Introduction to the Mohegan Tribe of Indians of Connecticut
The Mohegan Tribe of Indians of Connecticut, a vibrant and resilient Native American community, has a rich history that spans centuries. Originally part of the Pequot Confederacy, the Mohegan people have maintained their identity and cultural traditions despite facing numerous challenges over the years, including colonization and displacement. Nestled in the picturesque Connecticut River Valley, the Mohegan Tribe’s ancestral homeland is steeped in stories that reflect their deep connection to the land and their enduring spirit.
Today, the Mohegan Tribe operates a successful gaming and entertainment enterprise, with the renowned Mohegan Sun resort leading the way. This thriving establishment not only plays a pivotal role in Connecticut’s economy but also serves as a cultural hub that showcases the tribe’s heritage through art, performances, and educational programs. The Mohegan Tribe is dedicated to preserving their history and sharing their culture, ensuring that future generations have the opportunity to learn about their ancestry.
In this introduction, we will explore the captivating history of the Mohegan Tribe, its meaningful contributions to contemporary society, and the ongoing efforts to protect and promote their rich cultural legacy. Join us on a journey to discover the vibrant world of the Mohegan people,a tribe that continues to honor its past while looking forward to a promising future.
Origin Of The People
The Mohegan Tribe of Indians of Connecticut has a rich and complex history rooted in the ancient landscapes of New England. Traditionally, the Mohegan people descended from the Pequot Tribe, but over the centuries, they evolved into a distinct tribe marked by their unique cultural practices, language, and governance. The Mohegan people inhabited the region that is now southeastern Connecticut, where they relied on agriculture, fishing, and hunting for sustenance.
Archaeological evidence suggests that the Mohegan ancestors lived in the area for thousands of years, cultivating the land and forming intricate social structures. They spoke the Pequot language, part of the Algonquian linguistic family, which connected them to other Indigenous groups in the northeastern United States. The Mohegan’s skilled use of the natural surroundings allowed them to thrive in their territory, characterized by rivers, forests, and rich fertile soil.
The 17th century marked a significant turning point in the Mohegan’s history, as European colonization brought monumental challenges. Facing conflicts with English settlers and rival tribes, the Mohegan engaged in strategic alliances, notably during the Pequot War in 1637, where they allied with the English to defeat the Pequot Tribe. This pivotal moment in history not only altered the power dynamics of the region but also established the Mohegan Tribe as a significant political force in colonial New England.
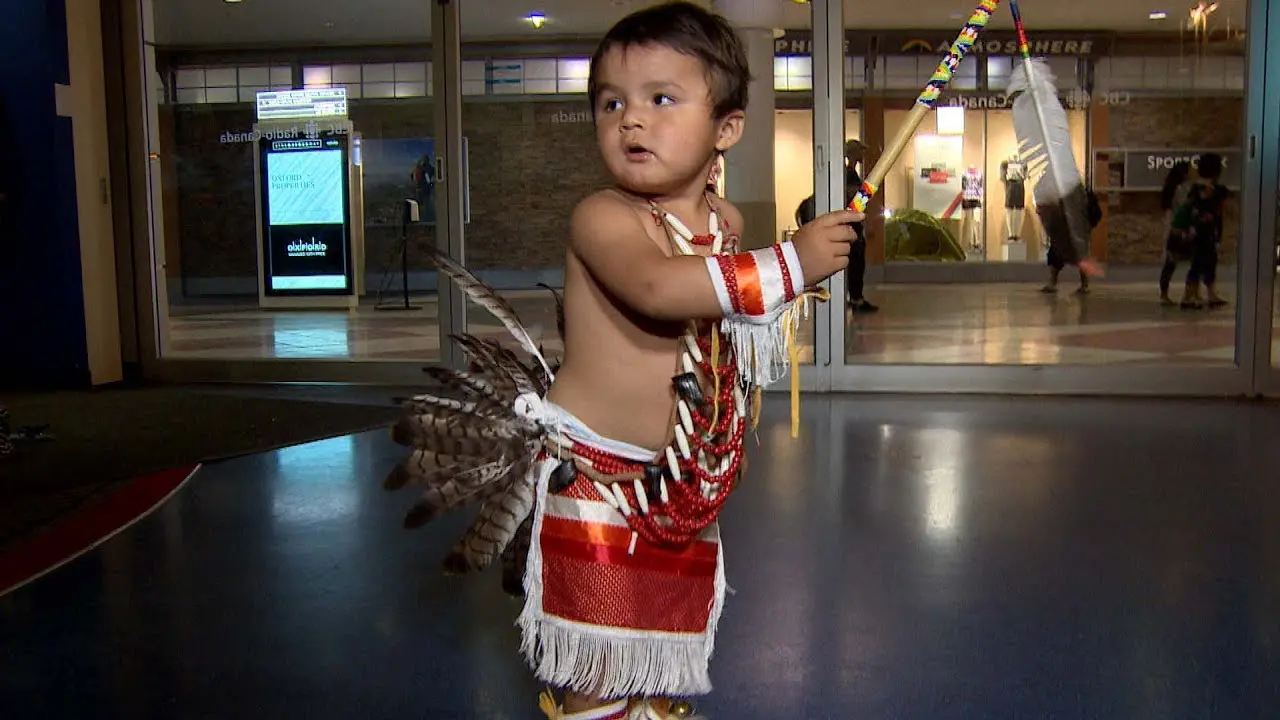
Throughout the years, the Mohegan people have preserved their cultural identity, engaging in conventional practices such as storytelling, drumming, and ceremonial dances that reflect their deep connection to the land and their ancestors. The tribe’s governance structure has adapted over time, with the establishment of a formal tribal government recognized today, emphasizing self-determination and the preservation of Mohegan heritage.
The Mohegan Tribe of Indians of Connecticut is also known for its significant contributions to modern society, particularly through the establishment of the Mohegan Sun, one of the largest and most successful gaming and entertainment venues in the United States. This development has not only provided economic opportunities for the tribe but also facilitated cultural outreach and preservation efforts aimed at educating the public about Mohegan history and culture.
the origins and enduring legacy of the Mohegan Tribe of Indians of Connecticut highlight a story of resilience, adaptation, and cultural pride, as they strive to maintain their identity while navigating the complexities of contemporary life.
Tribal Homelands
The Mohegan Tribe of Indians of Connecticut has a deep-rooted connection to their ancestral homelands, which are situated in the southeastern region of the state. Historically, the Mohegan people inhabited a vast territory that extended along the Thames River and into the surrounding forests and waterways. This land was not only vital for their survival through agriculture,fishing,and hunting,but it also held sacred meaning,with numerous sites considered crucial to their cultural and spiritual practices.
Today, the Mohegan Tribe is located primarily in Montville, Connecticut, where they have established a notable presence.One of the standout features of their homeland is the Mohegan Sun, a world-renowned resort and casino that has become a focal point for economic development and cultural engagement. This facility serves not just as a revenue generator, but also as a venue for showcasing Mohegan history and traditions through events, exhibits, and performances.
The tribe’s commitment to preserving their heritage is evident in their efforts to educate both tribal members and the broader public about the Mohegan people’s history, language, and customs. The Mohegan Cultural Preservation Program plays a vital role in revitalizing traditional practices and ensuring that the stories of their ancestors are passed down through generations. The connection to their land is celebrated in community events, traditional ceremonies, and through the ongoing reclamation of tribal lands.
Ecologically, the Mohegan homelands are rich in resources and biodiversity. The tribe is dedicated to environmental stewardship, engaging in conservation initiatives that protect and sustain the natural habitat they have inhabited for centuries. These efforts not only preserve the ecosystem but also reinforce the Mohegan’s connection to the land, embodying their identity as stewards of the earth.
Through cultural programs, language revitalization efforts, and community engagement, the Mohegan Tribe of Indians of Connecticut continues to honor the significance of their tribal homelands, weaving their heritage into the fabric of modern society while steadfastly looking to the future.
Interactions With Settlers
The interactions between the Mohegan Tribe of Indians of Connecticut and European settlers were complex and multifaceted,marked by both positive and negative experiences that shaped the tribe’s history.
On the positive side, the Mohegan Tribe initially welcomed European settlers in the early 17th century. The tribe engaged in trade with the newcomers, exchanging goods such as furs for European tools, weapons, and cloth. This interaction brought about new opportunities for economic growth and diversification for the Mohegan people. As skilled traders, the Mohegans capitalized on their strategic location along the Connecticut River, facilitating commerce between different European and Indigenous groups. Additionally, intermarriages between the Mohegan and settler communities fostered relationships that sometimes resulted in mutual support systems.
However, these interactions were not solely beneficial. As European settlement expanded, the Mohegan Tribe faced numerous challenges, including land dispossession and cultural disruption. Treaties were often misunderstood or manipulated,leading to significant loss of territory. The Pequot War in 1637 marked a turning point, as the Mohegan sided with English settlers against the Pequot tribe, altering alliances and intensifying conflicts between Indigenous groups. The settlers’ growing demand for land led to increased pressure on the Mohegan people and their resources. Diseases brought by Europeans, to which the Mohegans had no immunity, decimated their population, disrupting traditional ways of life and reducing their ability to resist encroachment.
The overall dynamic of the relationship between the Mohegan Tribe and settlers was characterized by a blending of cooperation and conflict. While the early encounters facilitated economic and cultural exchanges, the later stages led to significant displacement and struggles for sovereignty that continue to resonate in contemporary discussions about Indigenous rights and land reclamation. Understanding these historical interactions provides crucial insights into the identity and resilience of the Mohegan Tribe today.
Most Notable Events In Their Tribal History
The history of the Mohegan Tribe of Indians of Connecticut is rich and deeply intertwined with pivotal events that have shaped their identity and resilience. One of the most notable events in their tribal history occurred in the early 17th century with the arrival of European settlers, which marked the beginning of significant cultural changes and challenges for the Mohegan people.
In 1636, the Mohegan leader Uncas emerged as a critical figure during the Pequot War, a devastating conflict between the Pequot tribe and an alliance of English settlers and various Indigenous tribes, including the Mohegans. Uncas’s alliance with the English not only solidified his leadership but also positioned the Mohegan Tribe favorably in the region. As a consequence of the war, the Pequot tribe was greatly diminished, allowing the Mohegans to expand their territory and influence.
Another defining moment in Mohegan history occurred in 1786 when the tribe faced the challenge of colonial encroachment and legal disputes over their land. The Mohegans took significant legal action, culminating in the landmark case of “Mohegan Tribe v. Connecticut” in the 1970s. This case enabled the Mohegan Tribe to reclaim their sovereignty and assert their rights, leading to the establishment of a formal federal recognition in 1994.
The late 20th century brought about a significant economic turnaround for the Mohegan Tribe with the opening of the Mohegan Sun resort and casino in 1996.This venture not only provided economic stability and opportunities for tribal members but also positioned the Mohegan Tribe as a prominent player in the gaming industry. The success of Mohegan Sun has been instrumental in funding cultural revitalization efforts and community programs, enabling the tribe to preserve its heritage while embracing modernity.Additionally, the Mohegan Tribe has been active in efforts to preserve their language and cultural practices. The establishment of educational programs focused on Mohegan history and culture plays a critical role in empowering younger generations to connect with their heritage. Recent collaborations with local universities and cultural organizations have further enriched the tribe’s commitment to cultural preservation.
Through these notable events and continued initiatives, the Mohegan Tribe of Indians of Connecticut demonstrates a powerful legacy of resilience, adaptation, and cultural pride, ensuring that their story continues to thrive in both historical and contemporary contexts.
Where Are Their Tribal Lands Now And How Were They Established
The Mohegan Tribe of Indians of Connecticut currently occupies a significant and historical territory that spans approximately 300 acres, primarily centered around the Mohegan Reservation located in Uncasville, Connecticut. This reservation is a living testament to the tribe’s resilience and cultural heritage,symbolizing the enduring presence of the Mohegan people in their ancestral lands.
The establishment of the Mohegan Reservation traces back to a series of legal recognitions and agreements that shaped the tribe’s modern identity. In the early 17th century, the Mohegan people, led by leaders such as Uncas, began to negotiate and establish relationships with English settlers. The Mohegan Tribe received formal recognition in the 1970s, culminating in the granting of federal recognition by the Bureau of Indian Affairs in 1994. This recognition affirmed the tribe’s status and rights over their ancestral territories, allowing them to govern themselves and manage their resources effectively.
Throughout the years, various land reclamation efforts have enabled the Mohegan Tribe to consolidate their landholdings. The tribe has actively pursued economic development strategies that include the establishment of the Mohegan Sun,one of the largest casinos in the United States,which has generated significant revenue for community programs and land acquisition initiatives. In addition to the casino enterprise,the tribe is involved in ecologically sustainable practices on their lands,aiming to enhance the preservation of their culture and environment.Today, the Mohegan Reservation serves as a hub for cultural events, educational programs, and community gatherings, fostering a sense of identity and continuity among the Mohegan people.The tribal lands reflect a rich history of adaptability and perseverance, symbolizing the Mohegan Tribe’s enduring connection to their heritage while addressing contemporary challenges and opportunities.
Modern Concerns Of The Tribe
The Mohegan Tribe of Indians of Connecticut faces several modern concerns that reflect both their rich heritage and today’s socio-economic landscape. One of the primary challenges is economic development. While the tribe has made significant strides through its successful Mohegan Sun Casino, which began operations in 1996, there are ongoing efforts to diversify their economic portfolio. The tribe seeks to invest in various industries, including tourism, sustainable energy, and real estate, to ensure long-term financial stability and self-sufficiency.
Cultural preservation is another critical concern for the Mohegan Tribe. They actively work to revitalize their language, traditions, and ceremonies, which are vital for maintaining their identity and educating future generations. The tribe’s language revitalization programs are particularly critically important, as efforts to teach the Mohegan language to young members are enhancing their cultural connection.
Environmental stewardship also ranks high on the tribe’s agenda. The Mohegan Tribe is committed to preserving the natural resources of their ancestral lands. Their initiatives focus on sustainable practices in development and tourism,ensuring that the environment is protected for future generations. They advocate for responsible land management and have engaged in various conservation projects, including habitat restoration and the promotion of native species.
Healthcare access remains a significant concern, particularly with the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. The tribe is dedicated to addressing health disparities within their community by enhancing healthcare services, promoting wellness programs, and ensuring that members have access to quality medical care.Moreover, social justice and advocacy play a crucial role in the tribe’s contemporary issues. The Mohegan Tribe actively engages in dialog around sovereignty, representation, and Native rights at local, state, and national levels. By participating in broader movements advocating for Indigenous peoples, the tribe seeks to address historical injustices and empower their community through legislative changes.
the Mohegan Tribe of Indians of Connecticut remains resilient in the face of modern challenges,continuously working towards economic sustainability,cultural preservation,environmental protection,healthcare access,and advocacy for Indigenous rights. Their efforts not only strengthen their community but also contribute to the broader narrative of Native American resilience and empowerment.
Events And Other Social And Political Activities
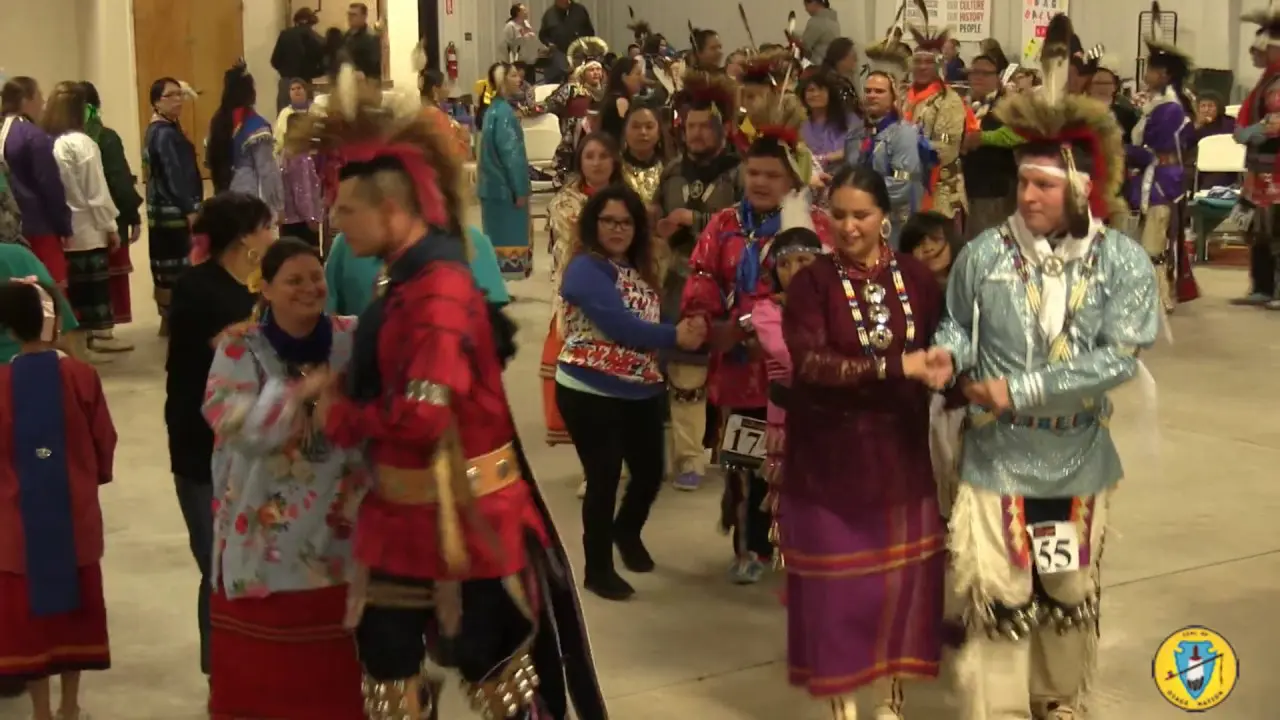
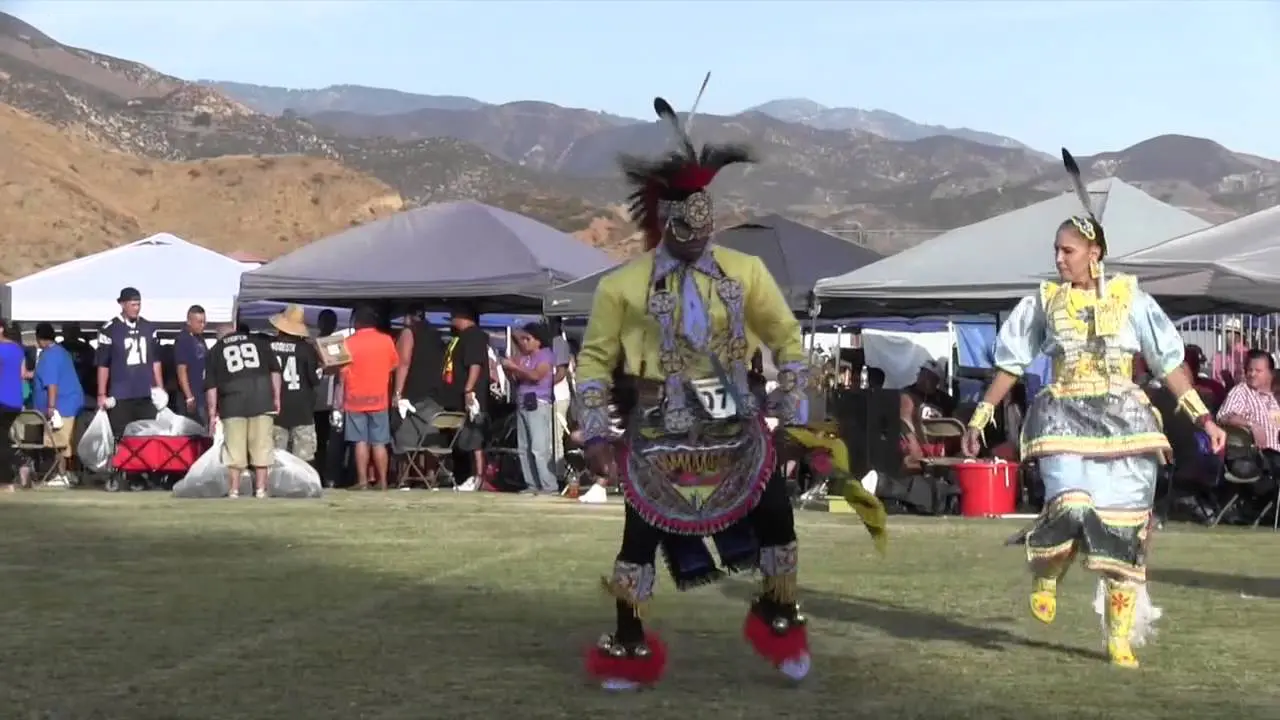
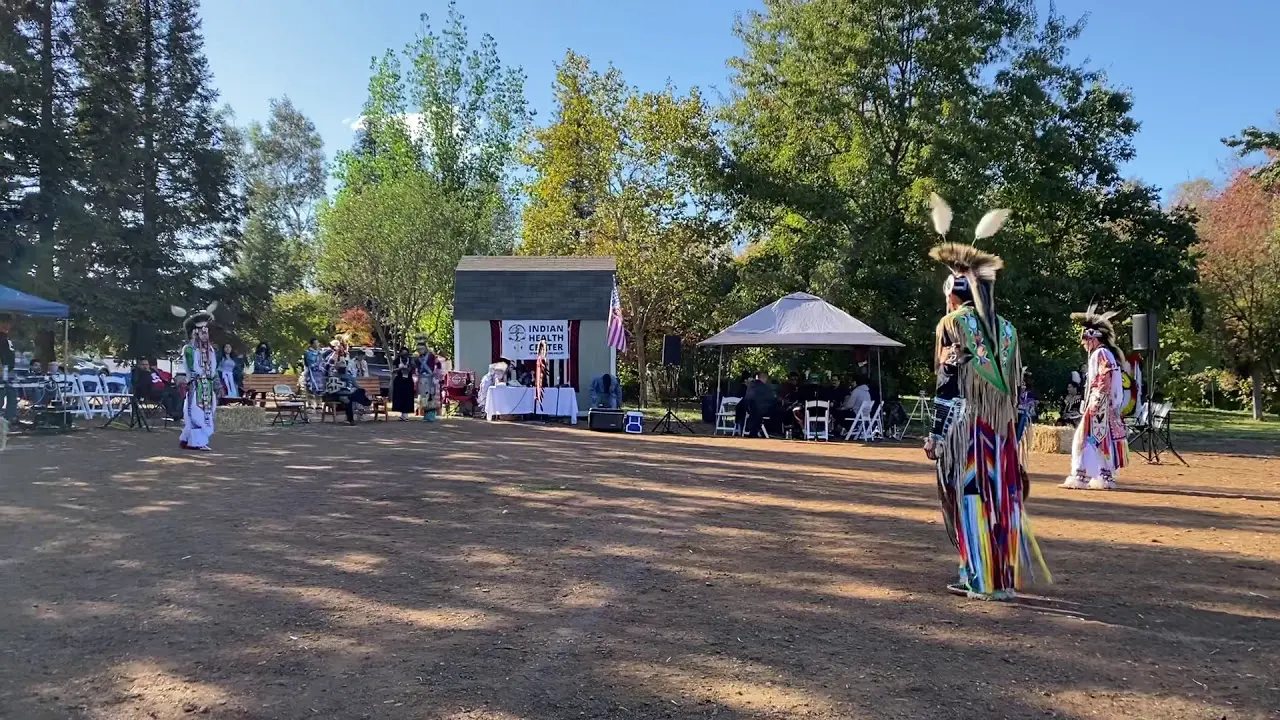
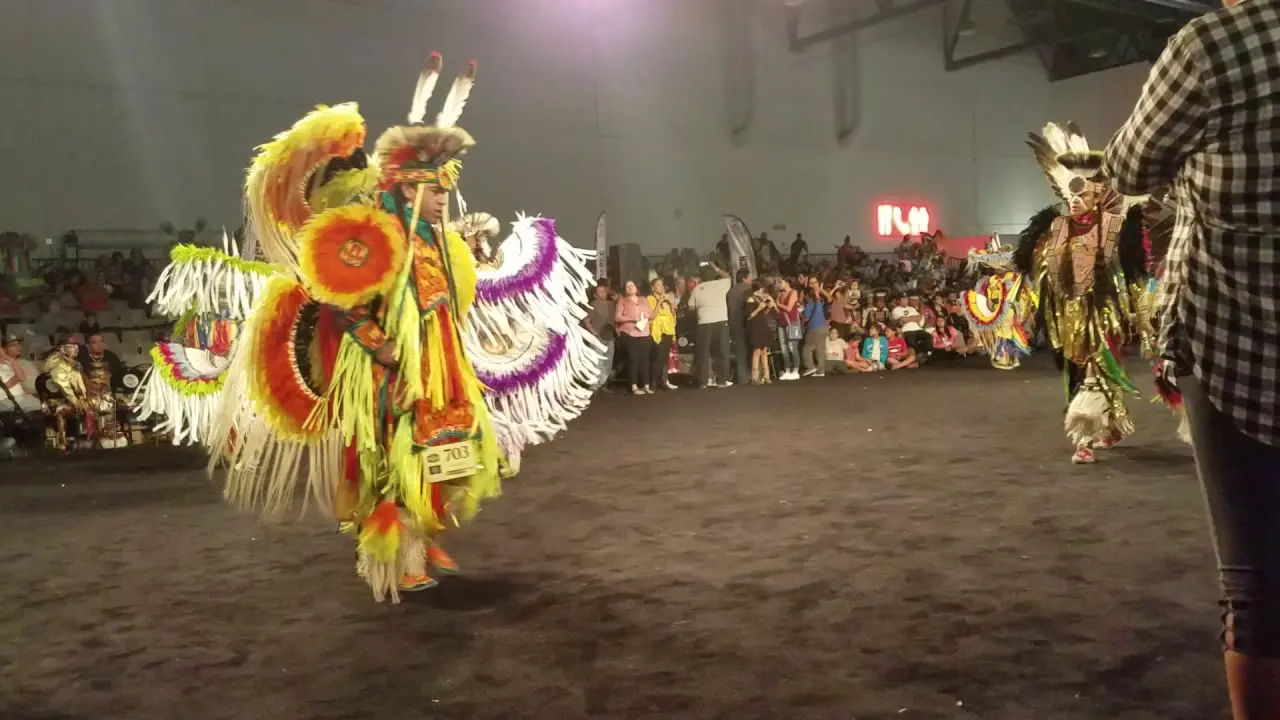
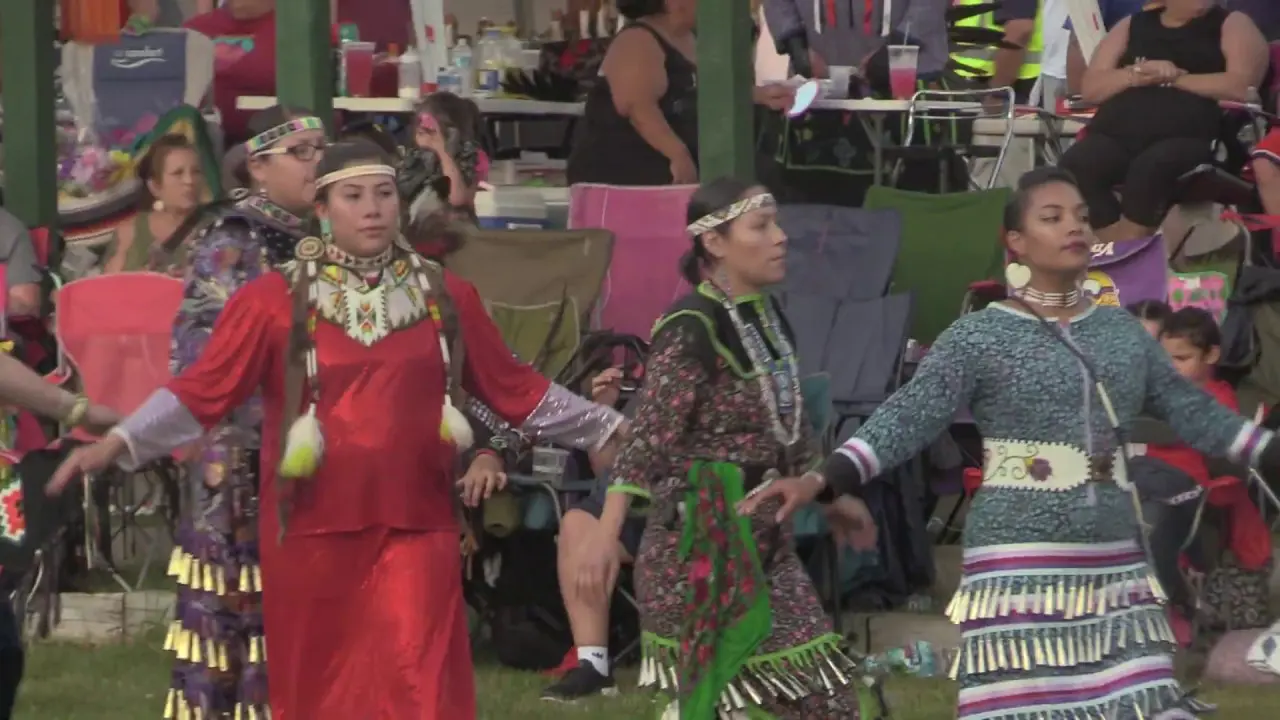
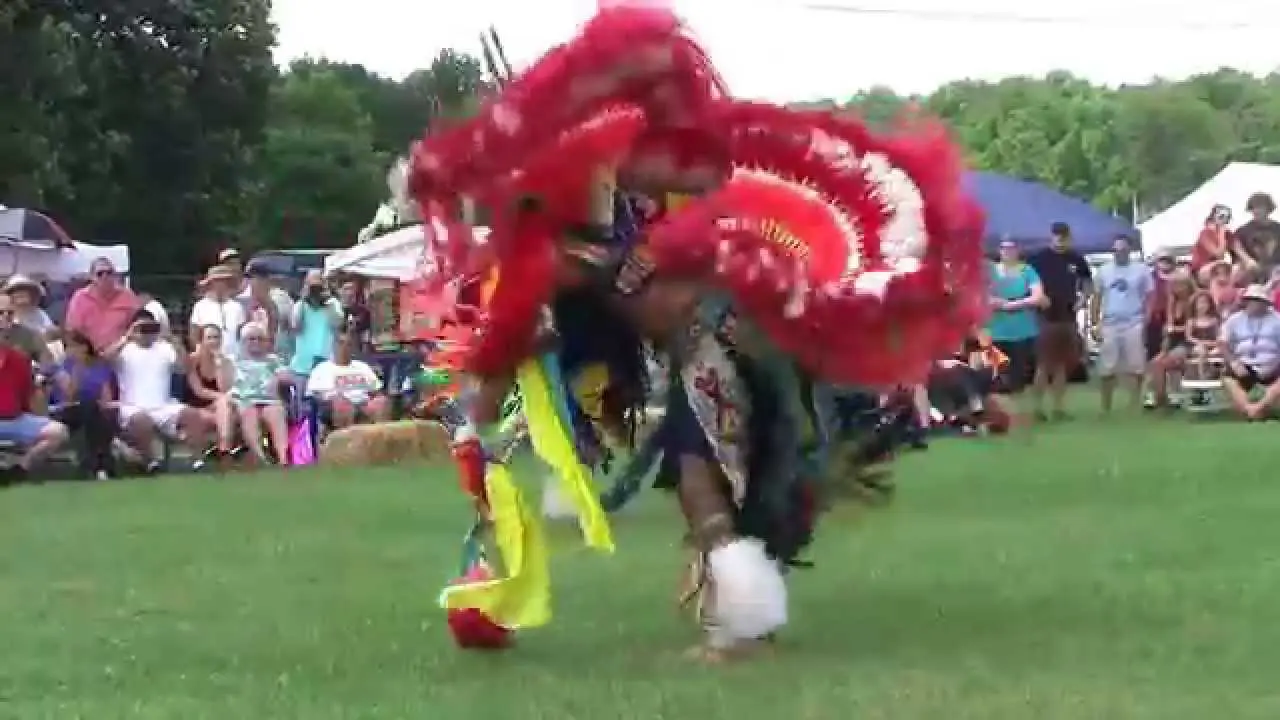
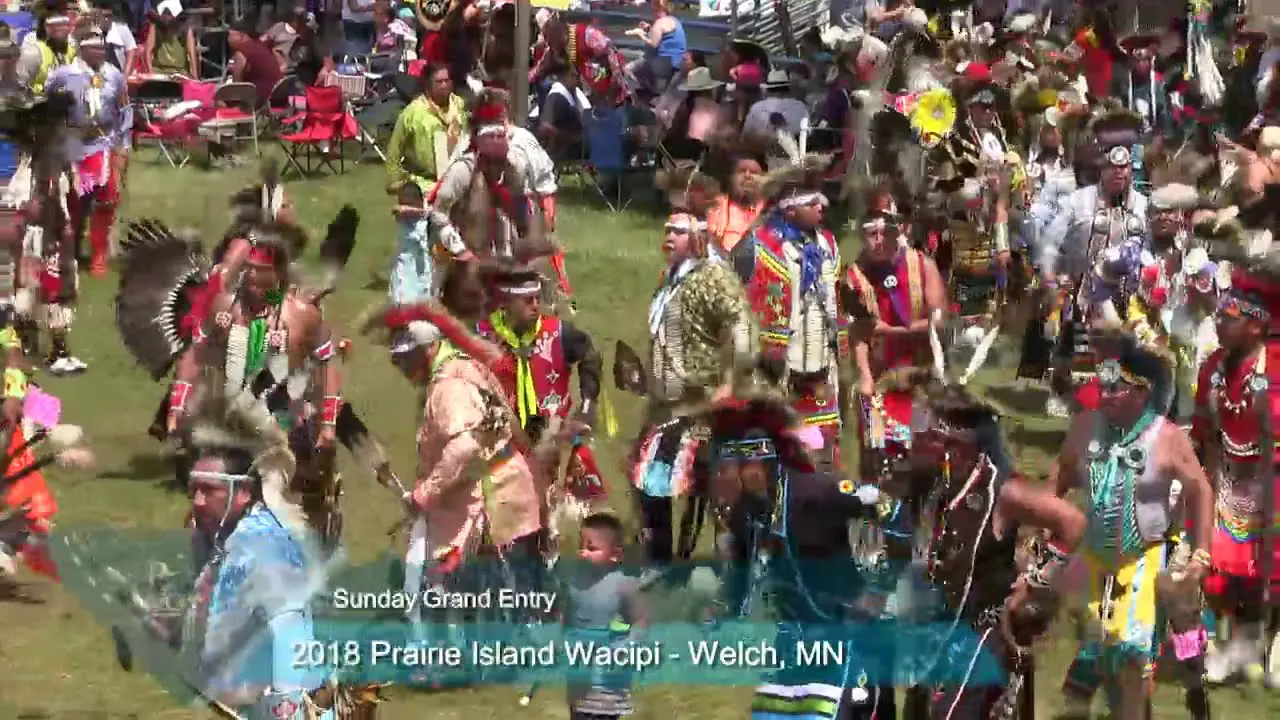
The Mohegan Tribe of Indians of Connecticut actively engages in a myriad of events and social activities that highlight their rich culture and commitment to community welfare. Chief among these is the annual Mohegan Sun Powwow, a vibrant festivity of Native American heritage filled with traditional dance, music, food, and crafts. This event not only showcases the artistry of tribal members but also attracts visitors from across the region, fostering a sense of connection and understanding between the Mohegan community and the general public.
Along with cultural events, the Mohegan Tribe participates in various political activities to advocate for tribal sovereignty and indigenous rights. The tribe is vocal in supporting legislation that protects their lands, resources, and cultural heritage. They are active members of national organizations that address native issues, ensuring their voices are heard in discussions surrounding federal recognition and the preservation of native languages and traditions.
Community outreach is also a pillar of the Mohegan Tribe’s social initiatives. They run programs that promote education, health, and youth engagement within both their tribal community and neighboring areas. The Mohegan Tribe’s commitment to social responsibility is evident in their partnerships with local organizations, focusing on initiatives such as environmental conservation and economic development.
Moreover, the tribe celebrates traditional holidays and important dates throughout the year, often incorporating cultural teachings and language preservation into these observances. This not only strengthens the tribal identity among younger generations but also creates opportunities for cultural exchange and dialogue within the broader community.The integration of educational workshops and public demonstrations reinforces the Mohegan Tribe’s role as a leader in promoting Native American culture and fostering relationships with fellow tribes and local residents. Through these multifaceted events and activities, the Mohegan Tribe of Indians of Connecticut continues to thrive, ensuring the vibrancy of their traditions for generations to come.