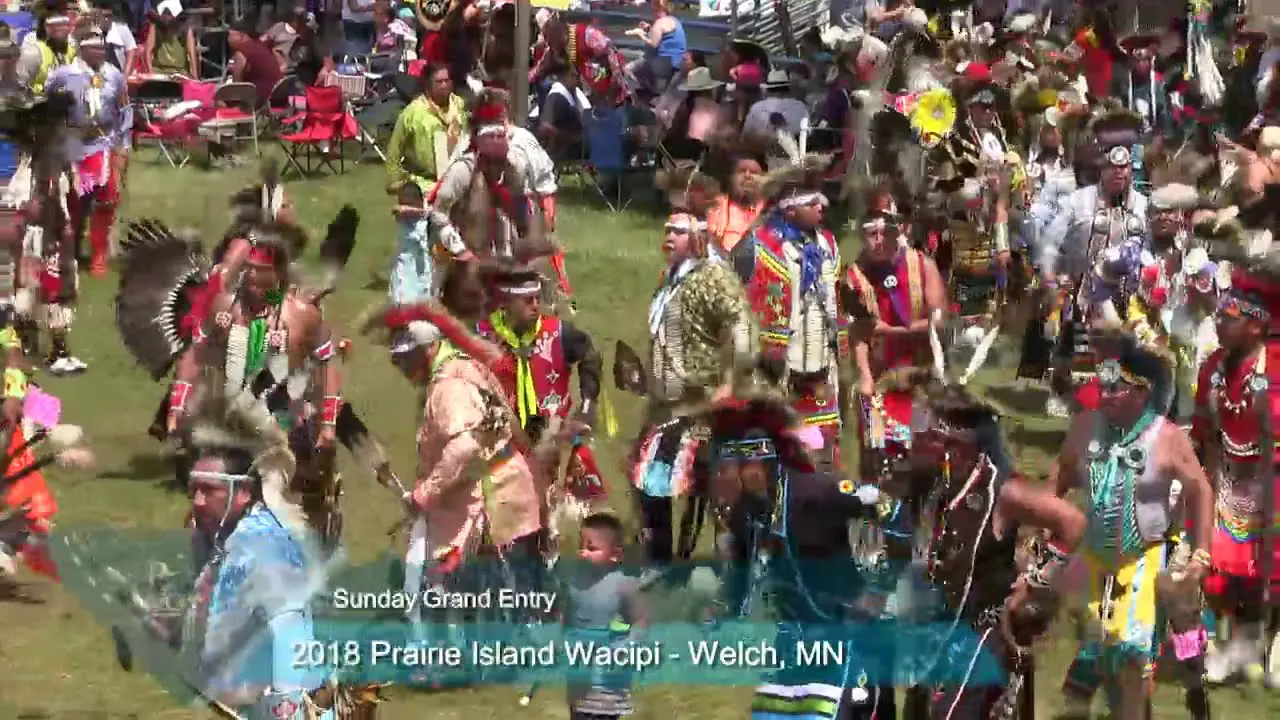
The people of Blue Lake Rancheria are committed to honoring their ancestors and preserving their unique identity.They celebrate their heritage through various cultural events, including the annual big Time celebration, which brings together tribal members and friends to share in traditional music, dance, and story-telling. Through these efforts,the Blue Lake Rancheria continues to flourish,highlighting the resilience and strength of the Wiyot people as they navigate the modern world while staying rooted in their rich cultural legacy.
tribal homelands
The Blue lake Rancheria, located in humboldt County, California, comprises the ancestral lands of the Wiyot Tribe. This area, enriched with lush forests, riverine habitats, and proximity to the pacific Ocean, holds profound spiritual and cultural significance for the Wiyot people. The rancheria itself, which encompasses approximately 100 acres, serves not only as a political and economic center but also as a beacon of cultural revitalization and community pride.
Historically, the Wiyot Tribe’s territory extended along the coastline and inland to the valleys and mountains of Northern California. The tribe engaged in lasting practices, such as fishing in the rivers, hunting in the forests, and gathering acorns and other native plants, which were vital to their diet and culture. The Blue Lake area is particularly important, as it is home to the ceremonial site of Tuluwat Island, which has been the focal point of various cultural and spiritual practices for centuries.
Recent efforts by the Blue Lake Rancheria have focused on land restoration and the revitalization of traditional practices, fostering a sense of identity and continuity among the tribal members. The tribe has invested in ecologically sustainable initiatives aimed at restoring fisheries, protecting natural resources, and enhancing habitat for native wildlife. such programs not only support environmental stewardship but also embody the tribe’s inherent connection to their lands.
Public awareness about the cultural and ancient significance of the Blue Lake Rancheria has grown, bolstered by educational programs and community engagement initiatives.These efforts play a vital role in preserving the Wiyot heritage, encouraging collaboration with local organizations, and promoting cultural understanding among visitors and residents. By sharing their story, the Blue Lake Rancheria continues to honor its past while charting a course for a sustainable and thriving future on their ancestral homelands.
Interactions With Settlers
The interactions between the Blue Lake Rancheria Tribe and settlers in California have varied considerably over time, encompassing both positive and negative elements that reflect the complex history of Native American and settler relations.
On the positive side, the blue Lake Rancheria Tribe has actively engaged in partnerships with nearby local and regional governments, fostering cooperation that benefits both the tribe and the surrounding communities. These collaborative efforts have focused on environmental stewardship, cultural preservation, and economic development. As a notable example, the tribe has developed sustainable practices in land management, protecting local flora and fauna while sharing traditional knowledge with community members and visitors alike.Additionally, through economic ventures such as the Blue Lake Casino, the tribe has contributed to the local economy, generating jobs and supporting businesses in the area. These successes exemplify how respectful partnerships can lead to mutual growth and cultural exchange.
Conversely, the historical context of settler interactions with the Blue Lake Rancheria Tribe has not been without its challenges. Like many Indigenous communities, the Blue Lake Rancheria has faced numerous struggles due to colonization and land displacement. Early settlers encroached upon traditional tribal lands, ofen leading to violent conflicts and a loss of cultural heritage. This history of displacement fostered longstanding grievances regarding land rights that persist today. While efforts have been made to address these injustices through legal channels, the quest for reparative justice continues to be a significant issue for the tribe.
In contemporary times, interactions can still be fraught with tension as the tribe navigates the complexities of modern governance, economic development, and cultural preservation.While many settlers recognize the historical injustices faced by the Blue Lake Rancheria, misunderstandings about tribal sovereignty and rights can lead to disputes. Successfully addressing these issues requires open dialog and education, aiming to bridge gaps between the tribe and the settler community.the narrative of interactions between the Blue lake Rancheria Tribe and settlers includes moments of collaboration and conflict, reflecting broader themes of resilience, adaptation, and the ongoing pursuit of reconciliation. This unique relationship underscores the importance of honoring Native American rights while fostering a spirit of cooperation and mutual understanding.
Most notable Events In Their Tribal History
The Blue Lake Rancheria, a federally recognized tribe situated in Northern California, has a rich and multifaceted history marked by resilience and cultural revival. One of the most notable events in their tribal history occurred in 1972 when the tribe successfully regained sovereignty over Blue Lake, a significant area historically tied to their ancestors. This was a pivotal moment, as the land had been unjustly taken from them in the 19th century during a time of rampant dispossession of Indigenous peoples across the United States.
The successful reclamation of Blue Lake was the result of tenacious advocacy and legal battles, culminating in a landmark agreement with the federal government and the state of California. This event not only restored a vital cultural landscape for the tribe but also symbolized a larger movement among Native American tribes to reclaim their rights and land. As part of this resurgence, the Blue Lake Rancheria embarked on extensive community development initiatives, emphasizing cultural preservation, education, and economic self-sufficiency.
Another significant milestone in Blue Lake Rancheria’s history came in 1985 with the establishment of the tribe’s first casino, the Blue Lake Casino, which became a crucial source of revenue. The casino has played an instrumental role in funding essential services and programs for the tribal community, including health care, education, and infrastructure improvements. This economic development allowed the tribe to invest in the future while fostering cultural identity and community well-being.
The tribe has also been involved in modern environmental stewardship initiatives, emphasizing the importance of sustainable practices and land management, which aligns with their traditional values of caring for the earth. This commitment to the environment has garnered attention and respect, showcasing the tribe’s dedication to protecting their natural resources for future generations.
In recent years,the Blue Lake Rancheria has made significant strides in renewable energy projects,such as the installation of solar energy systems to power tribal buildings. This initiative represents both an economic chance and a commitment to protecting the land, reflecting their heritage and stewardship of the environment.
the history of the Blue Lake Rancheria is characterized by resilience, innovation, and a deep commitment to cultural sovereignty and environmental sustainability. Their journey reflects a broader narrative of Native American tribes striving for recognition, rights, and revitalization in a modern landscape while holding steadfast to their ancestral roots.
Where Are Their Tribal Lands Now And How Were They Established
The Blue Lake Rancheria, located in Humboldt County, California, is home to the Wiyot Tribe. the tribal lands encompass approximately 70 acres situated near the community of blue lake, adjacent to the Mad river and the Pacific coastline. This area is significant not just for its natural resources but also for its cultural and historical importance to the Wiyot people.The establishment of Blue Lake Rancheria is a story of resilience and determination.In the late 1800s and early 1900s, the Wiyot people faced severe land loss due to colonization, forced assimilation, and policies aimed at eradicating their culture. The significant turning point for the tribe came in the mid-20th century when they began advocating for the return of their ancestral lands. In 1979, the federal government acknowledged the unjust treatment of Native American tribes and enacted the Indian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act.This legislation paved the way for tribes to regain control over their lands and resources.
After years of hard work, persistence, and legal battles, the Blue Lake Rancheria officially received federal recognition in 1983. This recognition enabled the tribe to establish its lands in a productive and sustainable manner. The Rancheria has as developed economic initiatives, including eco-amiable ventures, to support its community and promote environmental stewardship.
Today, the Blue Lake Rancheria is a multi-faceted enclave that not only protects its cultural heritage but also engages in sustainable development efforts. The tribe has worked to restore its connections to the land while ensuring the preservation of the Wiyot language and traditions for future generations. Through various programs and partnerships, the Blue Lake Rancheria continues to thrive, embodying the spirit of resilience that defines the Wiyot people.
Modern concerns Of The Tribe
The Blue Lake Rancheria, a federally recognized tribal government in California, faces a variety of modern concerns that underline the challenges of balancing tradition and contemporary issues. One significant area of focus is environmental sustainability. As stewards of their ancestral lands, the tribe is actively engaged in efforts to protect natural resources and promote ecological restoration. The preservation of air and water quality is paramount, particularly given the increasing threats posed by climate change and industrial pollution.
Economic development is another pressing concern for the Blue Lake Rancheria. The tribe has made strides in diversifying its economic portfolio, particularly through successful ventures in gaming and hospitality. However, there remains a strong emphasis on creating sustainable job opportunities that benefit both tribe members and the surrounding community. Initiatives include supporting local businesses and investing in training programs that equip tribal members with valuable skills.
Healthcare accessibility continues to be a critical issue for the Blue Lake Rancheria. The tribe is working to improve health services and increase access to quality medical care,especially in the face of historical disparities faced by Indigenous populations. Mental health resources,in particular,are an area where the tribe seeks to enhance offerings,recognizing the holistic connection between cultural identity and overall well-being.Moreover, cultural preservation is a vital concern for the Blue Lake Rancheria as younger generations engage with modern society. The tribe actively promotes educational programs that teach traditional practices and languages, aiming to ensure that cultural identity remains robust amid external pressures. This commitment to cultural heritage fosters a sense of community and belonging among tribe members, bridging the gap between their historic roots and contemporary lives.
Lastly, social issues such as housing and food security are prevalent in the Blue Lake Rancheria community. The tribe is exploring innovative solutions to address lack of adequate housing and to promote food sovereignty through community gardens and local agricultural projects.These initiatives aim to not only provide immediate relief but also empower tribe members in managing their resources sustainably.
Navigating these modern concerns while embracing their rich heritage remains a priority for the Blue Lake Rancheria, reflecting a dynamic relationship between past traditions and future aspirations.
Events And Other Social And Political Activities
The Blue Lake Rancheria, a federally recognized tribe in Northern California, actively engages in a range of social, cultural, and political activities that promote the well-being of its members and strengthen community ties. One of the tribe’s notable events is the annual Blue Lake Rancheria Celebration, which brings together tribal members and the wider community for a day of traditional music, dance, and local cuisine. This festive occasion not only showcases the tribe’s rich cultural heritage but also fosters a sense of unity among residents.
In addition to cultural celebrations, the Blue Lake Rancheria is deeply involved in local environmental initiatives. The tribe has made significant strides in sustainable practices, often participating in and hosting events that focus on habitat restoration and the protection of natural resources. Their commitment to environmental stewardship can be seen through programs aimed at preserving local ecosystems, including coastal wetlands and forests.
Politically, the Blue Lake Rancheria exercises its sovereignty with a focus on self-determination and tribal governance. The tribe engages in advocacy work at both state and federal levels, actively participating in discussions about land rights, healthcare access, and gaming regulations. This engagement ensures that the voices of tribe members are heard and that their interests are represented in broader policy decisions.
furthermore, the Blue Lake Rancheria places a strong emphasis on education and youth empowerment. The tribe runs several programs designed to provide educational resources and scholarship opportunities to its youth, thereby ensuring the next generation is well-equipped for future leadership roles. educational events, workshops, and partnerships with local schools play a pivotal role in this mission.
Through these diverse activities—cultural celebrations, environmental efforts, political advocacy, and educational programs—the Blue Lake Rancheria continually works to uplift its community, protect its resources, and honor its heritage. The tribe’s proactive stance ensures that its values and traditions not only survive but flourish in a modern context.