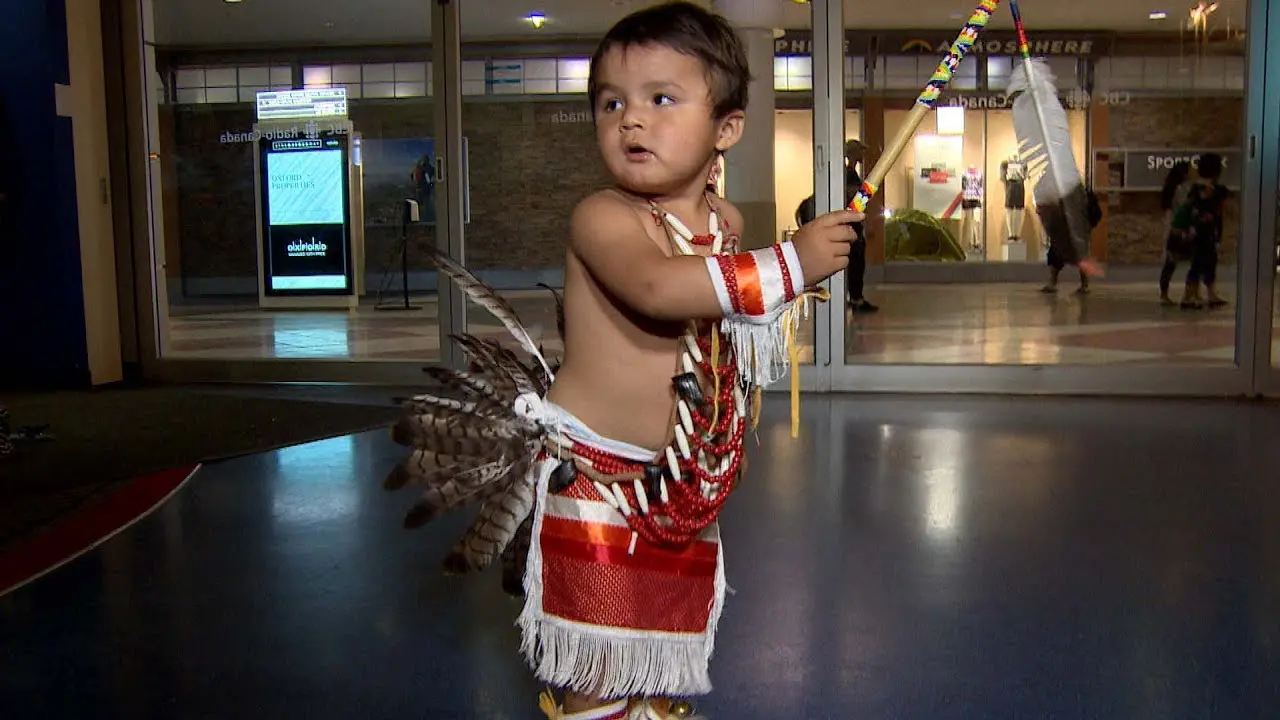
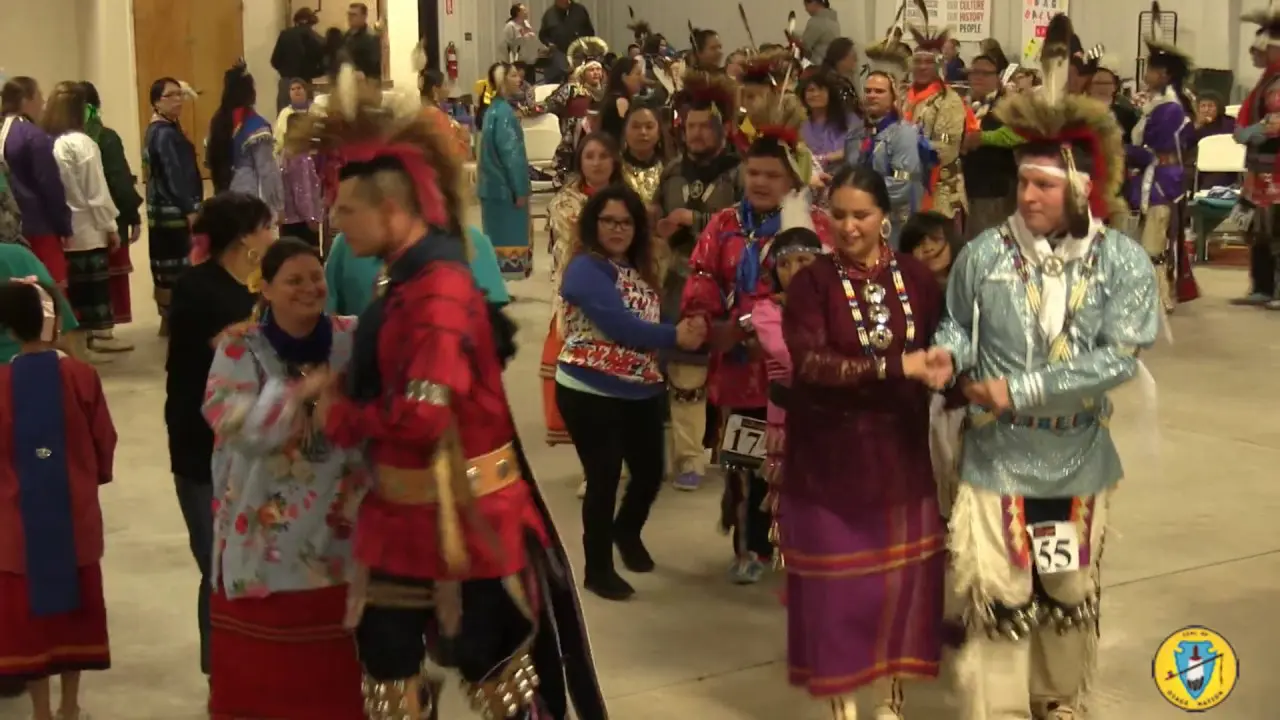
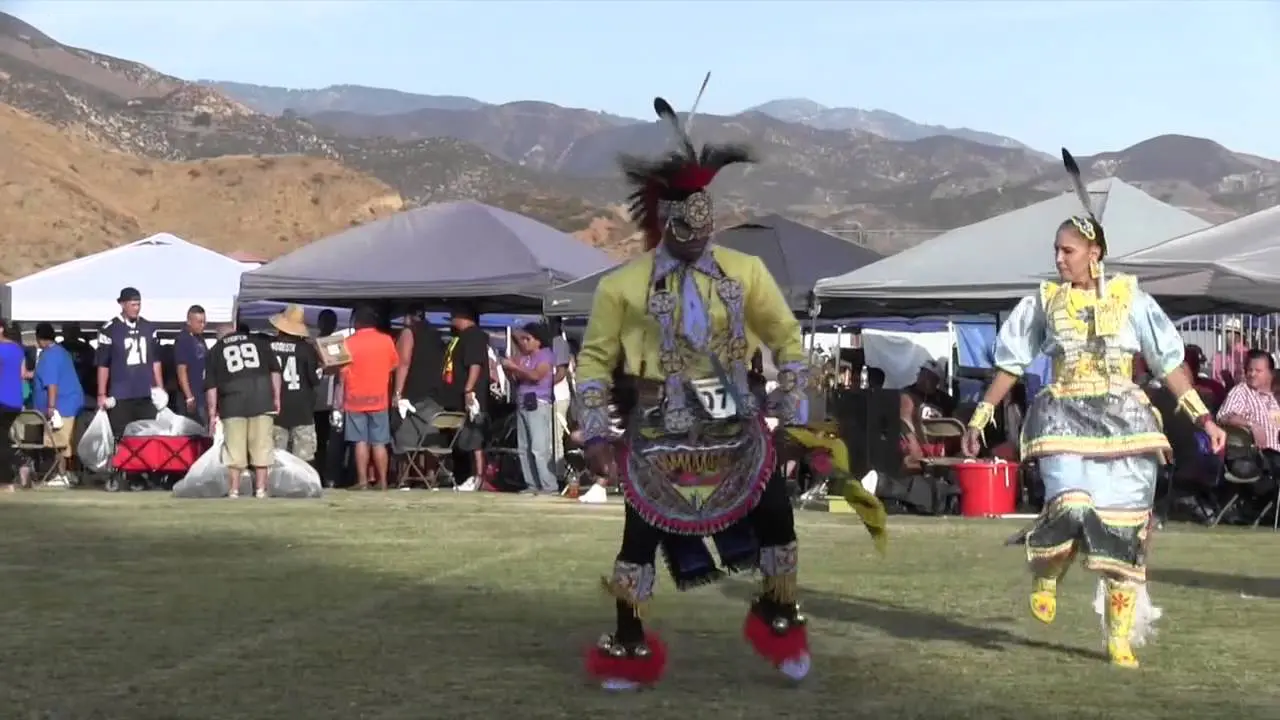
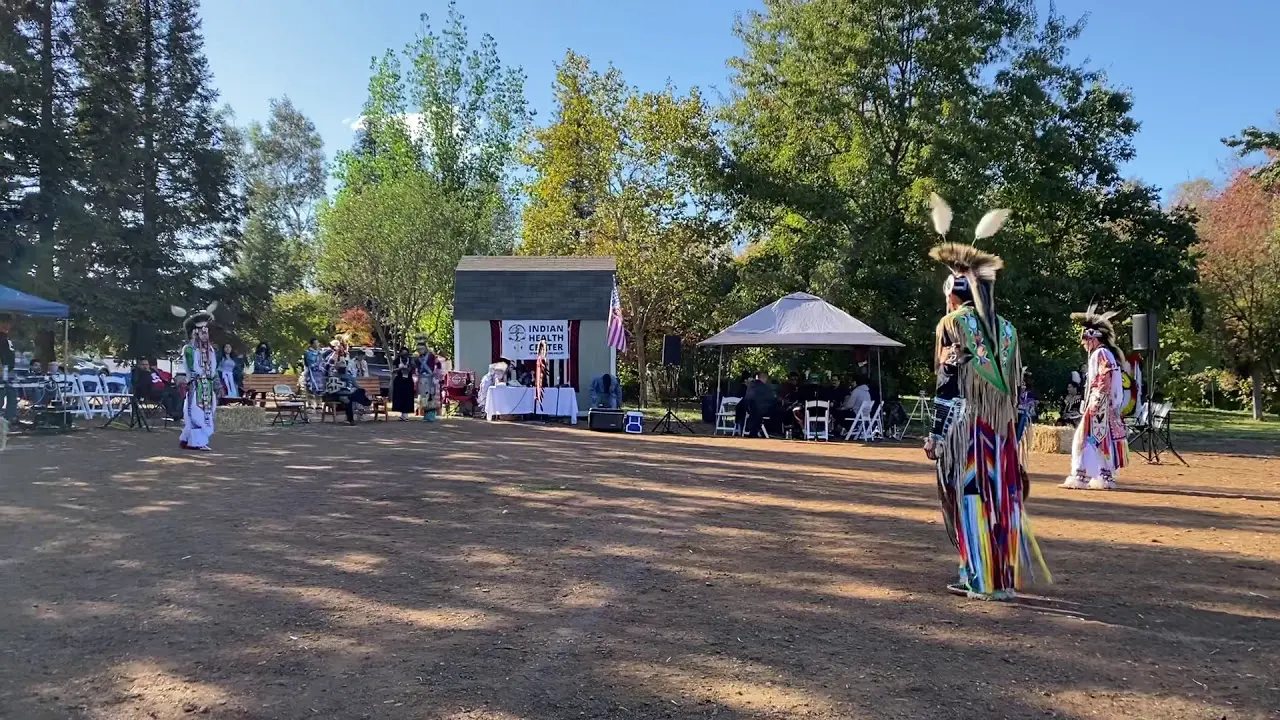
The Oneida Indian Nation, one of the original members of the Haudenosaunee Confederacy, holds a rich and storied history that dates back thousands of years. Located primarily in central New York, the Oneida Nation is not only recognized for its cultural heritage and resilience but also for its vibrant community and economic advancement efforts in modern times. As a sovereign nation, the Oneida Indians have worked tirelessly to preserve their traditions while adapting to the contemporary world, achieving significant milestones in various sectors including gaming, tourism, and agriculture.
The Oneida people played a crucial role in American history, notably in the American Revolution, where they sided with the colonists against British forces. Their commitment to justice and peace has been a hallmark of their identity,reflected in their belief systems and social structures. Today, the Oneida Indian Nation is actively involved in preserving their language, customs, and values, all while fostering relationships with neighboring communities and government entities.
With a focus on sustainable development and cultural education, the Oneida Indian Nation continues to thrive, making significant contributions to the economy and culture of the region. By embracing both tradition and innovation, the Oneida people serve as a powerful example of a community that honors its past while looking forward to a prosperous future. Whether through their award-winning casinos, cultural events, or commitment to environmental stewardship, the Oneida Indian Nation stands as a testament to resilience, community strength, and the enduring spirit of indigenous peoples in North America.
Origin Of The People
The Oneida Indian Nation, part of the Haudenosaunee Confederacy, traces its origins back to the early 17th century in what is now central New York. Historically, the Oneida people inhabited the rich landscapes of the region, characterized by lush forests and abundant waterways that provided essential resources for sustenance and trade.They primarily lived in longhouses in matrilineal clans, signifying the crucial role that women played in their society.
As one of the original five tribes of the Iroquois Confederacy, established around 1142 A.D., the Oneida Indians participated in a complex political structure that allowed for collective decision-making and conflict resolution among member tribes. This structure, known as the Great Law of Peace, emphasized principles such as mutual respect and shared governance, which are still celebrated by the Oneida Nation today.
The Oneida people historically engaged in agriculture, growing staple crops like corn, beans, and squash, often referred to as the “Three Sisters.” Their agricultural practices were complemented by hunting, fishing, and gathering, enabling them to create a well-rounded diet that sustained their communities. Furthermore, the Oneida developed a rich spiritual culture, deeply intertwined with their respect for nature, ancestors, and the Great Spirit.
During the American Revolution, the Oneida tribe took a notable stand by siding with the colonists, hoping to secure their sovereignty and protect their lands. This decision placed them in direct conflict with other tribes allied with the British. Unfortunately, the aftermath of the war resulted in significant land loss and challenges for the Oneida people, as treaties and governmental policies led to forced removals and infringements on their territory.
Despite these challenges, the Oneida Indian Nation has persevered and continues to thrive in the modern era. The tribe is actively engaged in cultural preservation, education, and community development. Today, the Oneida Indian Nation is recognized as a sovereign entity that has established various enterprises, contributing to the local economy while promoting the revitalization of Oneida language and traditions.
The enduring legacy of the Oneida people is evident in their rich history, vibrant culture, and commitment to their ancestral values. As they navigate the dynamics of contemporary society, the Oneida Indian Nation remains a testament to resilience, unity, and the ongoing importance of cultural heritage.
Tribal Homelands
The Oneida Indian Nation’s tribal homelands are rooted in the rich history and cultural heritage of the Oneida people, one of the five nations of the Haudenosaunee Confederacy. The original territory of the Oneida tribe was located in what is now central New York, specifically in areas around Oneida Lake and the surrounding regions. This land was not just a physical space but a vital part of the tribe’s identity, offering resources for sustenance, ceremonial practices, and a connection to ancestors.
In contemporary times, the Oneida Indian Nation has worked tirelessly to reclaim and preserve portions of their ancestral lands.The nation’s current jurisdiction includes approximately 32,000 acres in Madison and Oneida Counties. This land plays a crucial role in revitalizing the Oneida culture, language, and traditions.Key landmarks such as the Oneida Nation Museum and the Turtle Island Park are situated within these homelands, serving as central hubs for cultural education and community gatherings.
The Oneida Indian Nation also places significant emphasis on environmental stewardship, aligning with traditional ecological practices that respect and protect the land. Sustainable agriculture initiatives and wildlife conservation efforts are in place, reflecting the tribe’s commitment to maintaining harmony with nature. Their approach to land management not only benefits biodiversity but also reinforces the Oneida people’s connection to their heritage.
Historically, the Oneida Tribe has faced numerous challenges, including forced removal and land loss due to treaties and encroachments. However, through persistence and resilience, the Oneida Indian Nation has maintained its sovereignty and continues to advocate for the rights of Indigenous peoples. Today, the Oneida’s tribal homelands symbolize a stronghold of cultural revival, community well-being, and a vision for a sustainable future, making them an essential aspect of the Oneida identity.
Interactions With Settlers
The interactions between the Oneida Indian Nation tribe and European settlers in the 18th and 19th centuries illustrate a complex tapestry of both positive and negative experiences. On one hand, the Oneida were known for their diplomatic skills and willingness to work with European settlers, establishing cooperative relationships that led to mutual benefits. During the American Revolutionary War,such as,the Oneida sided with the colonists against the British,contributing critical support and gaining favor among the emerging American leaders. This alliance not only strengthened their political ties but also provided them with a degree of protection against other encroaching settlers.
Conversely, the interactions were not always positive. As colonial expansion intensified, the Oneida experienced significant pressure on their land and resources. The Treaty of Fort Stanwix in 1768 marked a pivotal moment where the Oneida were pressured into ceding a large portion of their territory. This loss considerably impacted their traditional way of life and led to resentment towards the settlers. The westward push of settlers in the 19th century further exacerbated these tensions,resulting in conflicts over land rights and resources.
Moreover, the Oneida faced cultural challenges as they navigated their relationships with European settlers.While some sought to assimilate and adopt certain European customs, others staunchly defended their traditions and way of life. Educational institutions established by settlers aimed to “civilize” Native populations, placing additional strain on cultural identity. Despite the hardships, the Oneida demonstrated resilience, gathering strength from their rich heritage and community ties to resist total assimilation.
Throughout the centuries, the legacy of these interactions has shaped the Oneida Indian Nation’s identity, highlighting a remarkable journey of adaptation, resistance, and survival. Their experiences with settlers serve as a reminder of the nuanced and frequently enough tumultuous history between indigenous nations and European colonizers, echoing the themes of cooperation and conflict that continue to resonate today.
Most Notable Events In Their Tribal History
The Oneida Indian Nation has a rich and resilient history characterized by significant events that shaped their culture and governance. One of the most notable events in their history occurred during the American Revolutionary War when the Oneida allied with the colonists against the British.This alliance was pivotal, as it showcased the tribe’s commitment to sovereignty and self-determination, despite facing enormous external pressures. The Oneida’s strategic contribution to the war effort earned them respect and recognition, helping to establish their place in the emerging narrative of the United States.
Following the war, the Oneida faced significant challenges, including land dispossession and the impact of U.S.policies. The Treaty of 1784 was a notable event as it marked one of the first treaties negotiated between the Oneida and the new American government.However, this treaty ultimately resulted in significant loss of territory for the tribe, highlighting the ongoing struggle for land rights that would characterize much of their later history.
In the late 19th century, the Oneida Indian Nation experienced a resurgence of cultural pride and sovereignty, particularly with the establishment of the Oneida Nation of New York in 1936. This was a significant moment in their tribal history, marking a renewed effort to govern themselves and preserve their cultural identity despite ongoing external pressures. The establishment of their own government allowed the Oneida to engage in economic development, ultimately leading to the creation of businesses that enhanced their community’s welfare.The 1980s marked another pivotal period for the Oneida Indian Nation as they confronted challenges related to land claims and federal recognition. In 1985, the Oneida Nation filed a land claims suit against New York State, seeking the return of ancestral lands. This legal battle underscored the ongoing struggle for rights and recognition and was a defining moment in their quest for justice.
Moreover,in recent years,the Oneida Indian Nation has made headlines for its progressive policies regarding economic development and social justice. Their commitment to community wellness and cultural revitalization has garnered national attention. Initiatives such as the establishment of educational programs and support for tribal environmental sustainability reflect their enduring commitment to their heritage and future,ensuring that the rich history of the Oneida Indian Nation continues to thrive in the modern world.
Where Are Their Tribal Lands Now And How Were They Established
The Oneida Indian Nation is primarily located in central New York, where their tribal lands encompass a portion of the homelands they have occupied for centuries. The primary reservation, known as the Oneida Reservation, spans approximately 32,000 acres in Madison County and is a testament to the tribe’s enduring presence and resilience.
Historically, the Oneida people were one of the founding members of the Iroquois Confederacy, which was established in the 16th century and played a pivotal role in governance and diplomacy among the nations of the Northeast. The establishment and recognition of their sovereign territory have evolved through various treaties and legal battles. Significant early treaties, such as the 1784 Treaty of Fort Stanwix, established formal boundaries for the Oneida lands, although these agreements were often violated or neglected by colonial and later state governments.
In the 19th century, following the loss of land due to pressure from settlers and the U.S. government, the Oneida Nation fought fiercely to preserve their remaining territories. This struggle continued well into the 20th century, involving court cases that sought to reclaim their rightful lands. The landmark 1974 court decision in Oneida Indian Nation v. County of Oneida affirmed the tribe’s sovereignty and enabled them to reacquire lands through purchase and negotiation.
Today, the Oneida Indian Nation actively works to expand and protect their tribal lands while preserving their cultural heritage. This commitment to land restoration is not only about reclaiming territory but also about re-establishing traditional practices, sustainable development, and economic growth. The Oneida Nation has developed diverse initiatives,including gaming and hospitality enterprises,which help fund community programs and enhance the quality of life for their members.
Through these efforts, the Oneida Indian Nation continues to navigate the complex landscape of land rights and sovereignty, ensuring their cultural identity and traditional practices thrive on their ancestral lands.
Modern Concerns Of The Tribe
The Oneida Indian Nation, one of the original members of the Iroquois Confederacy, faces a range of modern concerns that reflect their ongoing struggle for sovereignty, cultural preservation, and economic development. As a federally recognized tribe, the Oneida Nation has worked tirelessly to uphold its rights and continue its traditions, yet they encounter challenges that resonate in many Native American communities today.
One significant concern is the preservation of language and culture. The Oneida Nation has implemented educational programs aimed at revitalizing the Oneida language, which is essential for maintaining cultural identity. Language immersion programs in schools and community workshops have become pivotal in teaching younger generations about their heritage, alongside traditional crafts and practices. However, the challenge remains to keep these initiatives funded and supported in an era where resources can be limited.
Economic development is another critical focus for the Oneida Indian Nation. They have invested in various enterprises, including gaming, hospitality, and tourism, particularly through the successful operation of the Turning Stone Resort Casino. While this has bolstered the tribe’s economy and provided jobs for tribal members and non-members alike, the reliance on casino revenues has raised questions about diversification. The tribe is exploring new opportunities to reduce dependency on gaming, such as expanding agriculture and environmental initiatives, which align with their commitment to sustainability.
Health and wellness issues continue to impact the Oneida Nation, as with many Indigenous communities. Efforts to combat diabetes, substance abuse, and mental health challenges are ongoing, with programs tailored to enhance community wellness and access to healthcare services. The Oneida Nation’s Health Services department is actively working to integrate traditional healing practices with modern healthcare, emphasizing holistic wellness approaches that honor tribal values.
Moreover, sovereignty and land rights remain at the forefront of modern concerns for the Oneida Indian Nation. The tribe has engaged in legal battles to assert its territorial rights, particularly concerning the Oneida Land Claim. They strive to reclaim ancestral lands and ensure protection from encroachment by external development projects. Advocacy for these rights not only reflects the Nation’s desire for self-governance but also highlights the broader issues of Indigenous rights across the United States.
Environmental issues, including the impacts of climate change on natural resources and traditional lands, present additional challenges. The Oneida Nation is working towards sustainable land stewardship practices,embracing ecological conservation efforts that align with Indigenous knowledge and values. Their initiatives demonstrate a commitment to preserving not only their cultural heritage but also the habitat for future generations.
Through these multifaceted efforts, the Oneida Indian Nation continues to navigate the complexities of modern society while fiercely maintaining its identity, promoting resilience, and enhancing the well-being of its community members.
Events And Other Social And Political Activities
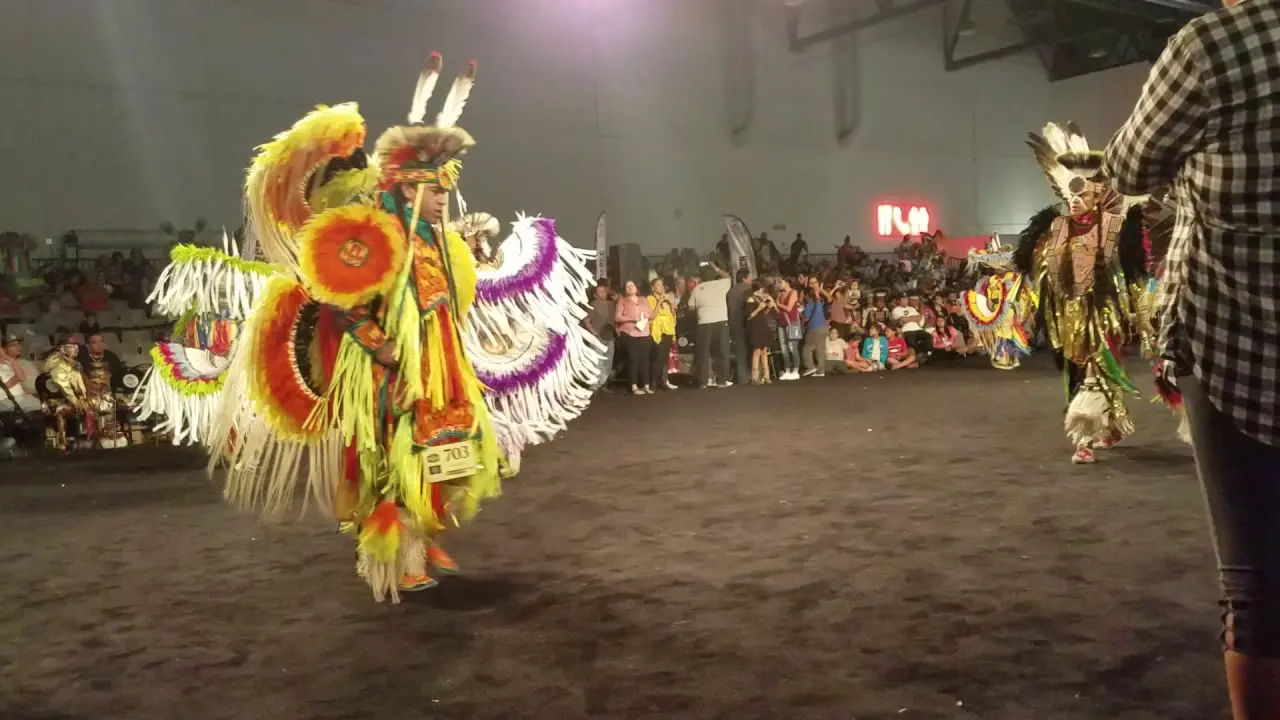
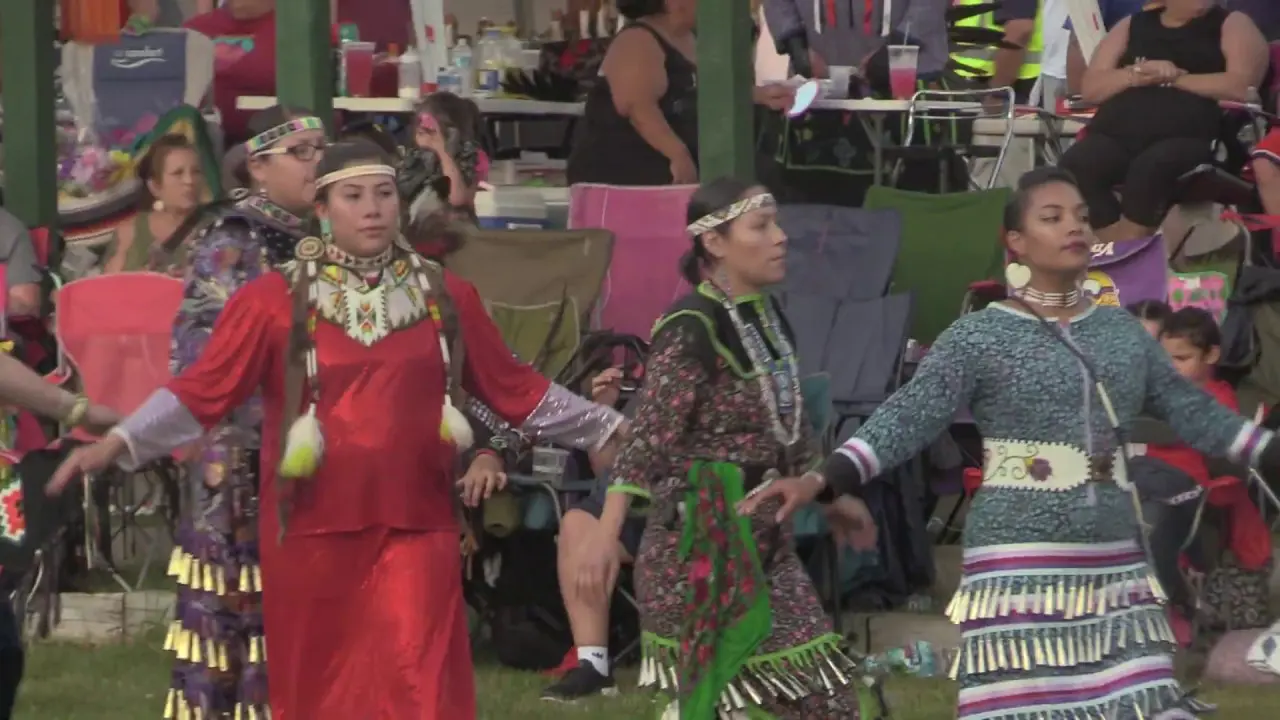
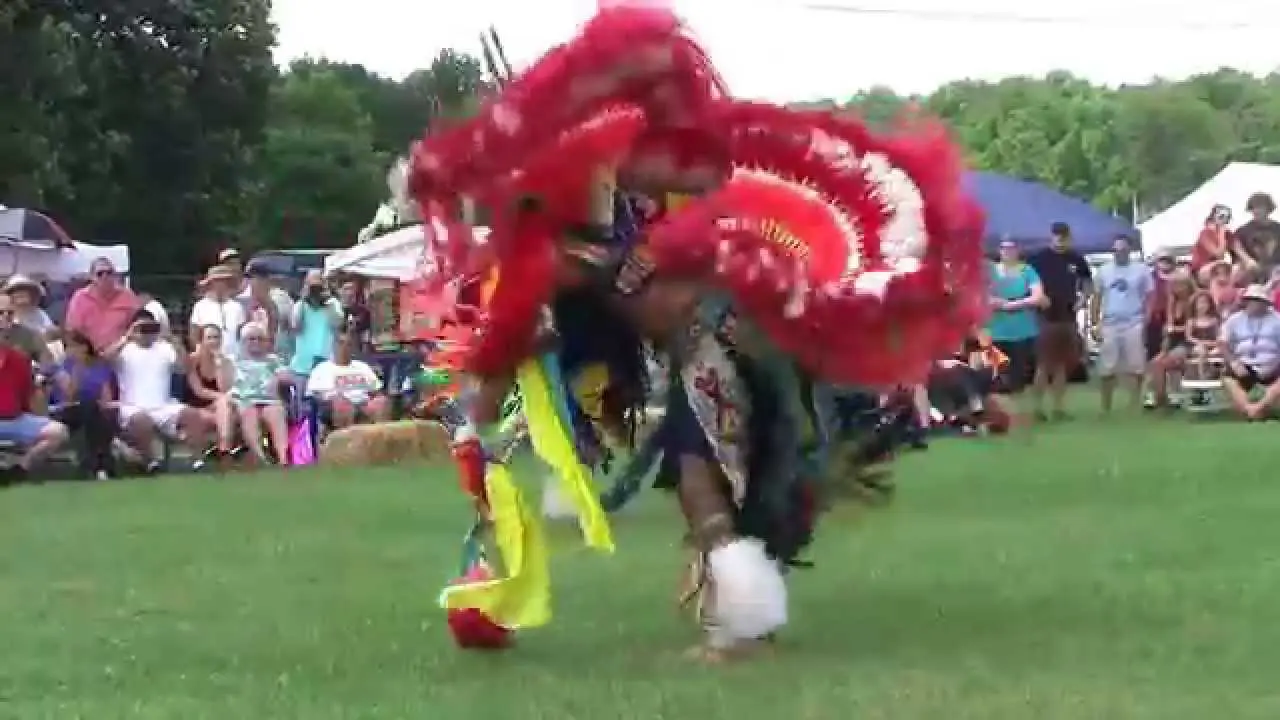
The Oneida Indian Nation,one of the most prominent tribes of the Haudenosaunee Confederacy,actively engages in a variety of social and political activities that reflect its commitment to preserving cultural heritage and advocating for the rights of Indigenous peoples. The Nation operates a number of community events and programs aimed at fostering connections both within the tribe and with the wider community.Annual gatherings like the Oneida Nation Annual Powwow celebrate traditional music, dance, and storytelling, inviting visitors to experience the rich culture of the Oneida people. These events not only promote cultural pride but also serve as educational opportunities for non-Native attendees to learn about Indigenous customs, history, and contemporary issues facing the nation.
In addition to cultural events, the Oneida Indian Nation is deeply involved in political advocacy. The tribe has been at the forefront of efforts to protect its sovereignty and land rights, negotiating with local and federal governments to establish policies that bolster self-governance. Their active participation in national conversations around tribal recognition and preservation of Native American rights positions them as a key player in broader Indigenous movements across the United States.
Furthermore, the Oneida Indian Nation invests in its community through social programs that address issues such as health care, education, and economic development. Initiatives like the Oneida Indian Nation Homelands Commission focus on land restoration and environmental stewardship, ensuring that future generations inherit a sustainable and thriving community.
In response to the ongoing challenges posed by historical injustices,the Oneida Nation also participates in public awareness campaigns aimed at educating the general populace about treaty rights and the importance of recognizing Indigenous sovereignty. Collaborations with other tribes and organizations highlight the collective strength of Indigenous peoples in advocating for justice, equality, and recognition.
Through these diverse social and political activities, the Oneida Indian Nation not only champions the well-being of its own members but also contributes significantly to the broader dialog about Indigenous rights and cultural preservation in the United States.