Introduction to the Prairie Island Indian Community in Minnesota
Nestled along the banks of the Mississippi River, the Prairie Island Indian Community is a vibrant and culturally rich tribe located in southeastern Minnesota. Comprising primarily members of the Mdewakanton Dakota Nation, the community is deeply rooted in history and tradition, serving as a testament to the resilience of Native American culture. With approximately 400 enrolled tribal members, the Prairie Island Indian Community not only thrives on its rich heritage but also emphasizes the importance of sustainability, education, and economic development.
The community’s name derives from Prairie Island, a natural landmark that has been significant to the Dakota people for generations. With its scenic views and access to abundant natural resources, the island plays a crucial role in both the spiritual and daily lives of the tribe. The Prairie Island Indian Community is committed to preserving its cultural identity while adapting to modern challenges, making it a unique blend of tradition and contemporary living.
Engaging in various economic initiatives, including the prosperous Treasure Island Resort & Casino, the community has worked diligently to promote job growth and educational opportunities for its members. Alongside these economic pursuits, the Prairie Island Indian Community places a strong emphasis on environmental stewardship, ensuring that the land and waters surrounding them are protected for future generations.
As we delve deeper into the history, culture, and achievements of the Prairie Island Indian Community, we invite you to discover how this remarkable tribe continues to honor its past while embracing the future. Whether it’s through cultural events, community outreach programs, or enduring practices, the Prairie Island Indian Community stands as a beacon of hope and resilience in the heart of Minnesota.
Origin Of The People
The Prairie Island Indian Community, located in southeastern Minnesota, is composed primarily of the Mdewakanton Sioux, a branch of the larger Dakota Sioux Nation. The origins of these Indigenous people can be traced back to the early inhabitants of the region, who have resided in the area for thousands of years. The Mdewakanton, meaning ” dwellers of the waters,” traditionally lived near the Minnesota River and the Mississippi River, utilizing the rich resources of these waterways for sustenance and cultural practices.
Historically,the Mdewakanton Sioux engaged in a nomadic lifestyle,following seasonal migrations for hunting,fishing,and gathering. They were known for their elegant social structures and spiritual beliefs,which were closely tied to the land and natural elements around them. Tribal legends frequently enough recount the story of the Seven Council Fires,highlighting their connection to other Sioux tribes and the broader Dakota culture.
The arrival of European settlers in the 17th century drastically altered the lives of the Mdewakanton. The fur trade introduced new economic opportunities but also led to conflicts,land dispossession,and a decline in population due to disease and warfare. The signing of treaties, particularly the Treaty of Fort Snelling in 1851, further restricted their territory, pushing them onto smaller, designated lands.
Despite these challenges, the Prairie Island Indian Community has shown resilience in preserving its cultural heritage. Today, they actively engage in promoting their history, language, and traditions, making significant efforts to educate younger generations about their Dakota roots. The community operates various enterprises that support economic development while also maintaining ties to their ancestral identity.
The Prairie Island Indian Community is recognized both federally and state-wise, a testament to their enduring presence and importance in Minnesota’s history. Members take pride in their heritage and work together to foster a strong community spirit, ensuring that the traditions and teachings of their ancestors continue to thrive for years to come.
Tribal Homelands
The Prairie Island Indian Community is a federally recognized tribe located in the southeastern part of Minnesota, primarily on the Prairie Island Reservation, which encompasses about 1,200 acres. This land plays a vital role in the community’s cultural, spiritual, and economic life. Nestled along the banks of the Mississippi River near Red Wing, Minnesota, the tribe’s homeland is rich in natural resources and holds historical significance for the Dakota people.
The Prairie Island Indian Community consists of descendants of the Mdewakanton Dakota, who have lived in this area for centuries. Their connection to the land is deeply woven into their traditions, spirituality, and community identity.The reservation is characterized by its lush natural landscape, including wetlands, forests, and waterways, which provide habitat for diverse wildlife and serve as a place for traditional practices and gathering.
In recent years, the Prairie Island Indian Community has taken significant steps to revitalize and manage their tribal homelands thoughtfully. This includes initiatives aimed at environmental sustainability and promoting biodiversity, and also efforts to restore native plant species. The community often engages in cultural events that highlight their heritage, ensuring that younger generations remain connected to their roots and the natural world around them.
Additionally, the tribe operates the Prairie Island Memorial Council, which plays a critical role in preserving the cultural and historical legacy of the Dakota people. This council oversees commemorative efforts and educational programs that raise awareness about the tribe’s history,traditions,and ongoing contributions to the region.
The Prairie Island Indian Community is also known for its economic ventures, including the Treasure Island Resort & Casino, which not only provides financial support for tribal initiatives but also creates job opportunities both for tribal members and the surrounding community. This successful enterprise plays a pivotal role in the tribe’s efforts to build a sustainable future while honoring their ancestral ties to the land.By fostering a deep respect for their tribal homelands and promoting sustainable practices, the Prairie Island Indian Community continues to be a vital part of Minnesota’s rich tapestry of cultural diversity.
Interactions With Settlers
The Prairie Island Indian Community, a tribal nation located in southeastern Minnesota, has a complex history of interactions with settlers that encompasses both positive and negative aspects. Over the years, these relationships have significantly influenced the cultural, economic, and social landscape of the tribe.
On the positive side, various partnerships have developed between the Prairie Island Indian Community and local non-Indigenous entities. Such as, collaborations in tourism and cultural exchange programs have helped to promote understanding and thankfulness of Native American culture among non-Indigenous populations.The tribe’s casino, Treasure Island Resort & Casino, has also created economic opportunities, providing jobs for both tribe members and community residents. This mutual economic benefit fosters a sense of community and cooperation,demonstrating the potential for positive interactions when both parties engage respectfully.
However, the historical context of settlers’ interactions with the Prairie Island Indian Community reveals significant negative aspects as well. The arrival of European settlers led to the displacement of Native populations through treaties that were often unfairly negotiated or outright ignored. In particular, the Treaty of 1851 resulted in significant land loss for the Dakota people, including those from the Prairie Island Community. This breach of trust established a pattern of mistrust and fragmentation that lingers today.
Additionally, environmental issues and industrialization have further strained relations. The construction of the nearby Xcel Energy nuclear power plant on the Mississippi River raised significant concerns within the community regarding environmental degradation, water quality, and the ongoing implications of historical trauma. Despite these challenges, the Prairie Island Indian Community has actively engaged in advocacy for environmental justice, seeking to protect their sacred lands and water sources.
These interactions highlight the dual narratives of cooperation and conflict between the Prairie Island Indian Community and settlers. Understanding this history is essential for fostering respectful relationships and supporting the tribe’s ongoing efforts for sovereignty, recognition, and sustainable development in Minnesota.
Most Notable Events In Their Tribal History
The Prairie Island Indian Community, comprised of the Dakota people, has a rich and storied history marked by resilience and cultural preservation. One of the most notable events in the tribe’s history occurred during the mid-19th century, when the U.S. government negotiated treaties that significantly impacted the tribe’s lands and way of life. The Treaty of 1851, for instance, led to significant territorial losses for the Dakota, forcing the community to adapt to a rapidly changing surroundings.
In the late 1800s, the results of the U.S.-Dakota War of 1862 left deep scars on the community and the surrounding regions. Following the conflict, many Dakota were forcibly removed from their ancestral lands, yet the Prairie Island Indian Community persevered. Their struggle for recognition and sovereignty gained momentum in the 20th century, leading to the establishment of their self-governance in 1971, which marked a turning point for the community.
The construction of the Prairie Island Nuclear Generating Plant in the 1970s brought both challenges and opportunities for the tribe. The proximity to the plant raised serious environmental concerns, prompting the Prairie Island Indian Community to advocate for regulatory measures and environmental protections that would safeguard their ancestral lands. This advocacy led to successful negotiations resulting in financial compensation and funding for community projects.
In recent years, the Prairie Island Indian Community has taken significant strides towards cultural revitalization and economic self-sufficiency. Efforts to promote traditional practices, language revitalization, and community wellness programs underscore their dedication to preserving Dakota culture. The establishment of the Prairie Island Plume, the community’s traditional botanical garden, serves as both an educational resource and a cultural repository, illustrating their commitment to maintaining their heritage for future generations.
Through these pivotal events, the Prairie Island Indian Community continues to navigate challenges while embracing opportunities, ensuring that their rich tribal history and cultural identity remain vibrant and relevant in today’s world.
Where Are Their Tribal Lands Now And How Were They Established
The Prairie Island Indian Community is located in southeastern Minnesota, specifically on the Prairie Island Reservation, which lies near the confluence of the Mississippi and Wisconsin Rivers.The reservation encompasses approximately 1,180 acres of land, primarily within Goodhue County and is just a few miles from the city of Red Wing. The establishment of the tribal lands dates back to the Treaty of 1837, when the Dakota people ceded a significant portion of their ancestral territory to the United States government.
However,the Prairie Island Indian Community emerged more formally as a recognized tribal entity in the late 20th century,when efforts were made to reclaim and reestablish their rights to the land. A pivotal moment for the community occurred in 1980 when the United States government reaffirmed the tribe’s status and granted them federal recognition. This acknowledgment allowed the Prairie Island Indian Community to regain control over their lands and governance and bolstered their sovereignty as a tribal nation.
Today, the Prairie Island Reservation hosts various enterprises aimed at economic development, including a casino and other business ventures that support the community’s well-being and sustainability. The tribe’s commitment to preserving their cultural heritage and environment is also evident in their ongoing efforts to manage natural resources responsibly. the Prairie Island Indian Community actively engages with both their tribal member constituents and the broader Minnesota community, striving to promote economic opportunities while honoring their historical roots and traditions.
Modern Concerns Of The Tribe
The Prairie Island Indian Community in Minnesota faces several modern concerns that reflect the tribe’s commitment to cultural preservation, economic development, and environmental protection. One of the most pressing issues is the impact of surrounding industries on natural resources. As the community is situated near the Mississippi River, contamination from nearby power plants and other industrial activities poses a threat to water quality and traditional fishing practices. The tribe has been active in advocating for environmental justice and ensuring that their sacred lands are protected from pollution.
Economic self-sufficiency is another major concern. While the Prairie Island Community operates a successful casino and other businesses, the tribe seeks to diversify its economic ventures to provide sustainable income for future generations.Investments in renewable energy sources, such as solar energy, are being explored to create jobs and promote environmental stewardship while reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Healthcare access is also a critical issue. With the ongoing challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, the tribe has prioritized health education and access to medical services for its members. Efforts are being made to improve health outcomes through community health initiatives and partnerships with local healthcare providers.
Cultural preservation remains a cornerstone of life in the Prairie Island Indian Community. The tribe actively works to revitalize its language and traditional practices,ensuring that younger generations connect with their heritage.Educational programs focusing on cultural teachings and history are essential for fostering identity and resilience within the community.
Additionally,legal and political challenges related to tribal sovereignty and land rights continue to shape the tribe’s engagement with state and federal governments.The Prairie Island Indian Community advocates for policies that respect tribal sovereignty and support their unique needs, ensuring that their voices are heard in the broader political landscape.
As the Prairie Island Indian Community navigates these modern concerns, the emphasis on sustainability, health, and cultural identity underscores their commitment to a resilient and thriving future for their people.
Events And Other Social And Political Activities
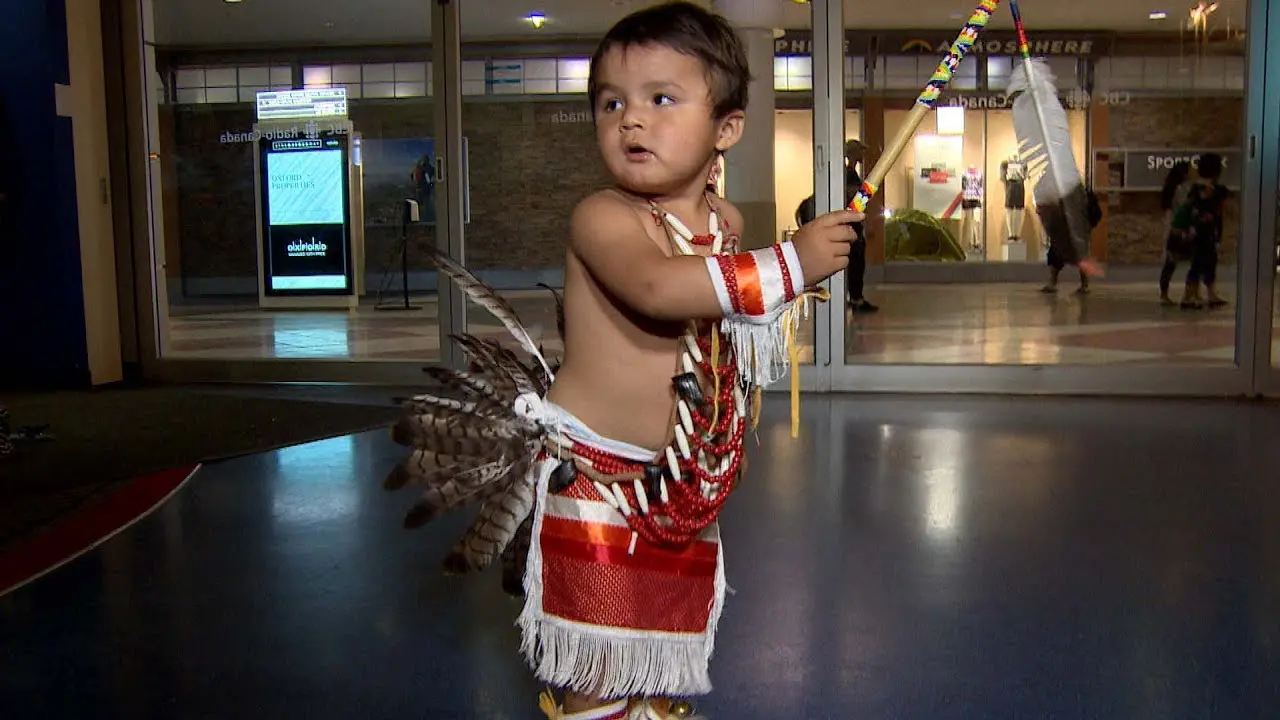
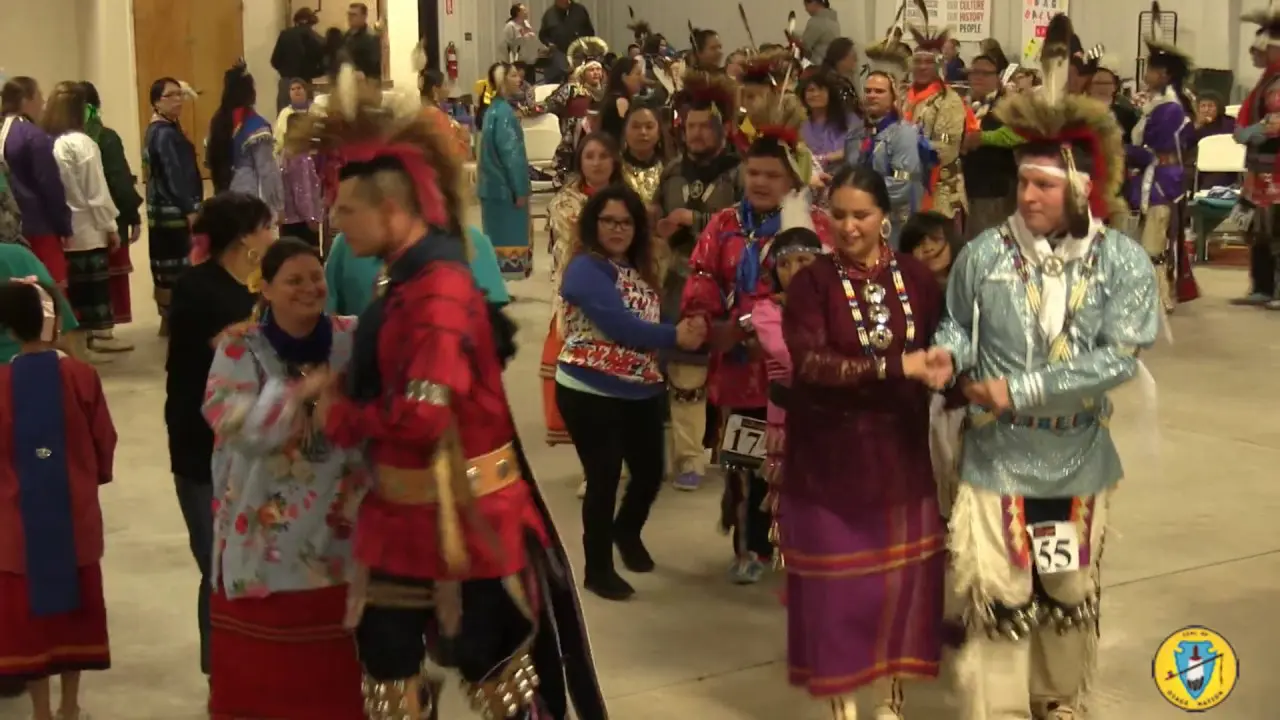
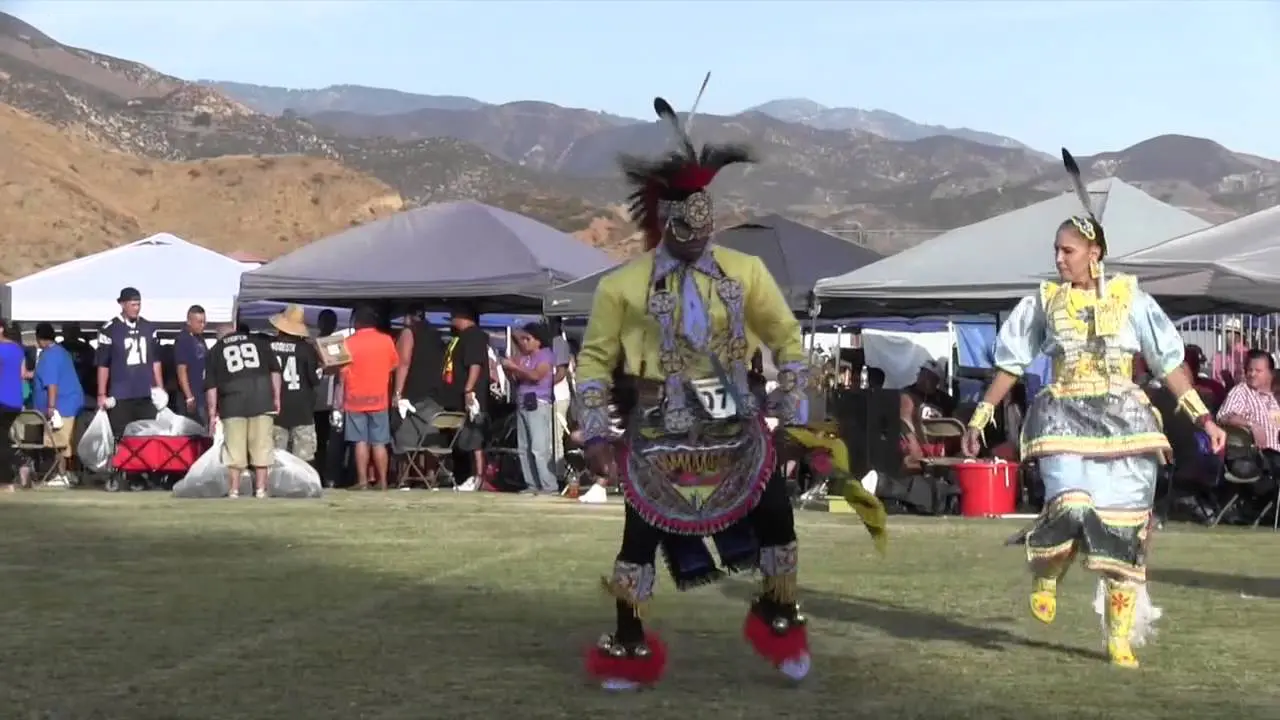
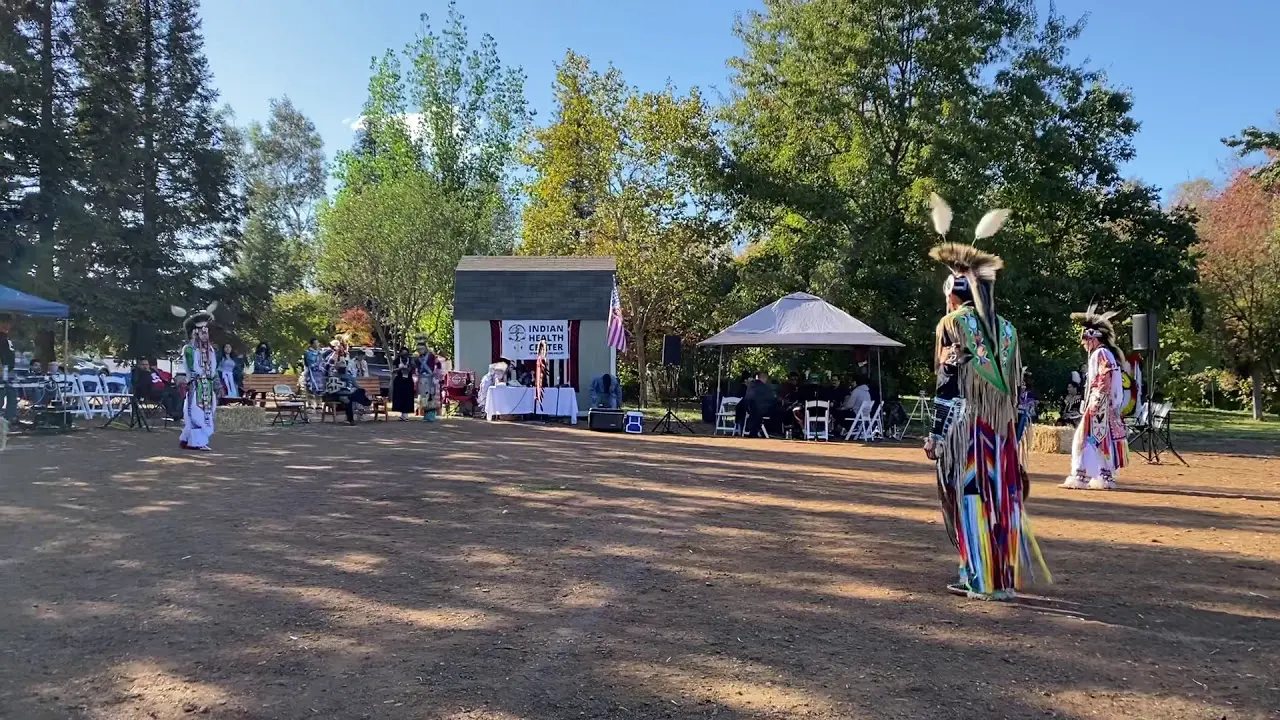
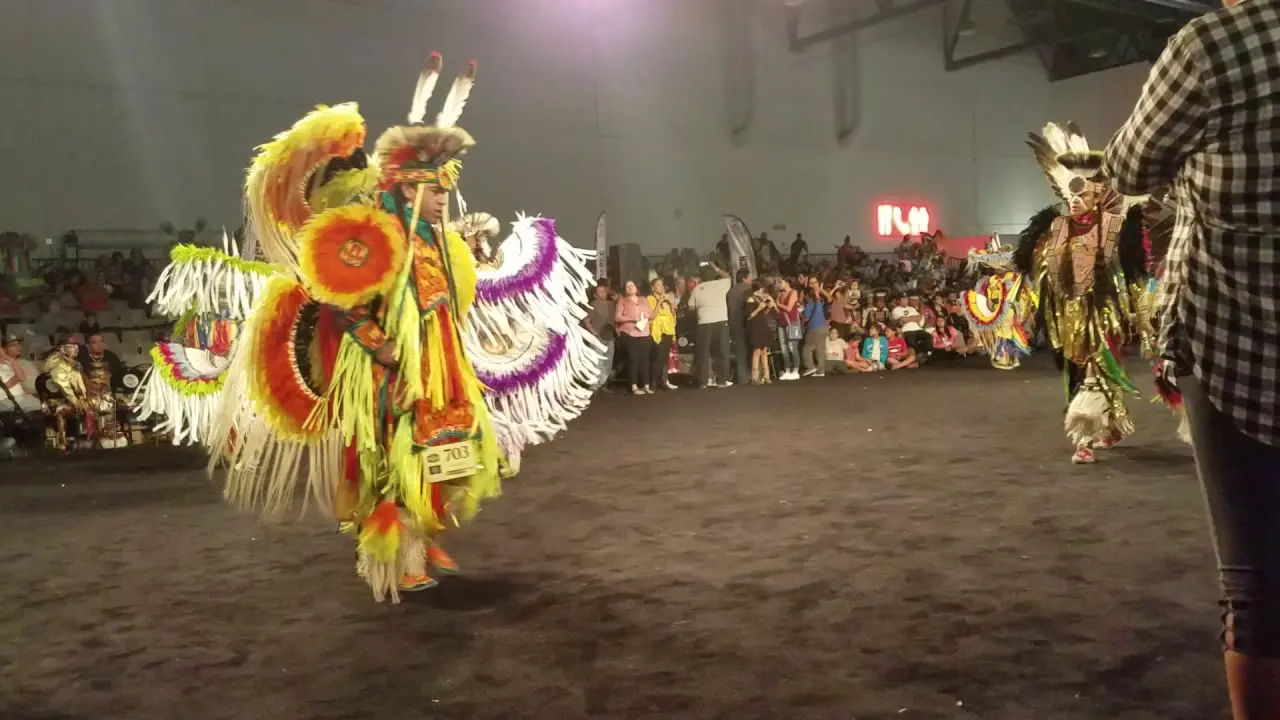
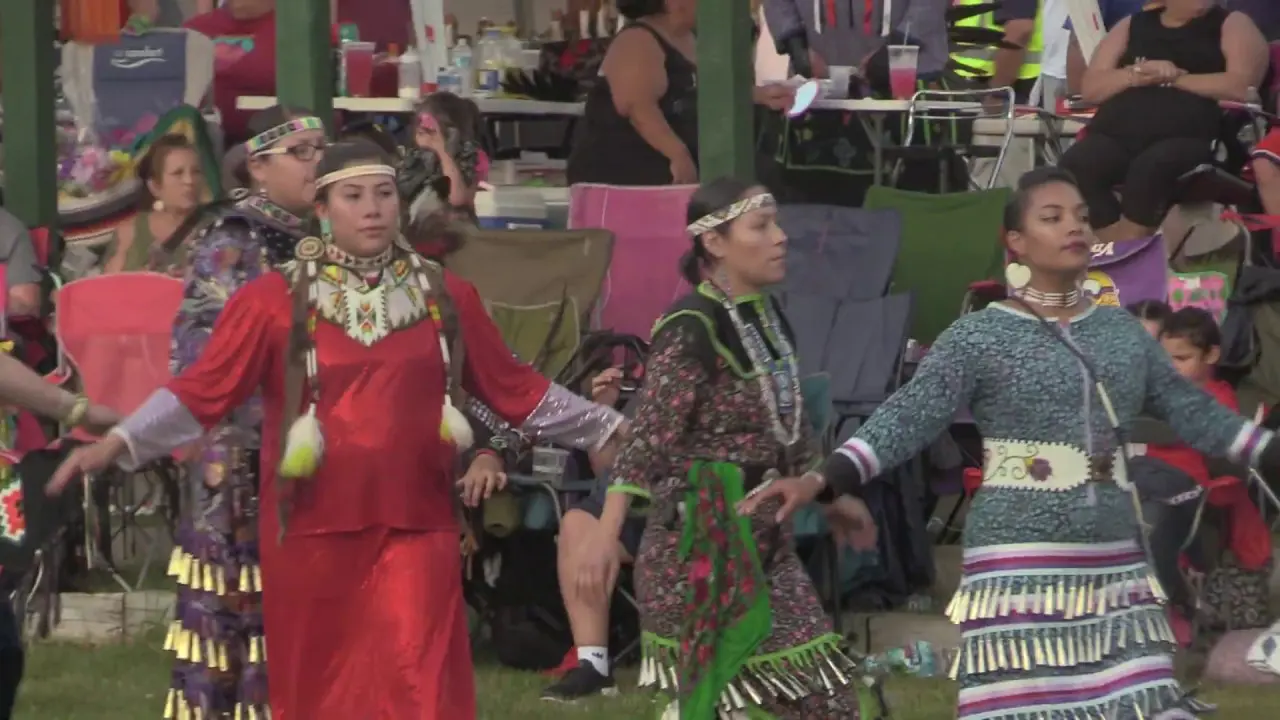
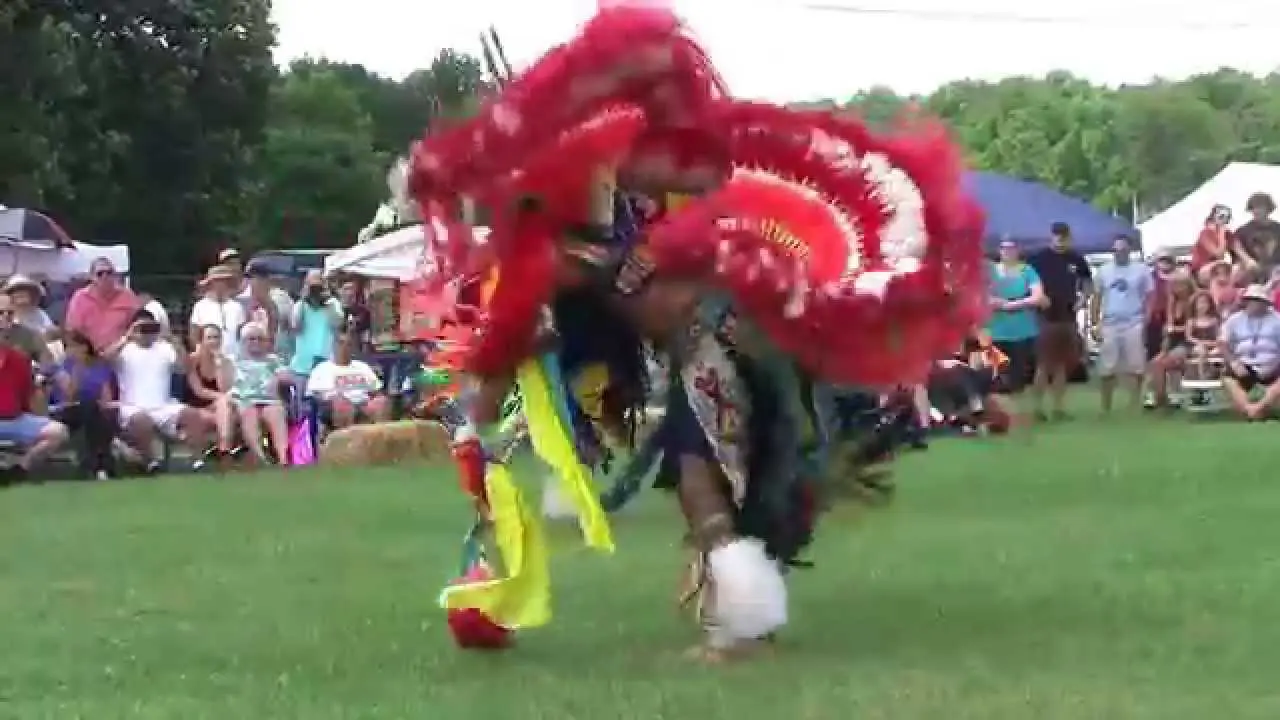
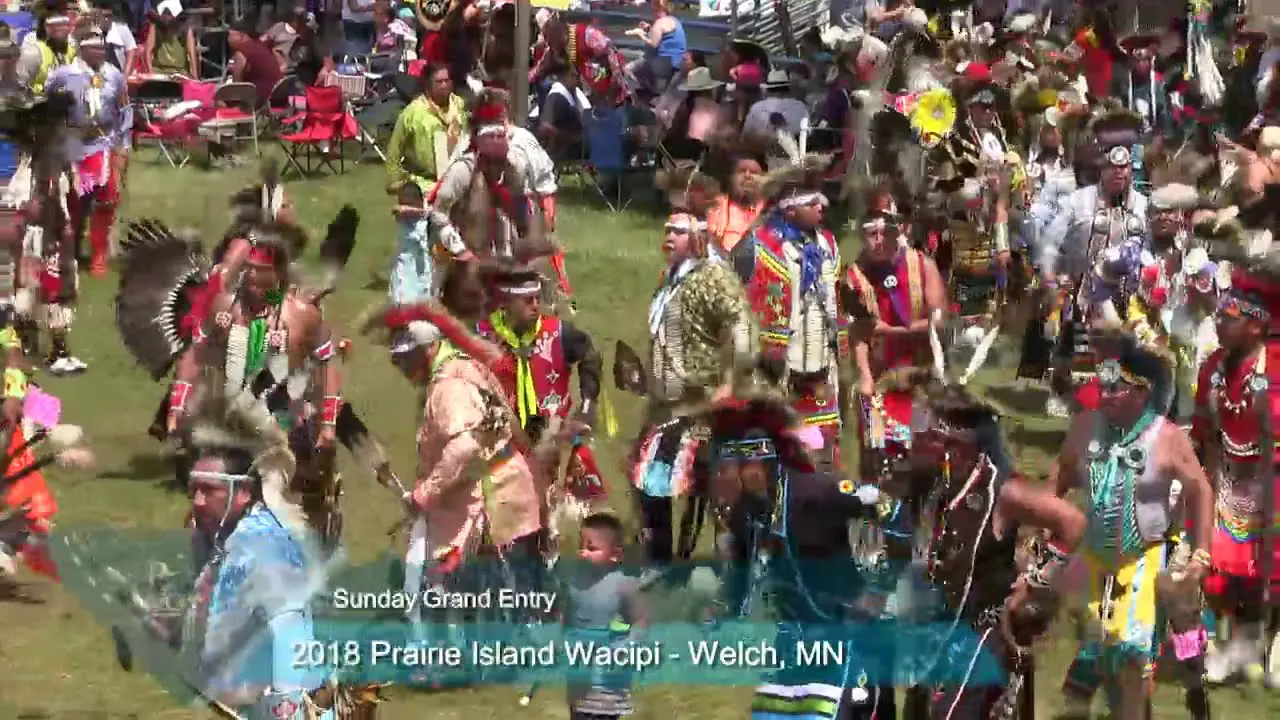
The Prairie Island Indian Community (PIIC), located near Welch, Minnesota, actively engages in a variety of social and political activities that reflect its rich culture and commitment to community development. The tribe is known for organizing events that not only celebrate their heritage but also foster collaboration with neighboring communities and governmental entities.One significant annual event is the Prairie Island Indian Community Pow Wow, which showcases traditional dances, music, and art. This vibrant gathering serves as an possibility for tribal members and visitors alike to immerse themselves in the cultural practices of the Dakota people while strengthening intertribal relations and promoting community spirit.The Pow Wow also features local artisans and food vendors, emphasizing traditional cuisine and crafts.
In addition to cultural events, the Prairie Island Indian Community is actively involved in political advocacy, particularly in matters related to environmental protection and sovereignty rights. Tribal leaders participate in discussions with state and federal agencies to address issues like land use, water rights, and public health, ensuring the voices of their community are heard and considered in decision-making processes.
The tribe also engages in educational outreach, hosting workshops and seminars that highlight the importance of environmental stewardship, sustainability, and the historical context of their land. Initiatives aimed at youth leadership development are a priority, empowering the next generation to take up roles within the tribe and the larger community.
The Prairie Island Indian Community cooperates with various organizations to promote social justice and equity, addressing issues such as health disparities and economic development. Partnerships with local non-profits and government agencies help to deliver crucial services such as healthcare access, housing support, and employment training programs.
Through these events and activities, the Prairie Island Indian Community not only preserves their cultural identity but also plays a proactive role in shaping the social and political landscape of Minnesota, illustrating their dedication to community well-being and sustainable development.