Introduction to the Northern Arapaho Tribe of the Wind River Reservation, Wyoming
Nestled within the scenic landscapes of the Wind River Reservation in Wyoming, the Northern Arapaho Tribe is a vibrant community with a rich cultural heritage and a compelling history. Often celebrated for their resilience and adaptability, the Northern Arapaho people have navigated the complexities of modern life while preserving their traditions and identity. With roots tracing back hundreds of years, the Tribe has become an integral part of Wyoming’s tapestry, contributing to the region’s cultural diversity and economic development.
The Wind River Reservation,established in the 19th century,provides a home for both the Northern Arapaho and the Eastern Shoshone Tribes. This area, characterized by breathtaking mountains, rivers, and plains, is not only significant for its natural resources but also serves as a gathering place for tribal ceremonies, festivals, and community events. The Northern Arapaho Tribe is known for its commitment to education, health, and economic growth, striving to enhance the quality of life for its members while proudly upholding its ancestral customs.
As you explore the rich cultural practices, past challenges, and modern-day initiatives of the Northern Arapaho Tribe, you will gain a deeper understanding of their unique contributions to the broader American Indian narrative and their ongoing efforts to preserve their way of life in today’s world. Join us as we delve into the history, culture, and future endeavors of the Northern Arapaho Tribe, shedding light on their lasting legacy in Wyoming and beyond.
Origin Of The People
The Northern Arapaho Tribe,primarily residing on the Wind River Reservation in Wyoming,possesses a rich history that is deeply intertwined with the culture and legacy of the Great Plains. The origins of the Northern Arapaho can be traced back to the larger Arapaho Nation, which is believed to have migrated from the Great Lakes region towards the Rocky Mountains in search of better hunting and living conditions. This migration began around the 16th century and was influenced by the availability of resources and the movement of other tribes.
Historically, the Arapaho people were nomadic hunter-gatherers, relying heavily on the buffalo for food, clothing, and shelter. Their intimate connection with the land guided their seasonal migrations,as they followed the vast herds across the plains. The Northern Arapaho often found themselves allied with neighboring tribes, such as the Lakota Sioux and Cheyenne, forming strategic partnerships for trade and mutual defense against common adversaries.
During the 19th century, the encroachment of European settlers and the U.S. government’s policies drastically impacted the Northern Arapaho tribe.The introduction of treaties, including the Treaty of Fort Laramie in 1868, aimed to secure land for the Arapaho but often led to the loss of traditional territories. Despite these challenges, the Northern Arapaho maintained their cultural identity through oral traditions, spiritual practices, and communal living.
Today, the Northern Arapaho Tribe plays a crucial role in preserving their language, traditions, and heritage. Efforts to revitalize their cultural practices are evident through community programs that focus on education, arts, and the promotion of their history. The tribe’s connection to their ancestral land continues to be a source of pride and resilience, allowing them to thrive in modern times while honoring their rich past.
Tribal Homelands
The Northern Arapaho Tribe, one of the primary tribal nations residing on the Wind River Reservation in Wyoming, has a rich history deeply intertwined with the landscapes of their ancestral homelands. The Wind River Reservation, established in 1868, encompasses approximately 2.2 million acres of breathtaking terrain,featuring rolling hills,mountains,and rivers,which are vital to the cultural and spiritual practices of the Northern Arapaho people.
Historically, the Arapaho people roamed the Great Plains and the Rocky Mountains, engaging in hunting, fishing, and gathering. Today, the Northern Arapaho Tribe continues to honor these traditions, nurturing a connection to the land that supports their identity and way of life. The reservation is not just a geographical area, but a living testament to the resilience of the Northern Arapaho culture.
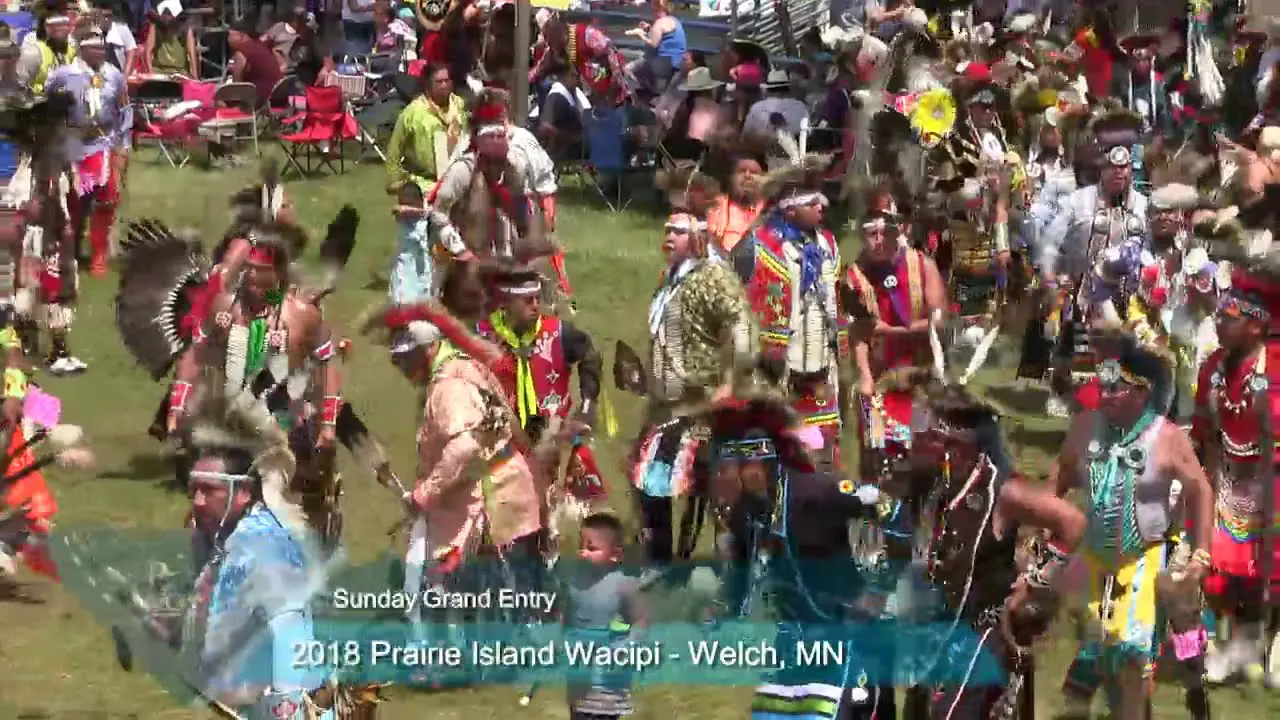
The tribe’s homelands are abundant with natural resources, offering opportunities for sustainable practices.Fishing in the Wind River and hunting in the hills remain integral to the community’s subsistence and cultural heritage. The tribe has been involved in various initiatives to preserve these resources, ensuring that future generations can continue to enjoy the same access to the land that their ancestors did.Beyond natural resources,the Northern Arapaho Tribe actively engages in revitalizing their language and traditions. Efforts to cultivate a sense of pride in their heritage are seen through cultural events, educational programs, and storytelling, which draw people back to their roots. The tribe’s commitment to cultural preservation is evident in various celebrations,such as the annual Northern Arapaho Powwow,which showcases traditional dances,crafts,and foods,fostering a sense of community and belonging.
The challenges faced by the Northern Arapaho people, including economic development and the preservation of their land, are critical issues that they navigate with determination and resilience. The tribe is focused on initiatives that promote self-sufficiency while respecting their cultural traditions and the natural surroundings. Through strategic partnerships and community engagement,the Northern Arapaho Tribe aims to uplift their community and ensure a vibrant future while honoring their rich past.
the Northern Arapaho Tribe’s connection to their tribal homelands on the Wind River Reservation encapsulates a profound relationship with the land that extends far beyond mere geography. It reflects a vibrant culture, steeped in history, that continues to thrive in the face of modern challenges. The community’s dedication to preserving its heritage and nurturing its environment serves as a reminder of the enduring legacy of the Northern Arapaho people.
Interactions With Settlers
Interactions between the Northern Arapaho Tribe and Euro-American settlers at the Wind River Reservation in Wyoming have been complex, marked by both positive and negative experiences. Initially, some settlers arrived with a spirit of cooperation. They sought peaceful trade relationships, exchanging goods such as tools and metal utensils for Native American crafts and animal pelts. The Northern Arapaho welcomed these exchanges, recognizing the potential benefits of acquiring new technologies that could enhance their way of life. This interaction laid the groundwork for shared knowledge, fostering a sense of cultural recognition, albeit limited.
However, as more settlers moved into the region during the 19th century, the dynamics shifted dramatically.The discovery of gold in nearby areas and the push for westward expansion intensified pressure on the land traditionally occupied by the Northern Arapaho and other Native tribes. Conflicts arose as settlers encroached upon hunting grounds and resources essential to the tribe’s survival. This led to a series of disputes, often resulting in violence, eviction, and a profound disruption of the Northern Arapaho’s traditional lifestyle.
Moreover, government policies during this period frequently enough favored settlement expansion over the rights of Native peoples. The signing of treaties frequently resulted in the loss of territory for the Northern Arapaho, diminishing their access to vital resources. As a notable example, the Treaty of Fort Laramie in 1868 created the Wind River Reservation, yet it still left the tribe vulnerable to further encroachments from settlers seeking land and resources.
Despite these challenges, the tribe has demonstrated resilience in maintaining their cultural identity and traditions. Initiatives that promote cultural exchange and understanding with settlers and visitors today illustrate a commitment to fostering positive relations. Programs aimed at educating both the Northern Arapaho community and the public about tribal history and culture serve as a bridge for reconciliation and respect.
These multifaceted interactions highlight the enduring complexities of relationships between Indigenous tribes and settlers, illustrating the need for ongoing dialogue and understanding. The Northern Arapaho Tribe of the Wind River Reservation continues to navigate this legacy while working towards a more equitable future.
Most Notable Events In Their Tribal History
The Northern Arapaho Tribe, residing on the Wind River Reservation in Wyoming, has a rich and complex history marked by pivotal events that have shaped their identity and culture. One of the most significant moments occurred in 1868 when the United States signed the Treaty of Fort Laramie, which formally recognized the Arapaho and their territory. This treaty granted the tribe a designated homeland in Wyoming, paving the way for their continued existence as a distinct cultural group.
However, the subsequent years brought challenges, including forced relocations and conflicts stemming from the encroachment of settlers on their lands. The Northern Arapaho suffered greatly during the late 19th century, particularly during the Bear River Massacre in 1863, where many Arapaho lives were lost. This tragic event exemplifies the struggle of the tribe against oppression and dispossession as they fought to maintain their way of life in the face of mounting external pressures.
The early 20th century saw a resurgence in tribal activism and cultural revival, particularly after the Indian Reorganization Act of 1934. This legislation encouraged tribes to establish self-governance and revive their cultural practices. The Northern Arapaho responded by expanding their political and economic initiatives, leading to the establishment of their own government and the formation of tribal enterprises.
A landmark event occurred in the latter half of the 20th century with the enactment of the Indian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act of 1975, which empowered the Northern Arapaho and other tribes to take control over their education and social services. This led to significant advancements in health care, education, and community development.
In recent years, the Northern Arapaho Tribe has faced the challenge of navigating contemporary issues while honoring their traditional values. The development of economic partnerships, such as the establishment of the Northern Arapaho Casino, has provided vital funding for various tribal programs and initiatives. Additionally, the resurgence of cultural practices and the revitalization of the Arapaho language have become central pillars in fostering community identity and heritage.
Throughout their history, the Northern Arapaho Tribe has demonstrated resilience and adaptability, continuing to honor their ancestors while striving for a sustainable future. Their journey reflects broader themes of survival, cultural revival, and the ongoing quest for sovereignty in a changing world.
Where Are Their Tribal Lands Now And How Were They Established
The Northern Arapaho Tribe resides primarily on the Wind River Reservation in Wyoming, which is located in the west-central part of the state.This reservation spans over 2.2 million acres,shared with the Eastern Shoshone Tribe. The establishment of these tribal lands has a complex history that dates back to the 1868 Treaty of Fort Laramie, where the U.S. government recognized the rights of the Arapaho and other tribes to their ancestral territories.
Initially,the Northern Arapaho were part of a much larger region that included areas of present-day Colorado,Nebraska,and Wyoming.Over time, through a series of treaties and governmental policies, their land was substantially reduced. The 1905 Act was particularly impactful as it led to the reduction of the Wind River Reservation and the forced allotment of tribal lands to individual members. This process fragmented the tribe’s collective land holdings, resulting in loss of cultural and social cohesion.
In the latter half of the 20th century, the Northern Arapaho began efforts to reclaim their sovereignty and strengthen their cultural roots. The tribe’s governance has evolved to include a multi-faceted approach to land management, community involvement, and economic development initiatives that honor their heritage while promoting sustainability. Today,the Wind River Reservation serves as a vital cultural and economic center for the Northern Arapaho people,as they continue to navigate the challenges of contemporary society while preserving their rich history and traditions.
Collectively,the Northern Arapaho Tribe remains committed to protecting their tribal lands and ensuring that future generations flourish in a place that reflects their identity and values. As they work toward revitalizing their community and culture, the significance of the Wind River Reservation as a lasting home for the Northern Arapaho people remains ever strong.
Modern Concerns Of The Tribe
The Northern Arapaho Tribe, residing on the Wind River Reservation in Wyoming, faces a myriad of modern concerns that reflect the ongoing challenges of preserving their cultural heritage while navigating contemporary issues. One of the most pressing challenges is the fight for sovereignty and self-determination. The tribe is actively working to reclaim their rights over land and resources, advocating for legislative measures that protect their autonomy within the framework of federal Indian law.Economic development is another significant concern for the Northern Arapaho, as they seek to improve living standards and create sustainable jobs for their community members. The tribe has invested in various enterprises, including renewable energy projects and tourism initiatives, but faces obstacles such as limited access to capital and infrastructure challenges. Encouraging economic growth while maintaining cultural integrity remains a balancing act for tribal leaders.
Education is crucial for the Northern Arapaho’s future, yet challenges persist in achieving educational equity. Many community members advocate for improved facilities, culturally relevant curricula, and increased funding for schools on the reservation. Ensuring that young Arapaho are equipped with the tools to thrive in a modern economy while instilling a strong sense of cultural identity is a priority for tribal leaders.Healthcare access is another critical concern, as many residents struggle with health disparities that are prevalent in indigenous communities. The Northern Arapaho Tribe is focused on developing complete healthcare services, addressing issues like chronic disease prevention, mental health support, and substance abuse recovery. Enhancing public health initiatives and outreach programs is vital to improving community wellness.Environmental issues, particularly related to water and land management, also loom large for the Northern Arapaho Tribe. Climate change has impacted traditional hunting and fishing grounds, raising concerns about food sovereignty and the preservation of sacred sites. The tribe engages in grassroots efforts to combat environmental degradation, working alongside other indigenous groups to advocate for stronger protections for their natural resources.
Lastly,the Northern Arapaho community is deeply invested in cultural preservation amid external influences that may threaten their traditions and languages. Initiatives to promote language revitalization and traditional arts are crucial to maintaining their unique identity. Through storytelling, ceremonial practices, and community gatherings, the tribe endeavors to pass on their rich heritage to future generations, ensuring that their story continues in an ever-evolving world.
Events And Other Social And Political Activities
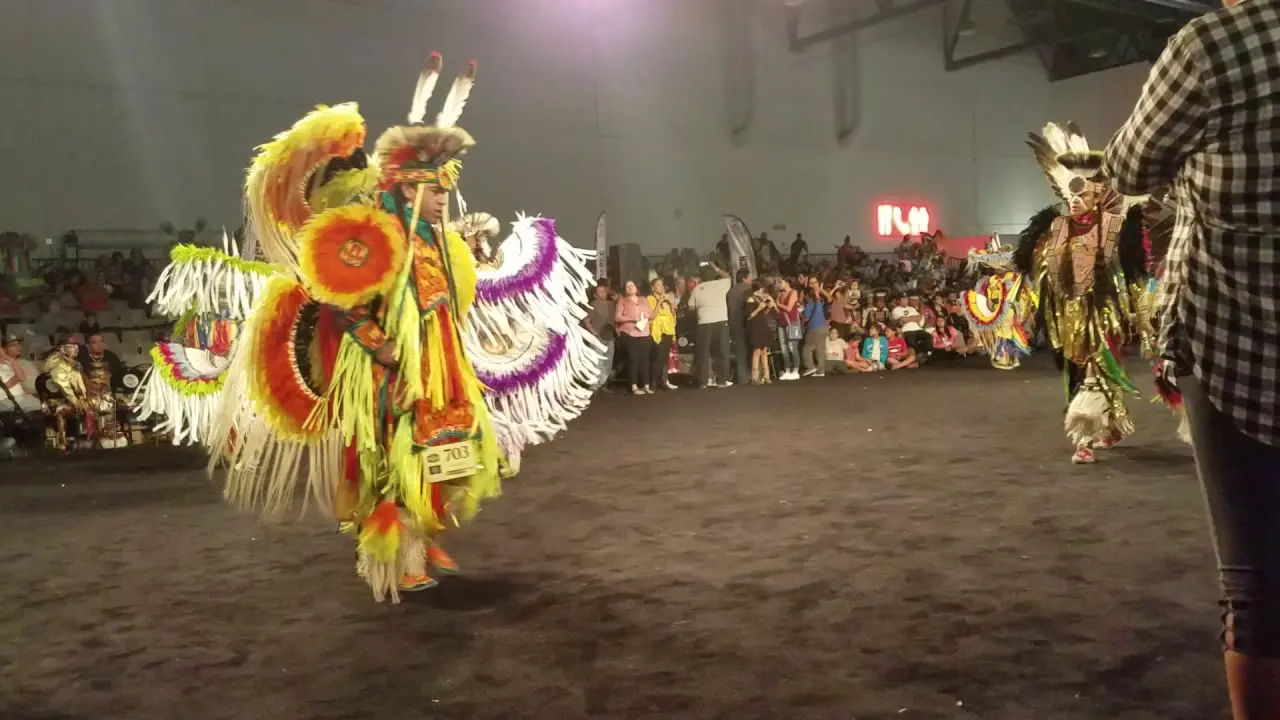
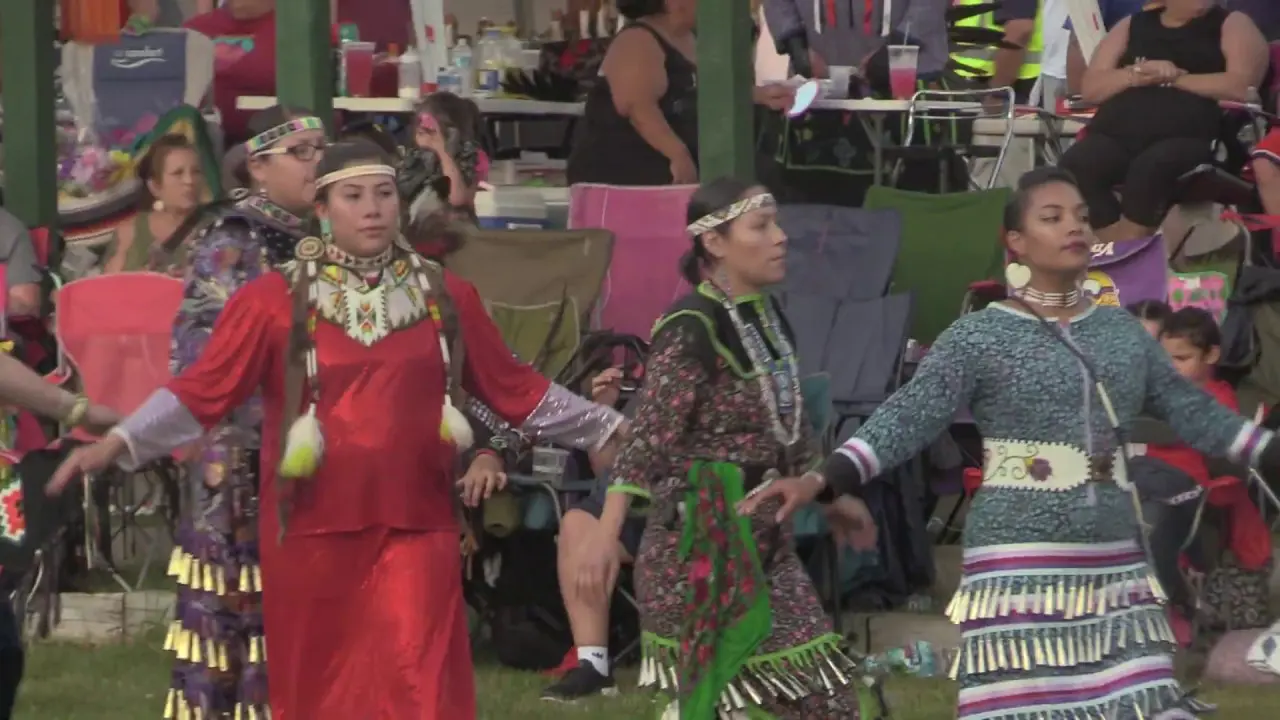
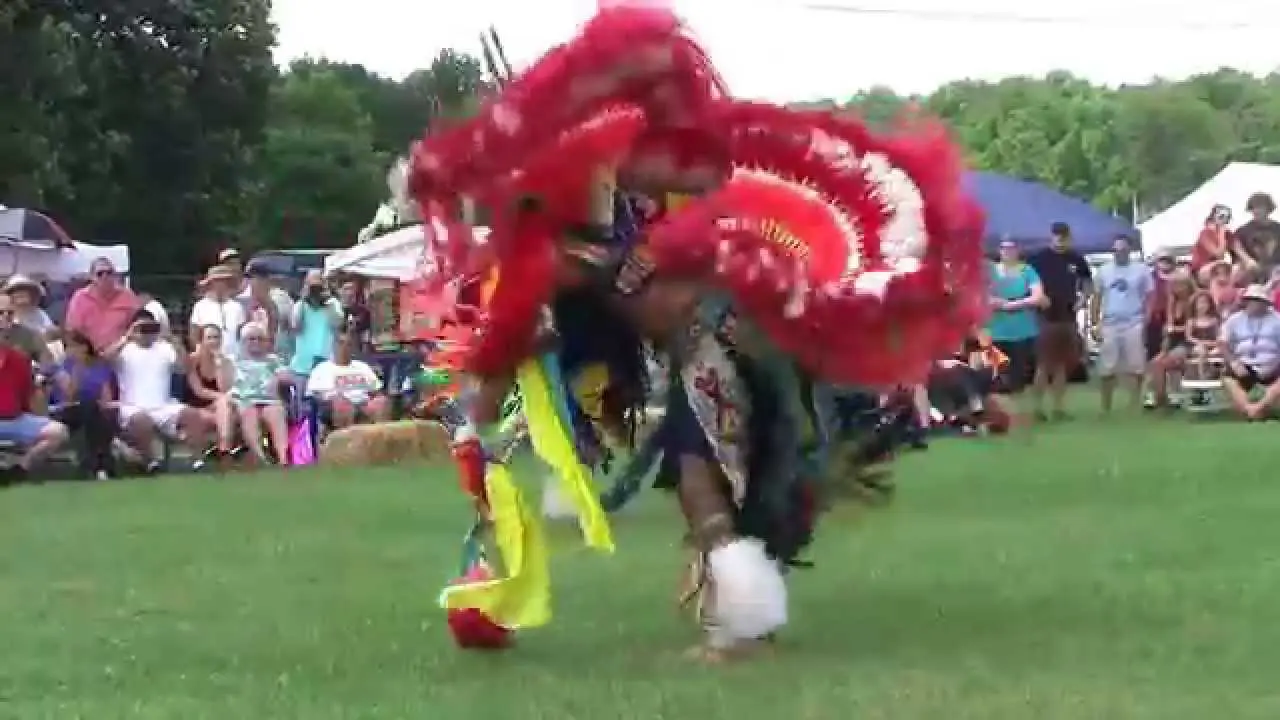
The Northern Arapaho Tribe, part of the Wind River Reservation in Wyoming, has actively engaged in a range of social and political activities that reflect its rich heritage and contemporary concerns. One of the key events is the annual Arapaho Jump Dance, a cultural party that honors traditional practices and serves as a gathering point for tribal members. This event not only showcases traditional music, dance, and food but also fosters a sense of community and identity among attendees.
Political activities within the tribe have seen significant developments, particularly with the establishment of the Northern Arapaho Tribal Council. This governing body plays a crucial role in advocating for the needs and rights of the Northern Arapaho people, addressing key issues such as land rights, sovereignty, and educational opportunities. The council regularly holds public meetings to ensure openness and community involvement in decision-making processes, allowing members to voice their concerns and aspirations.
Socially,the Northern Arapaho Tribe focuses on revitalizing language and cultural programs. Efforts to teach the Arapaho language to younger generations are evident in numerous workshops and classes, contributing to the preservation of their linguistic heritage. Additionally, the tribe organizes health awareness events that tackle issues like diabetes, addiction, and mental health, demonstrating a commitment to the well-being of its members.
Engagement with external organizations and alliances is also a crucial aspect of the tribe’s social and political landscape. Collaborations with state and federal agencies, and also partnerships with other tribal nations, emphasize mutual support and resource sharing, especially in areas like environmental stewardship and economic development. Events such as the annual Pow Wow not only celebrate Arapaho culture but also attract attention to broader issues facing Indigenous communities across the nation.
Through these various events and activities, the Northern Arapaho Tribe continues to assert its identity, enhance community bonds, and advocate for its sovereignty and rights within both local and national political arenas.