Introduction to the Southern Ute Indian Tribe
Nestled in the heart of the beautiful southern Colorado landscape,the Southern Ute Indian Tribe stands as a vibrant testament to the rich heritage and resilience of Native American culture. Located on the Southern Ute Reservation, which spans approximately 1,000 square miles in La Plata and Archuleta Counties, this tribe is one of the most prominent Indigenous communities in the region. With a history that dates back thousands of years, the Southern Ute people are dedicated to preserving their traditions, language, and identity while actively engaging in modern economic development.
The Southern Ute Indian Tribe is known for its strong cultural identity and commitment to self-governance. As a sovereign nation, the tribe manages a diverse portfolio of enterprises, including natural resources, gaming, and tourism, which fuels its economic growth and empowers its members. At the forefront of these endeavors is the Southern Ute Growth Fund, a strategic investment arm that helps secure the financial future of the tribe while promoting sustainable development.
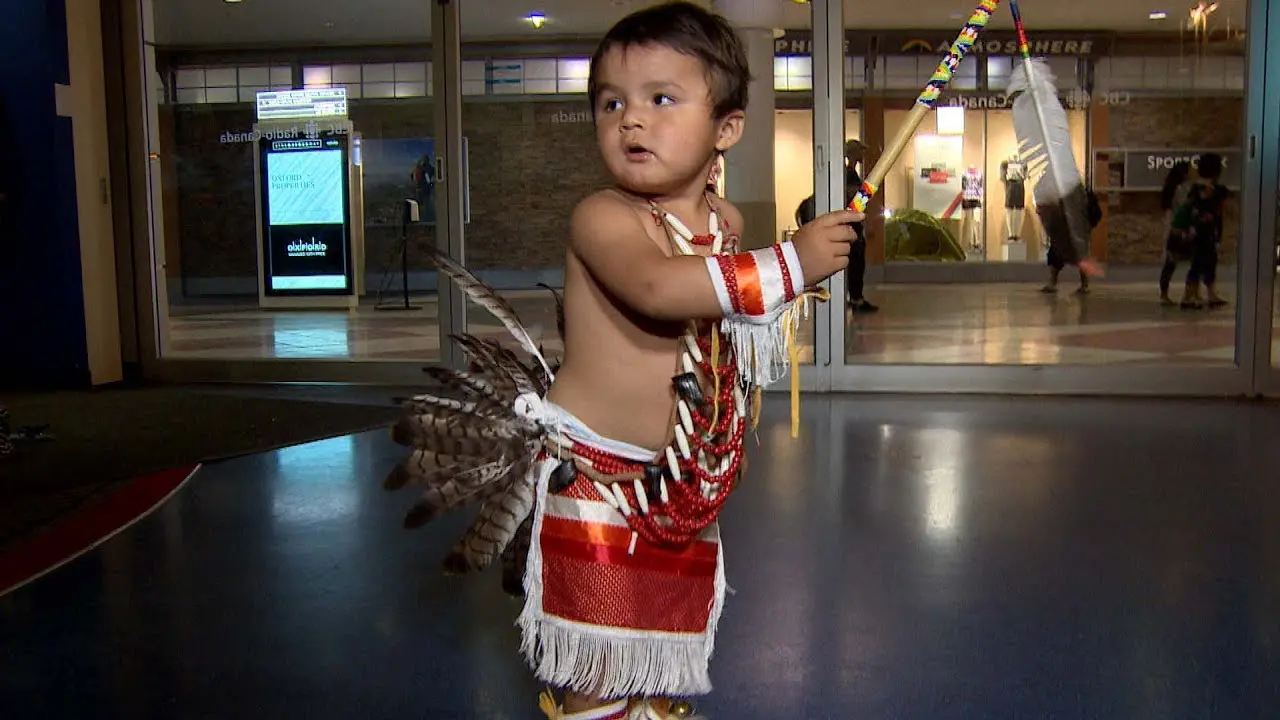
Within this richly woven tapestry of cultural heritage, the Southern Ute Tribe celebrates its traditions through vibrant ceremonies, music, and art, showcasing the profound connection their people have to their ancestral lands. The tribe is also dedicated to environmental stewardship, preserving the breathtaking landscapes of their territory for future generations. With a commitment to education, economic diversification, and community wellness, the Southern Ute Indian Tribe embodies the spirit of resilience, reflecting a powerful blend of history, culture, and modernity that continues to thrive today.
Origin Of The People
The Southern Ute Indian Tribe, located on the Southern Ute Reservation in Colorado, traces its origins back to the ancient inhabitants of the southwestern United States. Ethnographically, the Southern Utes are part of the larger Numic language group, a branch of the Uto-Aztecan languages. Their ancestors may have migrated into the Colorado region thousands of years ago, evolving into a distinct cultural and linguistic identity.
Historically, the Ute people were semi-nomadic hunters and gatherers, relying heavily on the natural resources of the Colorado mountains and surrounding plains. They engaged in extensive trade networks with neighboring tribes and European settlers, establishing themselves as skilled traders known for their baskets, tools, and animal hides. The Southern Utes developed a rich spiritual life centered around their connection to the land, utilizing various plants and animals in their cultural rituals.
With the arrival of European settlers in the 19th century,the dynamic landscape of Ute life began to shift dramatically. Treaties such as the 1868 Treaty of the San Juan River and the 1874 Treaty of the Uintah Valley substantially reduced their territory and changed their traditional way of life. Many Southern Utes resisted these encroachments and maintained their cultural practices, even as challenges grew in the face of assimilation pressures and changing economic conditions.
Today, the Southern Ute Tribe continues to celebrate its heritage while adapting to contemporary realities. Language revitalization efforts and cultural programs showcase their historic traditions, reinforcing a strong community identity grounded in ancestral ties. The Southern Ute Indian Tribe is also notable for its active participation in local governance, economic development, and environmental stewardship, demonstrating resilience and a commitment to maintaining their rich cultural heritage in a modern context.
Tribal Homelands
The Southern Ute Indian Tribe primarily resides in the Southern Ute Reservation, located in southwestern Colorado. This reservation encompasses approximately 1,000 square miles of breathtaking landscapes, which include mountains, rivers, and diverse ecosystems. The heart of the Southern Ute homeland lies within the San Juan Mountains, where the elevation varies greatly, creating a rich surroundings that supports both wildlife and vegetation critical to the tribe’s cultural and economic practices.The Southern Ute Reservation is bordered by the La Plata Mountains to the north and the picturesque Animas River to the east, providing access to natural resources that the tribe has long depended upon. Historically, the Southern Ute people utilized these lands for fishing, hunting, and gathering, maintaining a deep spiritual connection with the environment. This relationship with their ancestral lands remains integral to Southern Ute identity and heritage.
Within the reservation, several communities thrive, including Ignacio and the surrounding areas, which serve as cultural and administrative hubs for the tribe. The Southern Ute Indian Tribe has focused on revitalizing and preserving traditional practices while also engaging in modern economic initiatives such as renewable energy, gaming, and tourism. The tribe’s land management strategies prioritize both environmental stewardship and economic sustainability, ensuring that future generations can continue to benefit from their ancestral homeland.
The Southern Ute Tribal Government plays a vital role in managing the natural resources of the reservation, overseeing land use in a manner that respects the tribe’s rich history and cultural traditions. The tribe’s commitment to protecting their homeland extends to the stewardship of sacred sites, which hold significant historical and cultural importance for the Southern Ute people. Collaborative efforts with neighboring communities and environmental organizations further emphasize the tribe’s dedication to preserving their unique heritage while adapting to contemporary challenges.the Southern Ute Reservation not only serves as a home for the Southern Ute Indian Tribe but also stands as a testament to their resilience and commitment to cultural preservation amidst the evolving landscape of modern America.
Interactions With Settlers
Interactions between the Southern Ute Indian Tribe and European settlers present a complex tapestry of both positive and negative experiences, shaping the tribe’s history and relationships in Colorado.In the early stages of contact, some settlers established mutually beneficial relationships with the Southern Ute people.The tribes engaged in trade, exchanging goods such as furs, hides, and food supplies for manufactured items and tools. This early interaction often fostered a sense of cooperation,as both groups sought to adapt to their changing environments. Southern Ute guides played crucial roles in helping settlers navigate the rugged terrain of the Colorado region, leading to triumphant exploration and settlement.Though, as the influx of European settlers increased in the 19th century, the Southern Ute tribe faced mounting challenges. The finding of valuable resources, notably gold and silver, prompted a rush of miners and settlers into Ute territory.This led to erosion of traditional lands through treaties that often favored the settlers while marginalizing the needs and rights of the Southern Ute people. The Treaty of 1868 is a notable example, where the Southern Ute signed over vast tracts of land in a hurried attempt to secure their remaining territory, which was soon encroached upon by settlers.
Conflict arose as settlers began to compete for resources, leading to tensions and violence. Incidents such as the Bear Creek Massacre in 1879 exemplified these deteriorating relations, marking a tragic moment in the history of interactions between the Southern Ute and settlers. As the lifestyle of the Southern Ute relied heavily on their land, the encroachment not only threatened their way of life but also led to significant cultural losses.
Despite these adversities, the Southern Ute tribe demonstrated resilience, adapting their strategies to navigate the challenges posed by settlement expansion.In the modern era,the tribe has focused on economic development and cultural revitalization,making strides in areas like tourism and natural resource management. Today, the Southern Ute Indian Tribe actively engages with other communities, fostering partnerships that allow for cultural exchange and mutual respect, demonstrating how interactions can evolve positively over time.
Understanding the complexities of these historical interactions sheds light on the Southern Ute tribe’s enduring spirit and their ongoing journey toward self-determination in Colorado.
Most Notable Events In Their Tribal History
The Southern Ute Indian Tribe has a rich and complex history marked by significant events that have shaped its identity and resilience. One of the most notable events in their tribal history is the signing of the Treaty of Fort Laramie in 1868. This treaty established the Ute Reservation, which was initially a vast territory encompassing much of present-day Colorado and parts of Utah and New Mexico. The treaty acknowledged the Southern Ute’s sovereignty and guaranteed them the right to hunt and fish within their lands.
However, the discovery of gold and silver in the Colorado mountains led to increased encroachment by settlers. This ultimately resulted in the forced relocation of many Utes during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, including the infamous Meeker Massacre in 1879, where tensions boiled over, resulting in a violent confrontation between Ute leaders and government officials.This tragic event served as a pivotal moment in the tribe’s history, leading to the loss of their lands and the dilution of their cultural practices.
In the mid-20th century, the Southern Ute Tribe began to reclaim its identity and rights. The Indian Reorganization Act of 1934 allowed for increased self-governance, leading to the establishment of their tribal government and the Southern Ute Tribal Council. This period was marked by a cultural renaissance, where traditional practices, languages, and customs were revitalized.
Another significant milestone was the establishment of the Southern Ute Growth Fund in the 1980s, a move that harnessed economic opportunities from natural resource management and energy development. Through strategic planning and investment, the tribe has successfully generated revenue that supports its community programs, infrastructure, and education initiatives.
In recent years, the Southern Ute Indian Tribe has been actively involved in environmental stewardship and renewable energy projects, reflecting a commitment to sustainable development and the protection of their ancestral lands. Their efforts are emblematic of a broader trend among Indigenous communities aiming to balance economic growth with cultural preservation.
Through these pivotal events and developments, the Southern Ute Indian Tribe has demonstrated resilience, adaptability, and a strong commitment to their cultural heritage, paving the way for future generations while honoring their past.
Where Are Their Tribal Lands Now And How Were They Established
The Southern Ute Indian Tribe is primarily located on the Southern Ute Indian Reservation in southwestern Colorado, spanning approximately 1,000 square miles across La Plata and Archuleta counties. This reservation is rich in cultural history and natural resources, reflecting the tribe’s enduring connection to the land. Established through a series of treaties and agreements dating back to the late 19th century, the reservation was formally recognized in the Treaty of 1868, which aimed to protect the Southern Ute’s rights to their ancestral territories.
Over the years, the size and boundaries of the Southern Ute Reservation have fluctuated due to various federal policies, including the Dawes Act of 1887, which led to significant loss of lands.Though, through persistence and legal battles, the Southern Ute Tribe regained sovereignty and control over substantial portions of their original territory. In the 20th century, the tribe enhanced its economic base by tapping into natural resources, particularly through oil, gas, and mineral extraction, which play key roles in their current economic structure.Today, the Southern Ute Reservation not only serves as a cultural and spiritual home for the Southern Ute people but also stands as a testament to their resilience and determination to reclaim and revitalize their heritage.The tribe continues to manage its resources strategically, ensuring sustainability while fostering economic growth that benefits the entire community. The Southern Ute Indian Tribe remains committed to preserving their cultural practices and promoting the well-being of their members, ensuring that their tribal lands continue to thrive for future generations.
Modern Concerns Of The Tribe
One of the modern concerns facing the Southern Ute Indian Tribe of the Southern Ute Reservation in Colorado revolves around environmental sustainability and the management of natural resources. As stewards of their ancestral lands, the tribe is keenly aware of the impact that energy development can have on their environment. With significant oil and gas resources located on their reservation, the tribe has worked diligently to balance economic development with ecological preservation. This includes implementing sustainable practices in energy extraction and exploring alternative energy sources, such as solar and wind energy, to diversify their economy while minimizing ecological footprints.
Another pressing issue is the challenge of preserving cultural heritage in the face of modernization. The Southern Ute Tribe is actively engaged in efforts to revitalize their language, traditions, and cultural practices among the younger generation. Language preservation programs, cultural events, and educational initiatives are critical in fostering a strong sense of identity and continuity. The tribe is dedicated to ensuring that their rich history and traditions remain vibrant and relevant in today’s society.
Healthcare access is also a significant concern for the Southern Ute community. Like many indigenous populations, the tribe faces disparities in health outcomes, frequently enough influenced by socioeconomic factors. To combat these issues, the Southern Ute Tribe operates health services that prioritize holistic approaches to wellness, integrating traditional practices with modern healthcare solutions. This commitment to improving health services is vital for ensuring the well-being of tribe members and fostering a healthier future.economic development remains a key priority, as the Southern Ute Tribe seeks to create sustainable job opportunities for its members. While resource extraction provides considerable revenue,there is an increasing focus on diversifying the local economy. Initiatives aimed at business development, tourism, and cultural experiences are being explored to create self-sustaining revenue streams and enhance the overall quality of life for the tribe’s people. By navigating these modern concerns, the Southern Ute Indian Tribe continues to uphold its cultural legacy while striving for a prosperous future.
Events And Other Social And Political Activities
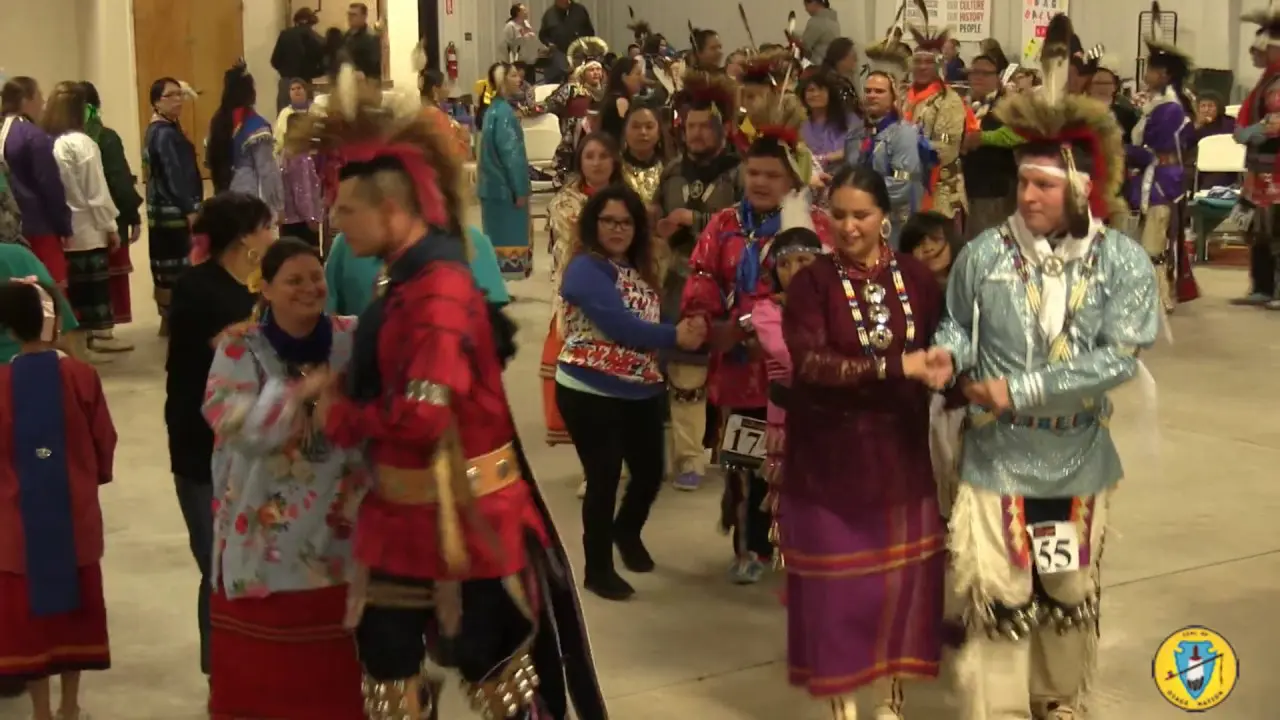
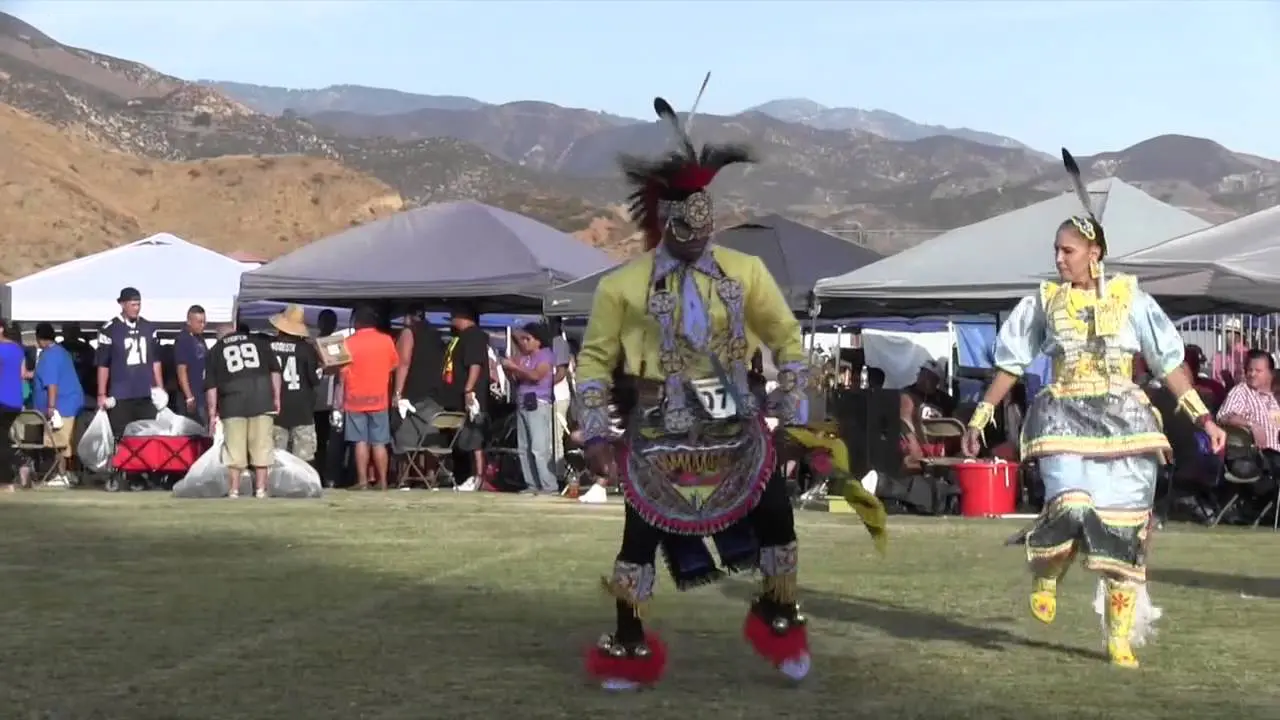
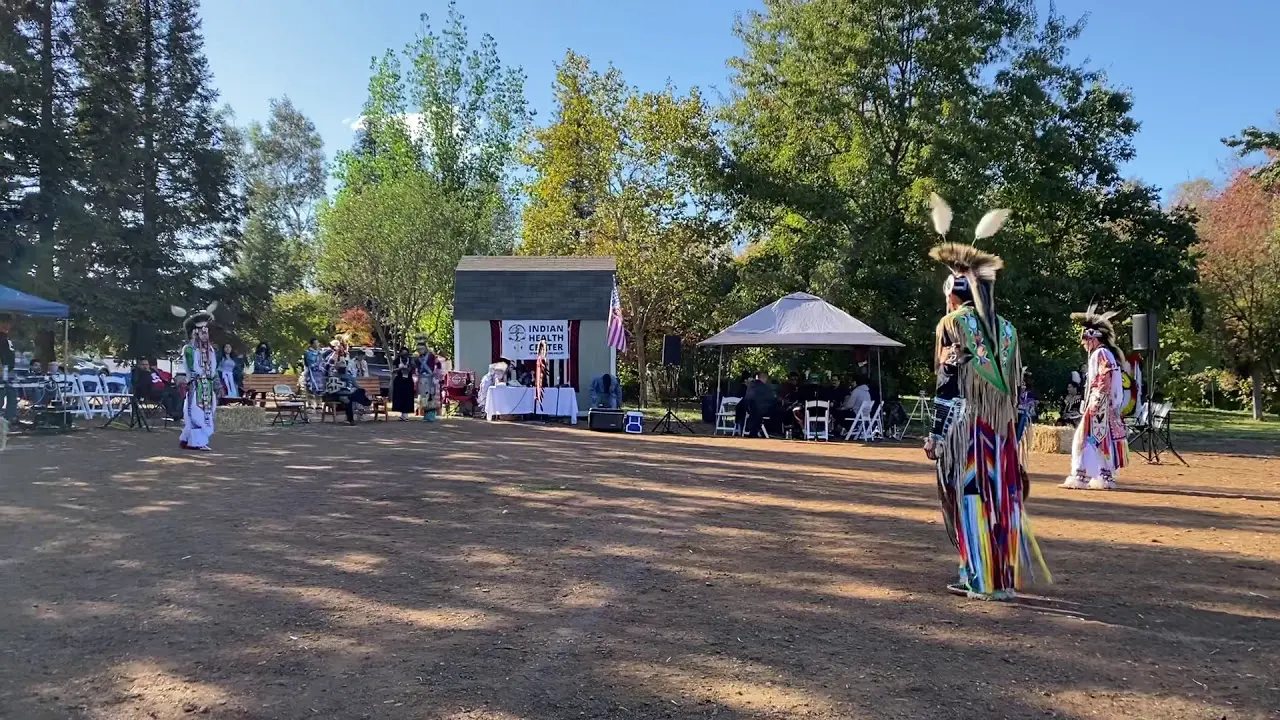
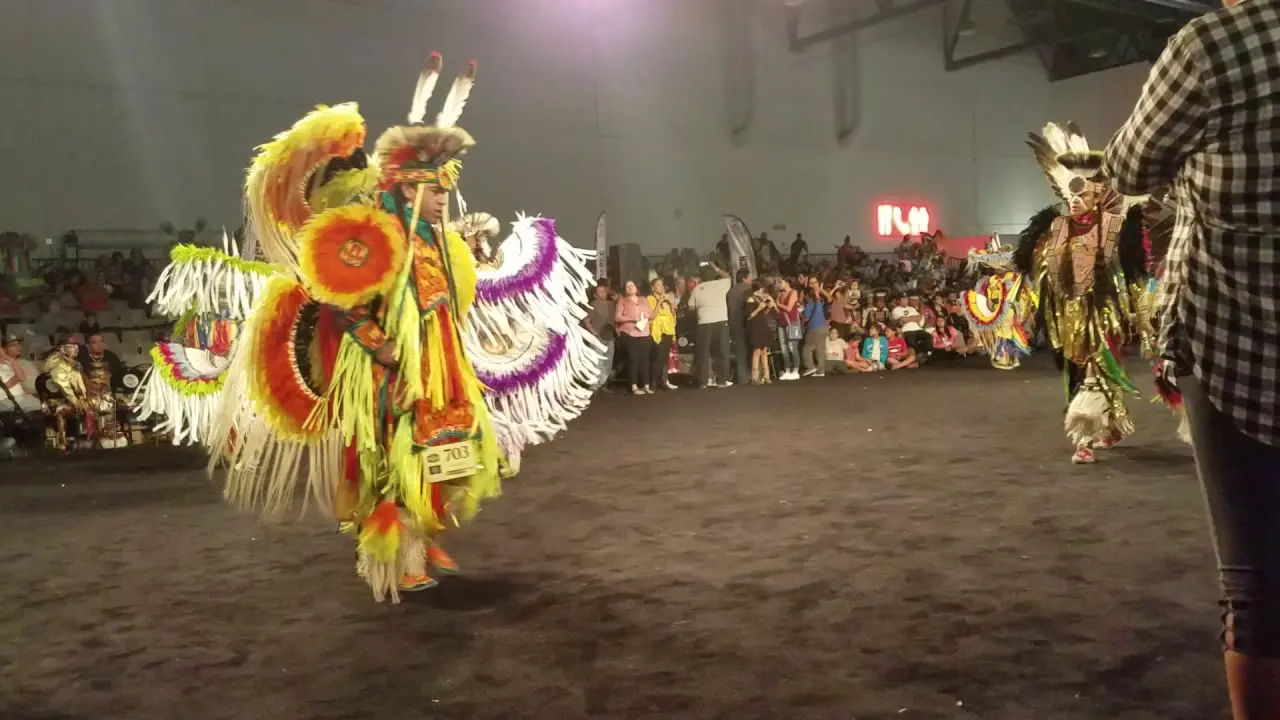
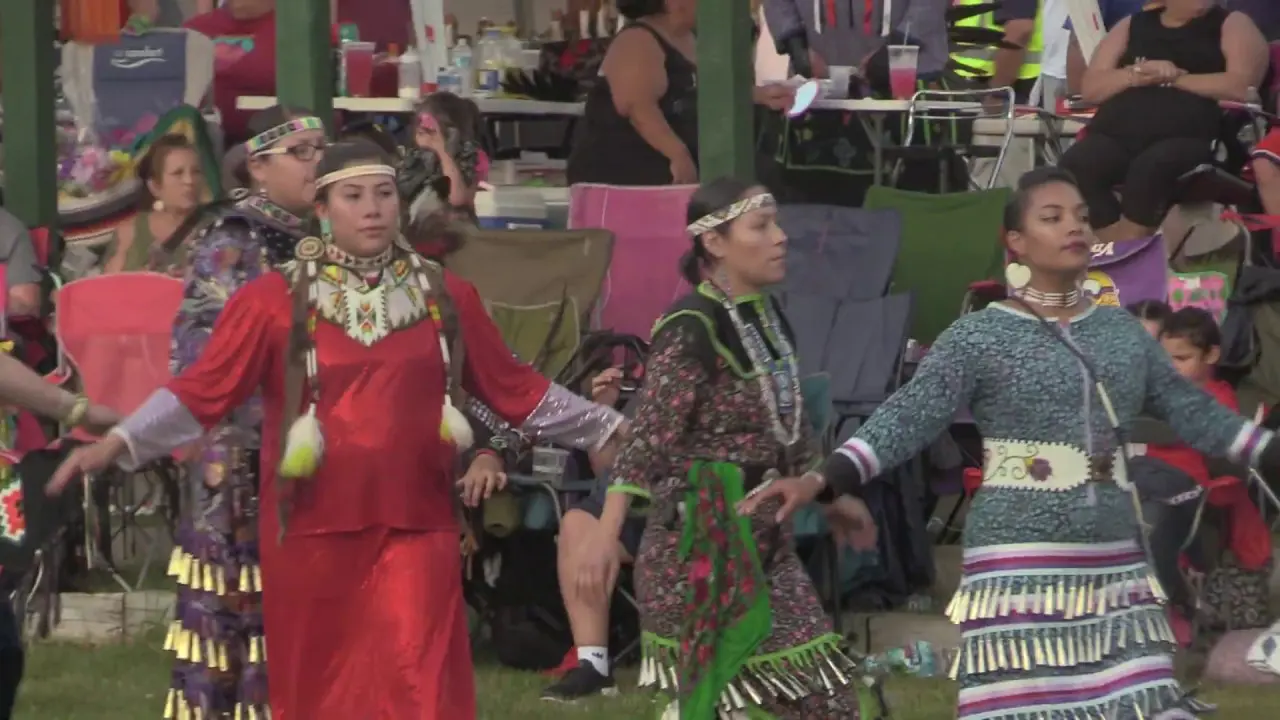
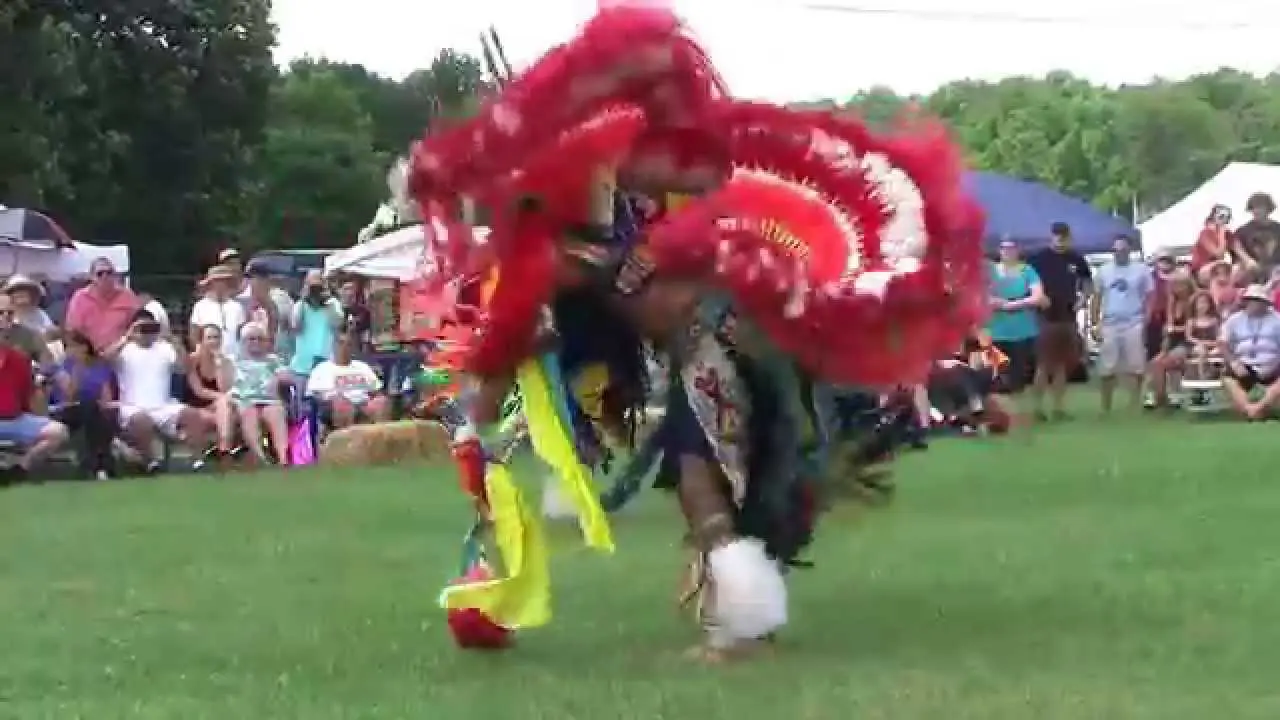
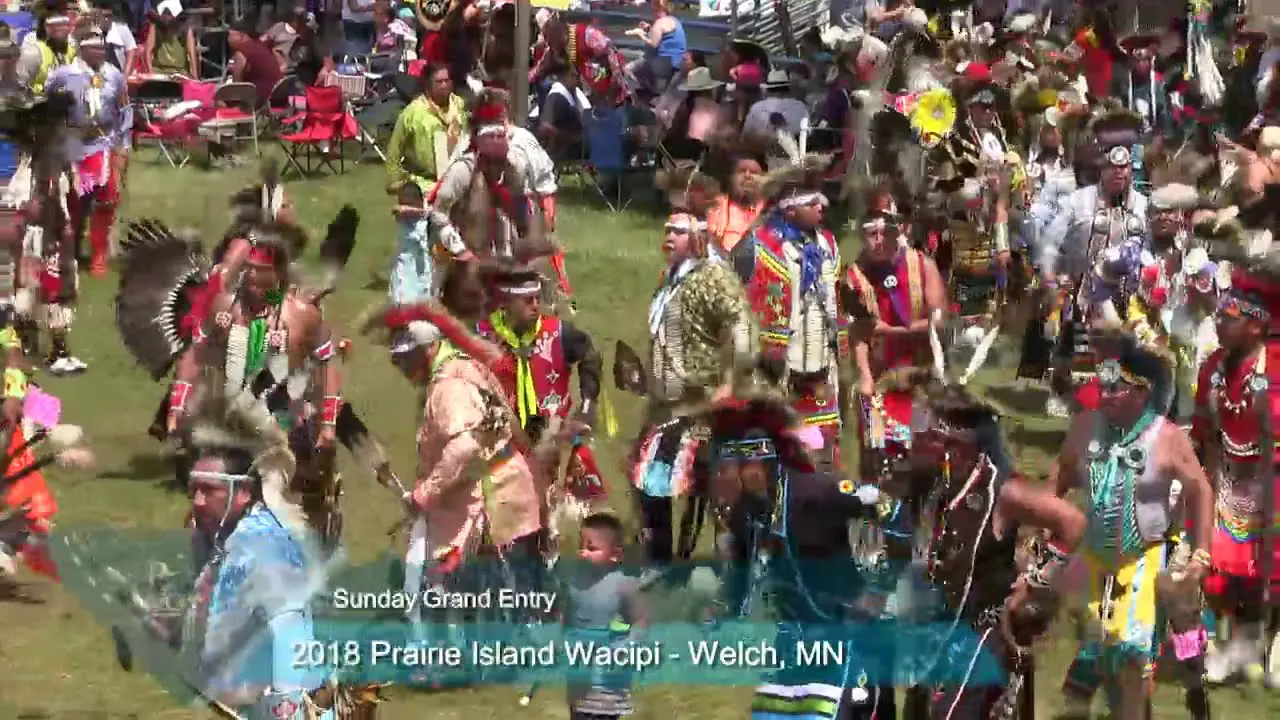
The Southern Ute Indian Tribe,located in southwestern Colorado,actively engages in a variety of social and political activities that highlight their rich cultural heritage and commitment to community development. Throughout the year, the tribe organizes numerous events, including cultural celebrations, traditional powwows, and educational programs, which serve as vital opportunities to share their history, language, and values with both tribal members and the broader public.
One of the hallmark events is the Southern Ute Tribal Fair and Powwow, typically held in the fall. This remarkable gathering showcases traditional dances, music, art, and cuisine, attracting visitors from neighboring communities and beyond. The tribe’s commitment to preserving and promoting their cultural identity is mirrored in these celebrations, where local artisans and performers can express their heritage and connect with younger generations.
Political engagement is equally important for the Southern Ute Tribe, as they assert their sovereignty and advocate for their rights. The Tribal Council regularly meets with state and federal officials to address issues such as land management, resource development, and environmental protection. The tribe’s participation in regional and national organizations allows them to influence policy decisions that affect their community and other indigenous groups, ensuring their voices are heard on platforms where vital issues are discussed.
Education is a cornerstone of the Southern Ute Tribe’s social initiatives. The tribe sponsors several scholarships and educational programs aimed at empowering youth. Events like the Southern Ute Education Enrichment Programme provide opportunities for tribal members to learn about their heritage while developing skills necessary for career readiness. Workshops on traditional crafts, language revitalization, and leadership training foster a sense of pride and duty among younger generations.
Community health and wellness initiatives are also crucial to the tribe’s activities. The Southern Ute Health Center frequently hosts health fairs, offering screenings and educational resources on topics such as nutrition, mental health, and substance abuse prevention. These events reflect the tribe’s commitment to the holistic well-being of its members, ensuring they have the resources and support needed to lead healthy lives.
By engaging in these various events and activities, the Southern Ute Indian Tribe not only preserves its cultural legacy but also empowers its members through education, advocacy, and health initiatives. Each event serves as an important platform for fostering unity, celebrating heritage, and promoting active participation within and beyond the tribe.