The Elk Valley Rancheria is a Native American tribe located in the picturesque region of Northern California, nestled within Del Norte County. With a history deeply rooted in the cultural heritage and traditions of the indigenous people of this area, the Elk Valley Rancheria represents a vibrant community that has persevered through challenges and changes over the centuries. The tribe is composed primarily of members from the Yurok and Tolowa tribes, who have historically thrived in the lush landscapes of the Pacific Northwest.
Incorporating both conventional practices and modern innovations,the Elk Valley Rancheria is committed to preserving its rich cultural identity while fostering economic development and community well-being. The tribe operates various enterprises, including a successful casino that not only generates revenue but also provides essential services and jobs for its members.
As stewards of the land, the Elk Valley Rancheria emphasizes the importance of sustainability and environmental conservation, ensuring that future generations can enjoy the natural beauty that surrounds them. With a focus on education, cultural preservation, and community health, the Elk Valley Rancheria serves as a powerful testament to the resilience of Native American communities.
In this article, we celebrate the history, culture, and ongoing efforts of the Elk Valley Rancheria, highlighting its meaning within the broader context of California’s indigenous tribes and their contributions to the rich tapestry of American heritage.
Origin Of The People
The Elk Valley Rancheria tribe, located in California, is comprised of the descendants of the indigenous people native to the region, primarily the Yurok and the Tolowa tribes. The history of these tribes stretches back thousands of years, long before European contact. The Yurok people primarily inhabited the northern coastal areas along the Klamath River, while the Tolowa lived along the Pacific Coast, particularly around the Smith River and its tributaries.
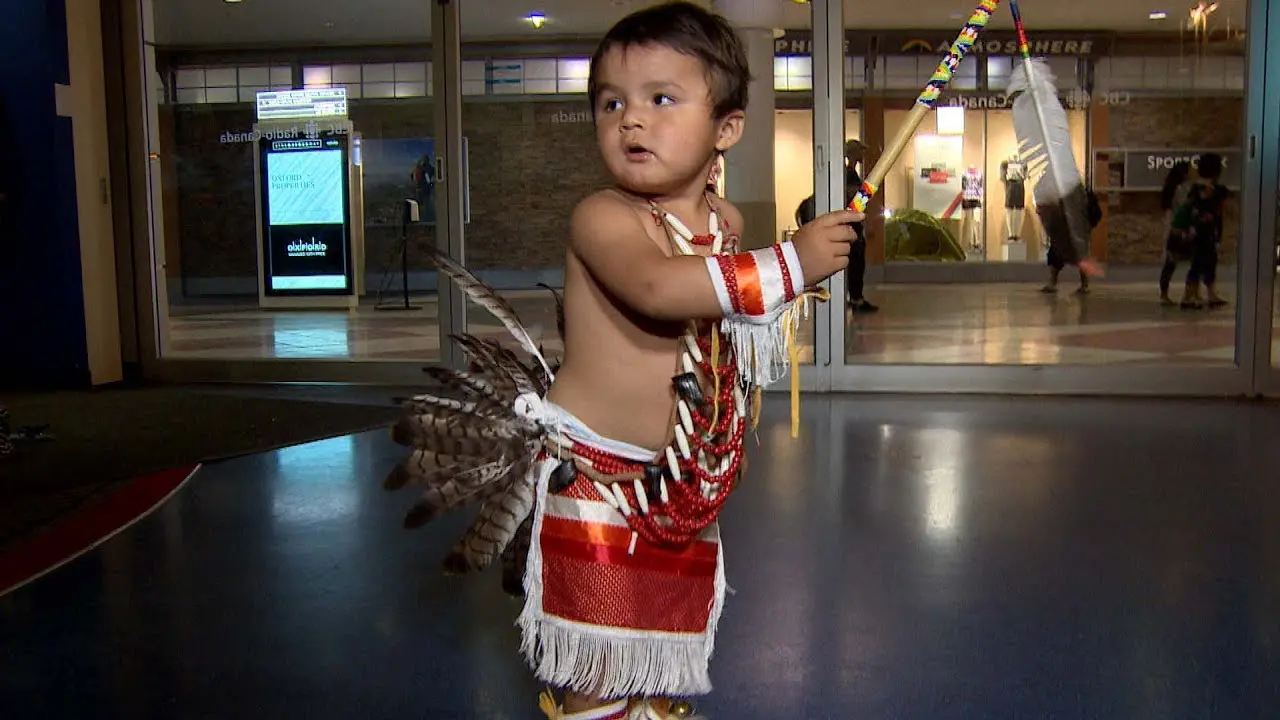
The blending of these tribes over the centuries led to a rich cultural tapestry that is evident in the traditions, languages, and practices of the Elk Valley Rancheria today. Cultural practices such as basket weaving, fishing, and the festivity of traditional ceremonies play a vital role in preserving their identity. The Elk Valley Rancheria community places a strong emphasis on the ancestry of their people, drawing from both Yurok and Tolowa roots to foster a sense of belonging and continuity.
Colonization brought significant challenges to the Elk Valley Rancheria, including loss of land, disruption of traditional lifestyles, and attempts to erase their cultural practices. However,the resilience of the Elk Valley people has allowed them to navigate these challenges. The establishment of the Elk Valley Rancheria in the late 20th century marked a resurgence of cultural pride and sovereignty, enabling the tribe to engage in self-determination and restore elements of their heritage.
Today, the Elk Valley Rancheria is actively involved in community empowerment initiatives, educational programs, and cultural revitalization efforts. These endeavors not only honor their lineage but also create pathways for future generations to connect with their rich past while adapting to the contemporary world. By emphasizing their unique heritage and fostering a strong community spirit, the Elk Valley Rancheria tribe continues to thrive as a vibrant and essential part of California’s indigenous landscape.
Tribal Homelands
The Elk Valley Rancheria is home to the Elk Valley Tribe,a federally recognized Native American tribe located in the picturesque region of Del Norte County,California. The tribal homelands span approximately 90 acres near the town of Crescent City, bordered by the stunning Pacific Ocean to the west and the lush forests of the redwood region to the east. This unique geography not only provides breathtaking views but also supports a diverse ecosystem that is integral to the tribe’s cultural and spiritual traditions.
The Elk Valley Rancheria’s historical territory encompasses traditional lands used for fishing, hunting, and gathering, which are vital to the tribe’s way of life. The nearby Smith River, renowned for its salmon runs, represents one of the tribe’s key resources, allowing them to engage in time-honored fishing practices that have sustained their community for generations. The tribe also emphasizes lasting land stewardship, honoring their ancestral connections to the environment and ensuring the preservation of natural resources for future generations.
Cultural activities based on traditional knowledge and practices are woven deeply into the fabric of the Elk Valley Rancheria’s identity. The tribe actively participates in celebrating their rich heritage through various events, art, and storytelling. The preservation of the Yurok language,music,and crafts reinforces their connection to the past and strengthens community bonds.
Moreover, the Elk Valley Rancheria works to maintain relationships with neighboring tribes, fostering a spirit of cooperation and mutual support.By collaborating on environmental stewardship projects, cultural events, and educational initiatives, the tribe plays a vital role in the broader Native American community in Northern California.
As environmental and social changes impact their homelands, the Elk Valley Tribe remains committed to resilience and adaptation, continually looking to honor their ancestors while navigating modern challenges. Through active engagement and a strong sense of identity,the Elk Valley Rancheria not only strives to protect their homelands but also enriches the cultural landscape of California’s Native American tribes.
Interactions With Settlers
The Elk Valley Rancheria tribe, located in California, has experienced a complex history of interactions with settlers that reflect both positive and negative aspects.Positive engagement frequently enough revolved around cooperative ventures and cultural exchange. As an example,the Elk Valley Rancheria has historically participated in community-building initiatives,which fostered goodwill between the tribe and local settlers. These collaborations included shared events, educational programs, and joint environmental projects aimed at preserving the natural landscape, a key element of the tribe’s heritage.
On the other hand,negative interactions have often stemmed from misunderstandings and conflicts over land use and resource management. As settlers expanded their agricultural and industrial activities, the Elk Valley Rancheria faced encroachments on their traditional territories. These challenges not only disrupted their way of life but also led to a loss of cultural practices tied to the land. Historical accounts detail tensions over water rights and timber resources, illustrating how the quest for economic development frequently enough clashed with the tribe’s need to maintain sustainable practices.
Despite these challenges,the Elk Valley Rancheria has shown remarkable resilience. The tribe has worked to assert its rights and reclaim its heritage, engaging in legal battles to secure land and protect sacred sites. This journey showcases the tribe’s commitment to preserving its identity while navigating the complexities of modern relationships with settlers. In recent years,there has been a growing movement towards reconciliation,with both the Elk Valley Rancheria and local communities seeking to acknowledge past grievances and build a more inclusive future.
By recognizing the multifaceted nature of these interactions, one can better appreciate the Elk Valley Rancheria’s ongoing efforts to celebrate its culture, reclaim its land, and foster positive relationships in the face of historical challenges.
Most Notable Events In Their Tribal History
The Elk Valley Rancheria, located in Del Norte County, California, is home to a rich history that reflects the resilience and cultural heritage of the Tolowa people. One of the most notable events in their tribal history occurred in the mid-19th century, during the California Gold Rush. The influx of settlers and miners into Northern California led to significant disruptions in the life of the Tolowa. Their traditional lands were encroached upon, and they faced numerous challenges, including loss of resources and exposure to diseases.In 1955, the federal government officially recognized the Elk Valley Rancheria, granting them a small parcel of land, which became a sanctuary for the Tolowa people.This recognition was a crucial step towards restoring some sovereignty and providing a foundation for cultural revitalization. The tribe worked tirelessly to secure their rights and preserve their traditional practices amid ongoing pressures from the surrounding non-Native communities.Another significant event was the return of the tribal governance in the late 20th century. After years of termination policies that sought to dissolve tribal identities,the Elk Valley Rancheria began to rebuild its governance structure and community programs. This revival was marked by the establishment of the Elk Valley Rancheria Tribal Council, which focused on fostering economic development and improving social services for tribal members.
In recent years, the tribe has engaged in partnerships to promote ecological stewardship and sustainable practices in the region. They have taken an active role in restoring habitats and protecting their ancestral lands, demonstrating a commitment to both cultural and environmental preservation. Notably, the tribe’s efforts to revitalize the traditional language and cultural ceremonies reflect a broader movement towards healing and reconnection among the Tolowa people.
The Elk Valley Rancheria continues to celebrate its history and cultural identity through various modern initiatives while facing contemporary challenges. The resilience displayed through their efforts to uphold traditions and strengthen community bonds serves as an inspiring testament to the spirit of the Elk Valley Rancheria and its people.
Where Are Their Tribal Lands Now And How Were They Established
The Elk Valley Rancheria, located in Del Norte County, California, represents the ancestral lands of the Elk Valley Tribe, primarily composed of the Tolowa Dee-ni’ people. These tribal lands cover an area roughly encompassing 8.5 acres near Crescent City, California, strategically positioned near the Pacific coastline and bordering the lush landscapes of the Redwood National Forest.
The establishment of the Elk Valley Rancheria as a federally recognized tribe came about through a series of historical events and legal efforts. In 1983, the Elk Valley Rancheria submitted an application for federal recognition, asserting their enduring connection to their ancestral territory. After rigorous investigations and documentation of their historical ties and cultural practices, the tribe achieved federal recognition in 1987, affirming their rights to govern their land and participate in economic development initiatives.
The Elk Valley Rancheria’s property has been instrumental in supporting the tribal government and engaging in community development projects.Over the years, the tribe has utilized its land for various purposes, including cultural preservation, social services, and economic opportunities such as the establishment of a casino to generate revenue for community projects. Through focused efforts on land restoration and cultural revitalization, the Elk Valley Rancheria continues to strive for a sustainable future while honoring the traditions and heritage of the Tolowa Dee-ni’ people.
Modern Concerns Of The Tribe
The Elk Valley Rancheria Tribe,located in California,faces several modern concerns that intertwine cultural preservation,economic development,and environmental sustainability. One of the tribe’s primary focuses is on safeguarding their ancestral lands and natural resources. As the effects of climate change become increasingly prominent, issues such as water scarcity and habitat loss have emerged, threatening both the ecosystem and the tribe’s traditional ways of life.
In recent years, the Elk Valley Rancheria has prioritized economic development initiatives to create sustainable revenue streams for their community. The tribe operates a successful casino and other enterprises, which not only provide jobs for tribal members but also contribute to the local economy. However, balancing economic growth with cultural integrity remains a significant concern. Community leaders are dedicated to promoting initiatives that respect their heritage while embracing modern economic opportunities.Education is another critical focus for the Elk Valley Rancheria. The tribe emphasizes the importance of providing quality educational resources and support for its youth, fostering a sense of identity and pride in their Native American heritage. Programs aimed at teaching traditional crafts, language, and history are essential for cultivating a deeper understanding of their culture among younger generations.Furthermore, as tribal sovereignty continues to evolve, the Elk Valley Rancheria actively engages in discussions around legal and political matters that impact their rights and resources. This includes navigating complex relationships with state and federal government entities to ensure their interests are represented. The tribe’s commitment to advocacy extends to collaborating with other tribes and organizations to protect their collective rights.
Health and wellness are also paramount concerns, especially in light of the ongoing challenges posed by the pandemic and related public health issues. Ensuring access to healthcare services and mental wellness support for tribal members is vital for their overall well-being. The Elk Valley Rancheria is working on programs that promote healthy lifestyles, addressing both physical and mental health in culturally responsive ways.the modern concerns of the Elk Valley Rancheria revolve around the dual goals of preserving their rich cultural heritage while navigating the challenges of contemporary life. Their commitment to sustainability, education, economic development, and advocacy exemplifies their resilience and dedication to thriving as a community in today’s world.
Events And Other Social And Political Activities
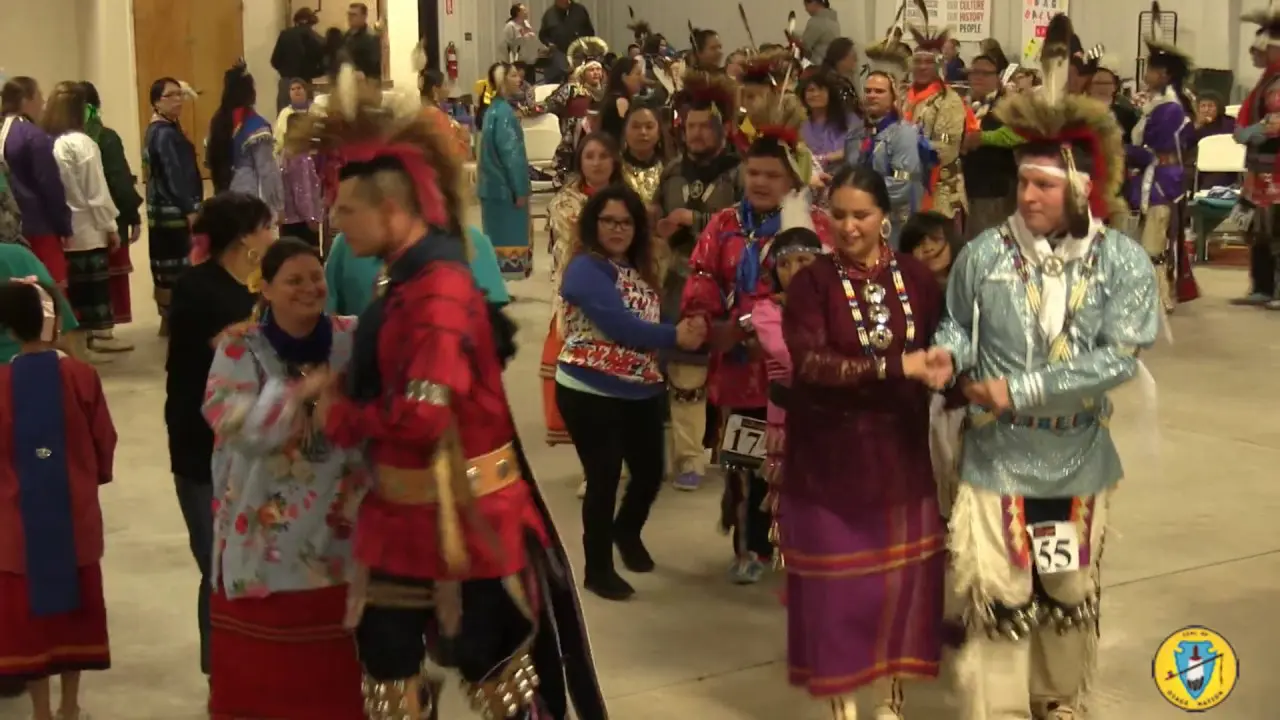
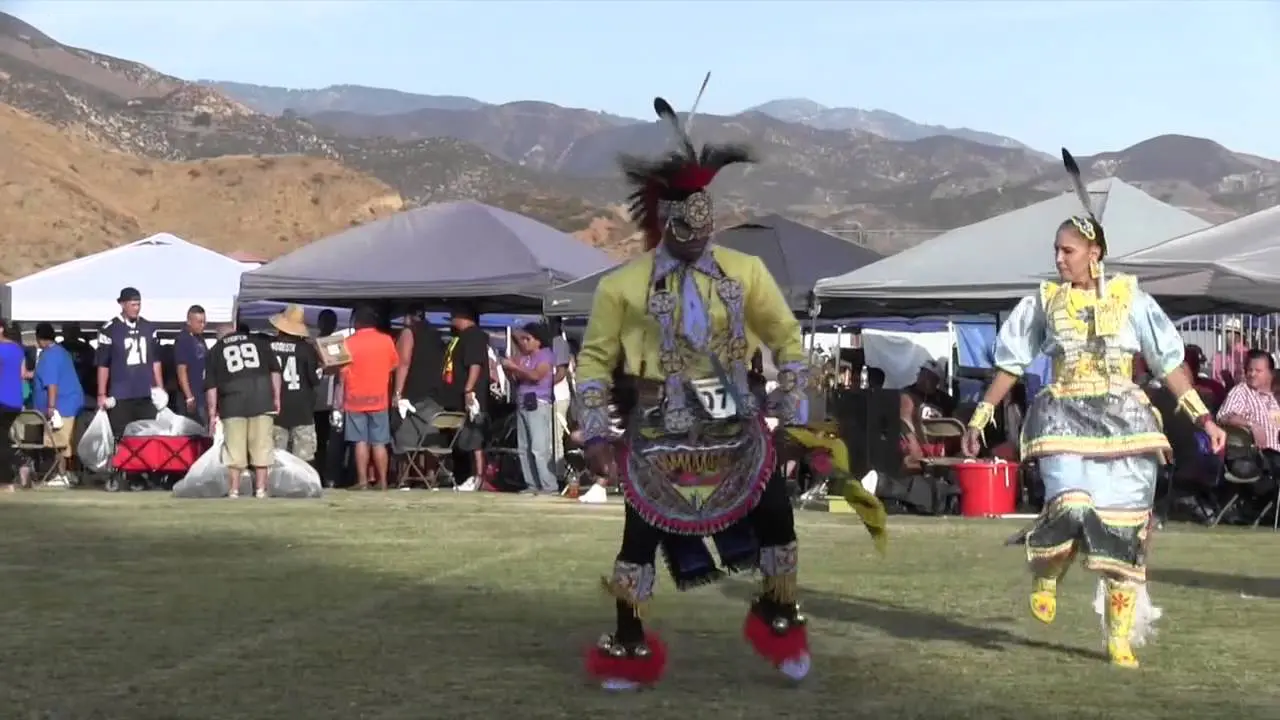
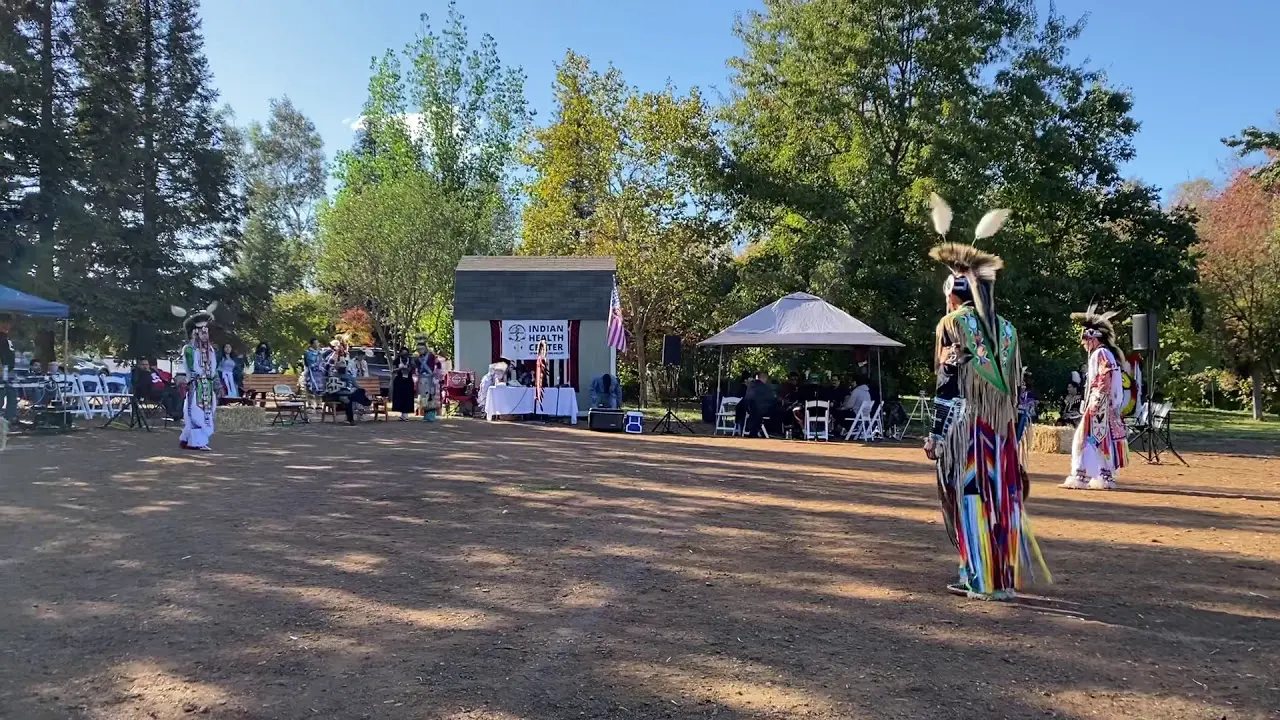
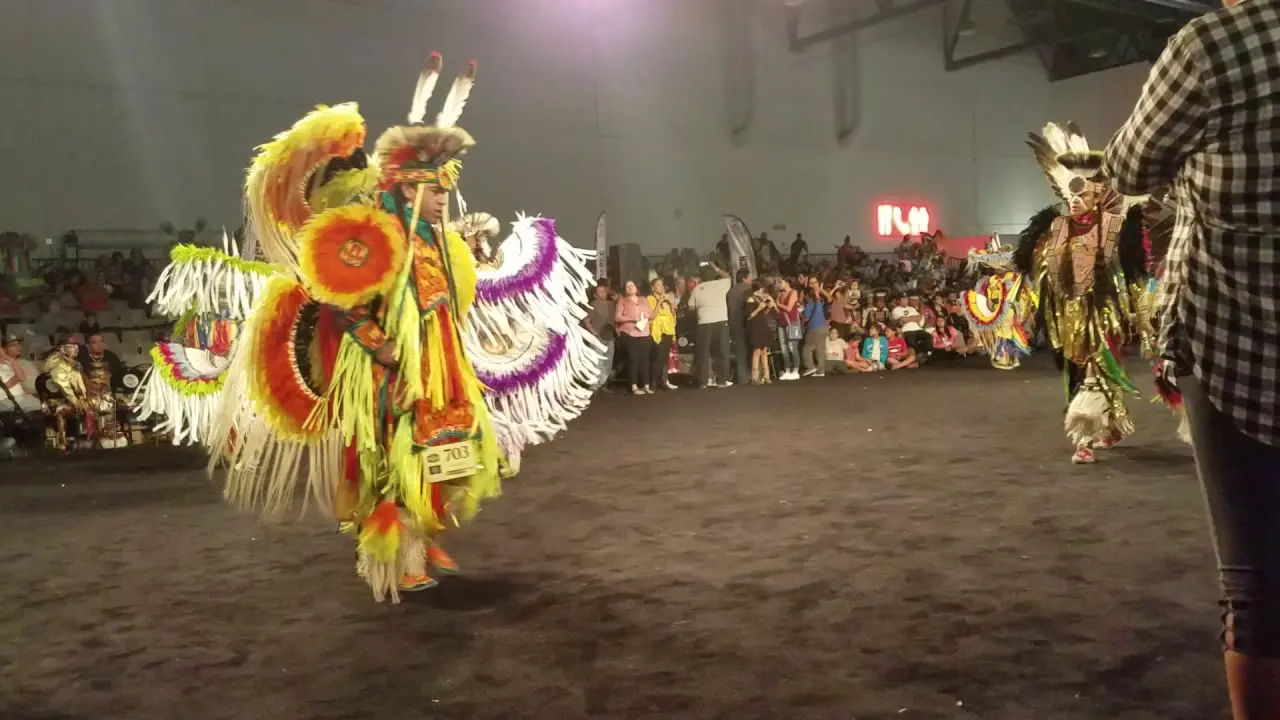
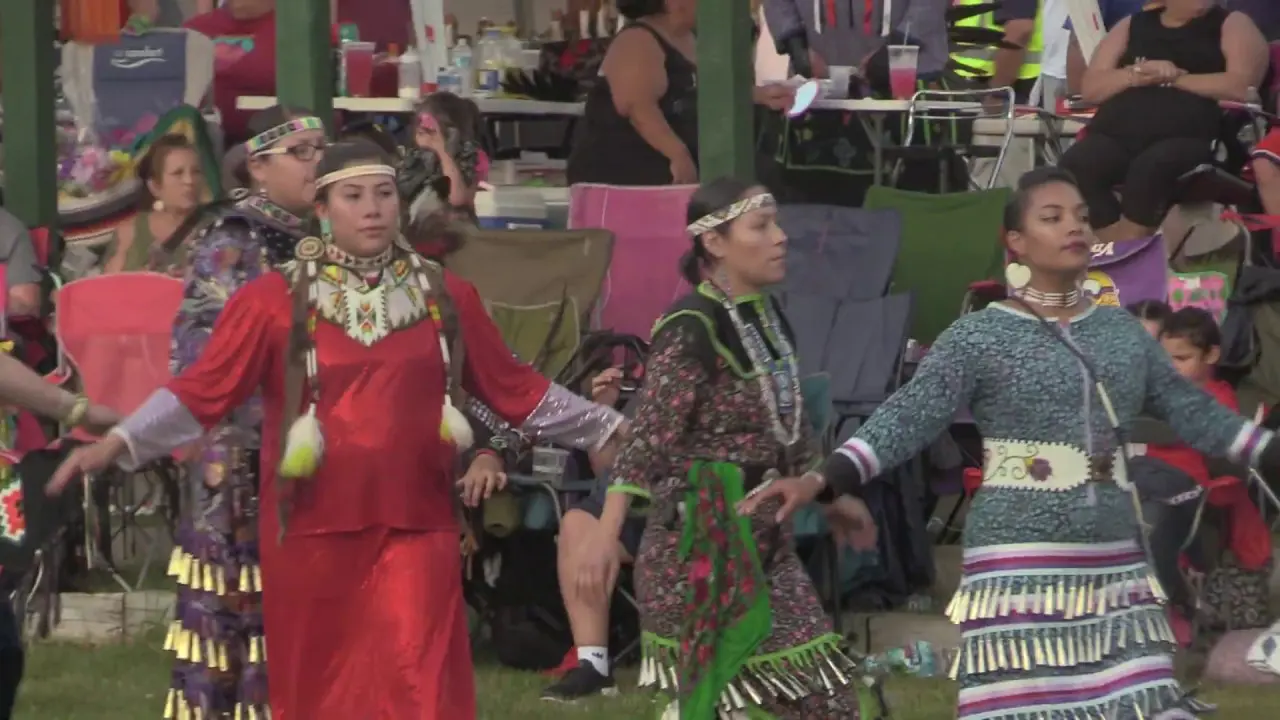
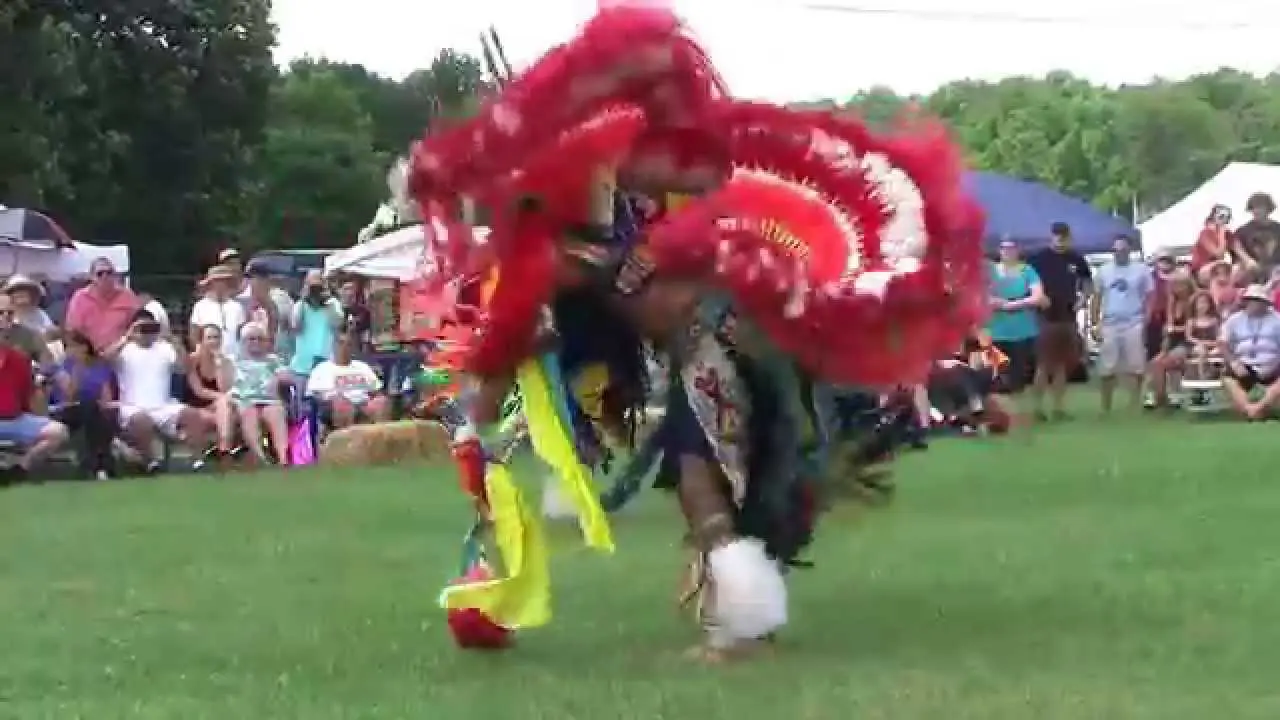
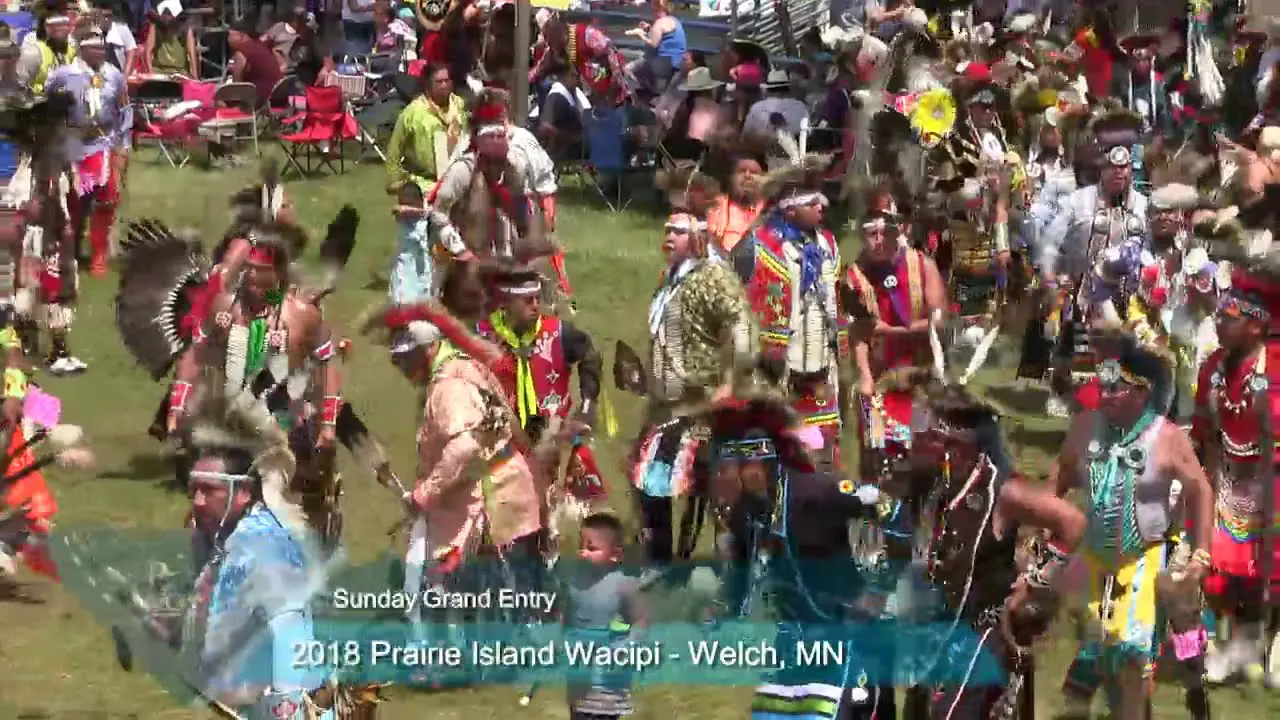
The Elk Valley Rancheria, located in California, actively engages in a variety of events and social activities that foster community spirit and cultural heritage. One of the tribe’s hallmark events is the annual Elk Valley Rancheria Pow Wow, which serves as a gathering point for tribe members, allies, and visitors. This vibrant celebration features traditional Native American dance competitions, authentic tribal music, and a showcase of indigenous crafts and foods. The pow wow not only promotes cultural awareness but also enhances community bonds among members and tribal descendants.
Along with ceremonial events,the Elk Valley Rancheria is deeply involved in social initiatives that prioritize the well-being and education of its members. The tribe organizes youth programs that emphasize cultural preservation, leadership skills, and environmental stewardship.These programs often include workshops,field trips,and mentoring opportunities that empower young tribal members to take pride in their heritage while equipping them with essential life skills.
Politically, the Elk Valley Rancheria is active in advocating for tribal sovereignty and the rights of indigenous peoples. Members participate in regional and national conferences aimed at addressing key issues such as land rights, environmental protection, and health care access.The tribe works closely with various stakeholders, including government agencies and other tribal organizations, to ensure that their voice is heard in decision-making processes that affect their community.
The Elk Valley Rancheria also engages in outreach activities that connect them with the broader community. They often host open forums, health fairs, and cultural workshops that invite participation from non-tribal members, fostering greater understanding and gratitude of Native American cultures. These initiatives serve to break down barriers and promote dialogue around shared values and commitments to social justice.
Through these events and activities, the Elk Valley Rancheria not only celebrates its rich cultural heritage but also actively contributes to the ongoing dialogue about indigenous rights and community wellness. Whether through pow wows, educational programs, or advocacy efforts, the tribe’s commitment to its members and to the surrounding community is evident.